Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Walter, H.*; Colonna, M.*; Cozma, D.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Kumar, R.*; Ono, Akira*; Tsang, M. Y. B*; Xu, J.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; et al.
Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, 125, p.103962_1 - 103962_90, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:96.94(Physics, Nuclear)Transport models are the main method to obtain physics information on the nuclear equation of state and in-medium properties of particles from low to relativistic-energy heavy-ion collisions. The Transport Model Evaluation Project (TMEP) has been pursued to test the robustness of transport model predictions to reach consistent conclusions from the same type of physical model. To this end, calculations under controlled conditions of physical input and set-up were performed by the various participating codes. These included both calculations of nuclear matter in a periodic box, which test individual ingredients of a transport code, and calculations of complete collisions of heavy ions. Over the years, five studies were performed within this project. They show, on one hand, that in box calculations the differences between the codes can be well understood and a convergence of the results can be reached. These studies also highlight the systematic differences between the two families of transport codes, known under the names of Boltzmann-Uehling-Uhlenbeck (BUU) and Quantum Molecular Dynamics (QMD) type codes. On the other hand, there still exist substantial differences when these codes are applied to real heavy-ion collisions. The results of transport simulations of heavy-ion collisions will have more significance if codes demonstrate that they can verify benchmark calculations such as the ones studied in these evaluations.
Miao, Z.-Q.*; Xia, C.-J.*; Lai, X.-Y.*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Xu, R.-X.*; Zhou, E.-P.*
International Journal of Modern Physics E, 31(4), p.2250037_1 - 2250037_20, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:86.5(Physics, Nuclear) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)
Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,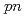 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
 decay of
decay of 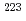 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:79.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics) resonances in a box
resonances in a boxOno, Akira*; Xu, J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Wolter, H.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; Chen, L.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044617_1 - 044617_35, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:98.56(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number and energies of collisions during the time evolution. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). This study showed that time step in the calculation is one of the biggest causes of the discrepancies. For example, the calculation by JQMD comprises 1-fm/c time steps, each of which is composed of transport, scattering and decay phases. Therefore a sequence of scattering, and decay followed by another scattering in 1 fm/c cannot be considered. Moreover, in JQMD particles are labeled by sequential numbers and scattering reactions are simulated by the order. Therefore scattering between low ID numbers, that between high ID numbers and that between the first (low ID) pair is overlooked in JQMD. Above indications obtained in this study must be kept in our mind for future JQMD upgrades.
Zhang, Y.-X.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ono, Akira*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wolter, H.*; Xu, J.*; Chen, L.-W.*; Cozma, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034625_1 - 034625_20, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:98 Percentile:99.11(Physics, Nuclear)International comparison of heavy-ion induced reaction models were discussed in the international conference "Transport2017" held in April 2017. Owing to their importance for safety assessment of heavy-ion accelerators and dosimetry of astronauts, various models to simulate heavy-ion induced reaction models are developed. This study is intended to clarify the difference among them to pinpoint their problems. In the comparison study, 320 protons and 320 neutrons were packed in a 20-fm-large cube to calculate the number of particle-particle collisions as well as the energies of collisions during the time evolution. In addition to the calculation, their algorithms were compared. The author contributed to this study by running calculation using JQMD (JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics). The results were compared with those calculated by the other 15 codes from over the world. Algorithm comparison showed that JQMD calculates collision probabilities from protons at first and collisions by neutrons are simulated later, which might be unreasonable. On the other hand, it was clarified that the calculation by JQMD agrees with those by the others. Despite the fact that some codes deviate from the average by a factor of 2, JQMD exhibited stable performance.
Wang, Y.-Q.*; Gai, W.-Z.*; Zhang, X.-Y.*; Pan, H.-Y.*; Cheng, Z.-X.*; Xu, P. G.; Deng, Z.-Y.*
RSC Advances (Internet), 7(4), p.2103 - 2109, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:64.07(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) [503] band of
[503] band of  Pt
PtLi, G. S.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Zheng, Y.*; Liu, M. L.*; Hua, W.*; Zhou, H. B.*; Ding, B.*; Wang, H. X.*; Lei, X. G.*; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 38(9), p.095105_1 - 095105_9, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.77(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states in  Pt have been investigated by means of in beam
Pt have been investigated by means of in beam  -ray spectroscopic method at the JAEA tandem facility. Low-spin signature inversion is revealed in the 7/2
-ray spectroscopic method at the JAEA tandem facility. Low-spin signature inversion is revealed in the 7/2 [503] band. The inversion can be interpreted as a configuration change from the 7/2
[503] band. The inversion can be interpreted as a configuration change from the 7/2 [503] orbital to the 7/2
[503] orbital to the 7/2 [514] orbital with increasing spin, which is supported by a theoretical calculation of the semi-classical Donau and Frauendorf approach.
[514] orbital with increasing spin, which is supported by a theoretical calculation of the semi-classical Donau and Frauendorf approach.
Chen, L.-M.; Kando, Masaki; Xu, M. H.*; Li, Y.-T.*; Koga, J. K.; Chen, M.*; Xu, H.*; Yuan, X.-H.*; Dong, Q. L.*; Sheng, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 100(4), p.045004_1 - 045004_4, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:93 Percentile:92.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed the increase of the K- X-ray conversion efficiency (hK) produced by a 60 fs frequency doubled high contrast laser pulse focused on Cu foil, compared to the case of the fundamental laser pulse. hK shows a strong dependence on the nonlinearly skewed shape of the laser pulse. It reaches a maximum for a 100 fs negatively skewed pulse. The electron spectrum shaping contributes to the enhancement of hK. Simulations demonstrate that high contrast lasers are an effective tool for optimizing the X-ray emission, via the enhanced Vacuum Heating mechanism.
