Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lin, Z. M.*; Liu, B. X.*; Ming, K. S.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F. X.*; Zheng, S. J.*
Scripta Materialia, 263, p.116692_1 - 116692_7, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Hu, F.-F.*; Qin, T.-Y.*; Ao, N.*; Xu, P. G.; Su, Y. H.; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Shobu, Takahisa; Kang, G.-Z.*; Ren, M.-M.; et al.
Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 25(2), p.75 - 93, 2025/04
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
Jiao, J. C.*; Chen, K. W.*; Hillier, A. D.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Li, Z.*; Lv, B.*; Xu, Z.-A.*; Shu, L.*
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214516_1 - 214516_9, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hu, F. F.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; Zhou, L.*; Xu, P. G.; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Chen, J.*; Wu, S. C.*
Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 306, p.110267_1 - 110267_18, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:55.14(Mechanics)Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; Xu, P. G.; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Yin, F.*
Scripta Materialia, 249, p.116046_1 - 116046_6, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.76(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Zhou, L.*; Zhang, H.*; Qin, T. Y.*; Hu, F. F.*; Xu, P. G.; Ao, N.*; Su, Y. H.; He, L. H.*; Li, X. H.*; Zhang, J. R.*; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(7), p.2175 - 2185, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:70.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Liao, J.*; Huang, Z.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Zhang, B.*; Cheng, S.*; Xu, H.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Bao, S.*; Wen, J.*
Physical Review B, 109(22), p.224411_1 - 224411_10, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Mg; Bridging the
Mg; Bridging the 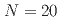 and
and 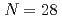 islands of inversion
islands of inversionMadurga, M.*; Christie, J. M.*; Xu, Z.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Poves, A.*; King, T.*; Allmond, J. M.*; Chester, A.*; Cox, I.*; Farr, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(6), p.L061301_1 - L061301_6, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Liss, K.-D.*; Han, J.-K.*; Blankenburg, M.*; Lienert, U.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Xu, P. G.; Yukutake, Eitaro*; Kawasaki, M.*
Journal of Materials Science, 59(14), p.5831 - 5853, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:73.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)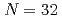
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
R hm, W.*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Chen, J.*; Li, C.*; Dobynde, M.*; Durante, M.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Ozasa, Kotaro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
hm, W.*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Chen, J.*; Li, C.*; Dobynde, M.*; Durante, M.*; El-Jaby, S.*; Komiyama, Tatsuto*; Ozasa, Kotaro*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
Journal of Medical Physics - Zeitschrift f r medizinische Physik -, 34(1), p.4 - 13, 2024/02
r medizinische Physik -, 34(1), p.4 - 13, 2024/02
The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) provides independent recommendations on radiological protection for the public benefit. For more than 90 years, the ICRP System of Radiological Protection has been guiding the development and implementation of national and international standards and regulations on radiological protection. In 2019, ICRP established Task Group (TG) 115 to address a broader range of topics related to dose and risk assessment for radiological protection of astronauts. This paper gives an overview of the System of Radiological Protection and a brief summary of ICRP's work on radiological protection of astronauts.
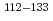 Sb
SbLechner, S.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Bissell, M. L.*; Blaum, K.*; Cheal, B.*; Devlin, C. S.*; Garcia Ruiz, R. F.*; Ginges, J. S. M.*; Heylen, H.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 847, p.138278_1 - 138278_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:79.71(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(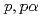 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The cluster structure of the neutron-rich isotope  Be has been probed via the (
Be has been probed via the (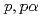 ) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the
pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the  Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:83.85(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary) decay near doubly magic
decay near doubly magic  Sn
SnHeideman, J.*; Grzywacz, R.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Madurga, M.*; Escher, J. E.*; Kawano, Toshihiko*; Algora, A.*; Andreyev, A. N.; 41 of others*
Physical Review C, 108(2), p.024311_1 - 024311_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.48(Physics, Nuclear) Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 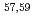 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 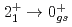 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 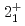 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 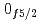 and
and 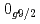 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:87.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.