X-ray conversion efficiency (hK) produced by a 60 fs frequency doubled high contrast laser pulse focused on Cu foil, compared to the case of the fundamental laser pulse. hK shows a strong dependence on the nonlinearly skewed shape of the laser pulse. It reaches a maximum for a 100 fs negatively skewed pulse. The electron spectrum shaping contributes to the enhancement of hK. Simulations demonstrate that high contrast lasers are an effective tool for optimizing the X-ray emission, via the enhanced Vacuum Heating mechanism.
Kamada, Yutaka; Leonard, A. W.*; Bateman, G.*; Becoulet, M.*; Chang, C. S.*; Eich, T.*; Evans, T. E.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Guzdar, P. N.*; Horton, L. D.*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English

 X-ray emission from intense femtosecond laser-solid interactions
X-ray emission from intense femtosecond laser-solid interactionsXu, M. H.*; Chen, L.-M.; Li, Y.-T.*; Yuan, X.-H.*; Liu, Y.-Q.*; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Tajima, Toshiki; Wang, Z.-H.*; Wei, Z.-Y.*; Zhao, W.*; et al.
Acta Physica Sinica, 56(1), p.353 - 358, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The characteristics of 
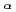 X-ray sources generated by p-polarized femtosecond laser-solid interactions are experimentally studied in the relativistic regime. By use of knife-edge image technique and a single-photon-counting X-ray CCD camera, we obtain the source size, the spectrum and the conversion efficiency of the
X-ray sources generated by p-polarized femtosecond laser-solid interactions are experimentally studied in the relativistic regime. By use of knife-edge image technique and a single-photon-counting X-ray CCD camera, we obtain the source size, the spectrum and the conversion efficiency of the 
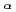 X-ray sources. The experimental results show that the conversion efficiency of
X-ray sources. The experimental results show that the conversion efficiency of 
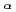 photons reaches an optimum value 7.08
photons reaches an optimum value 7.08 10
10 /sr at the laser intensity of 1.6
/sr at the laser intensity of 1.6 10
10 W/cm
W/cm , which is different from the Reich's simulation results. We find that about 10% of laser energy is converted into the forward hot electrons at the laser intensity of 1.6
, which is different from the Reich's simulation results. We find that about 10% of laser energy is converted into the forward hot electrons at the laser intensity of 1.6 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Chen, Z. Q.; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Xu, Y.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Yuan, X. L.*; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
Physical Review B, 71(11), p.115213_1 - 115213_8, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:106 Percentile:93.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ZnO crystals were implanted with 20-80 keV hydrogen ions up to a total dose of 4.4 10
10 cm
cm . Positron annihilation measurements show introduction of zinc vacancies, which are filled with hydrogen atoms. After isochronal annealing at 200-500
. Positron annihilation measurements show introduction of zinc vacancies, which are filled with hydrogen atoms. After isochronal annealing at 200-500  C, the vacancies agglomerate into hydrogen bubbles. Further annealing at 600-700
C, the vacancies agglomerate into hydrogen bubbles. Further annealing at 600-700  C causes release of hydrogen out of the bubbles, leaving large amount of microvoids. These microvoids are annealed out at high temperature of 1000
C causes release of hydrogen out of the bubbles, leaving large amount of microvoids. These microvoids are annealed out at high temperature of 1000  C. Cathodoluminescence measurements reveal that hydrogen ions also passivate deep level emission centers before their release from the sample, and lead to the improvement of the UV emission.
C. Cathodoluminescence measurements reveal that hydrogen ions also passivate deep level emission centers before their release from the sample, and lead to the improvement of the UV emission.
Chen, Z. Q.; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Xu, Y.; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yuan, X. L.*; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 97(1), p.013528_1 - 013528_6, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:147 Percentile:96.39(Physics, Applied)Phosphorus ions were implanted into ZnO crystals with energies of 50-380 keV to a dose of 10 -10
-10 cm
cm . Positron annihilation measurements show the introduction of vacancy clusters after implantation. These vacancy clusters evolve to microvoids after annealing at a temperature of 600
. Positron annihilation measurements show the introduction of vacancy clusters after implantation. These vacancy clusters evolve to microvoids after annealing at a temperature of 600 C, and disappear gradually up to 1100
C, and disappear gradually up to 1100 C. Raman scattering measurements show the production of oxygen vacancies (V
C. Raman scattering measurements show the production of oxygen vacancies (V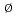 ). They are annealed up to 700
). They are annealed up to 700 C accompanying the agglomeration of vacancy clusters. The light emissions of ZnO are suppressed due to the competing nonradiative recombination centers introduced by implantation. Recovery of the light emission occurs above 600
C accompanying the agglomeration of vacancy clusters. The light emissions of ZnO are suppressed due to the competing nonradiative recombination centers introduced by implantation. Recovery of the light emission occurs above 600 C. The vacancy-type defects detected by positrons might be part of the nonradiative recombination centers. Hall measurement shows n-type conductivity for the P
C. The vacancy-type defects detected by positrons might be part of the nonradiative recombination centers. Hall measurement shows n-type conductivity for the P -implanted ZnO layer, which suggests that phosphorus is an amphoteric dopant.
-implanted ZnO layer, which suggests that phosphorus is an amphoteric dopant.