Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Otobe, Tomohito; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review B, 93(4), p.045124_1 - 045124_9, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:86.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate the dynamical Franz-Keldysh effect in femtosecond time resolution, that is, the time-dependent modulation of a dielectric function at around the band gap under an irradiation of an intense laser field. We develop a pump-probe formalism in two distinct approaches: first-principles simulation based on real-time time-dependent density functional theory and analytic consideration of a simple two-band model. We find that, while time-average modulation may be reasonably described by the static Franz-Keldysh theory, a remarkable phase shift is found to appear between the dielectric response and the applied electric field.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Lee, K.-M.*; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 92(20), p.205413_1 - 205413_6, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:84.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the energy deposition by very short laser pulses in SiO (
( -quartz) with a view to establishing systematics for predicting damage and nanoparticle production. The theoretical framework is time-dependent density functional theory, implemented by the real-time method in a multiscale representation. We find that the deposited energy in the medium can be accurately modeled as a function of the local electromagnetic pulse fluence. The energy deposition function can in turn be quite well fitted to the strong-field Keldysh formula. We find reasonable agreement between the damage threshold and the energy required to melt the substrate. The ablation threshold estimated by the energy to convert the substrate to an atomic fluid is higher than the measurement, indicating significance of nonthermal nature of the process. A fair agreement is found for the depth of the ablation.
-quartz) with a view to establishing systematics for predicting damage and nanoparticle production. The theoretical framework is time-dependent density functional theory, implemented by the real-time method in a multiscale representation. We find that the deposited energy in the medium can be accurately modeled as a function of the local electromagnetic pulse fluence. The energy deposition function can in turn be quite well fitted to the strong-field Keldysh formula. We find reasonable agreement between the damage threshold and the energy required to melt the substrate. The ablation threshold estimated by the energy to convert the substrate to an atomic fluid is higher than the measurement, indicating significance of nonthermal nature of the process. A fair agreement is found for the depth of the ablation.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review B, 90(17), p.174303_1 - 174303_8, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:81.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the dielectric response of excited crystalline silicon in electron thermal equilibrium by adiabatic time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) to model the response to irradiation by high-intensity laser pulses. We find that the extracted effective mass are in the range of 0.22-0.36 and lifetimes are in the range of 1-14 fs depending on the temperature.
 -quartz irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulse
-quartz irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulseLee, K.-M.*; Kim, C. M.*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Otobe, Tomohito; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro; Jeong, T. M.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 115(5), p.053519_1 - 053519_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:72.71(Physics, Applied)A computational method based on a first-principles multiscale simulation has been used for calculating the optical response and the ablation threshold of an optical material irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulse. The method was applied to investigate the changes in the optical reflectance of quartz bulk, half-wavelength thin-film and quarter-wavelength thin-film and to estimate their ablation thresholds. Despite the adiabatic local density approximation used in calculating the exchange-correlation potential, the reflectance and the ablation threshold obtained from our method agree well with the previous theoretical and experimental results. The method can be applied to estimate the ablation thresholds for optical materials in general.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 89(6), p.064304_1 - 064304_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:89.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the dielectric response of crystalline silicon following irradiation by a high-intensity laser pulse, modeling the dynamics by the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equations in the presence of the laser field. As expected, the excited silicon shows features of an electron-hole plasma of nonequilibrium phase in its response, characterized by a negative divergence in the real part of the dielectric function at small frequencies. We also find that the imaginary part of the dielectric function can be negative, particularly for the parallel polarization of pump and probe fields.
Okamoto, Minoru*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
Physical Review C, 88(2), p.025801_1 - 025801_10, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:92.61(Physics, Nuclear)In neutron star crust, non-uniform structure of nuclear matter is expected, which is called the "pasta" structure. From the recent studies of giant flares in magnetars, these structures might be related to some observables and physical quantities of the neutron star crust. To investigate the above quantities, we have numerically explored the pasta structures with a fully three-dimensional geometry and have studied the properties of low-density nuclear matter, based on the relativistic mean-field model and the Thomas-Fermi approximation. We have observed typical pasta structures for fixed proton number-fraction and droplet and rod for cold catalyzed matter. We have also explored the crystalline configuration of "pasta". Although it was believed that spherical nuclei (droplets) form a body-centred cubic lattice as a ground state, we have shown that a face-centred cubic lattice is energetically more favored than body-centred cubic lattice near the transition density to rod.
Okamoto, Minoru; Maruyama, Toshiki; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 146, p.218_1 - 218_6, 2013/04
In low-density nuclear matter which is relevant to neutron star crust, non-uniform structures called "nuclear pasta" are expected. In most of the previous studies, the crystalline of "nuclear pasta" and uniform background electron are assumed and/or the Wigner-Seitz (WS) cell approximation is used. For matter with droplets, body-centered cubic (bcc) lattice is found to be more favored than face-centered cubic (fcc) and simple cubic. This conclusion has been obtained by comparing the Coulomb energy with a fixed size of droplets. To be more precise, we should take into account the effect of non-uniformity of electron and optimal sizes of the droplets. We perform numerical calculations of non-uniform nuclear matter based on the relativistic mean field theory and Thomas-Fermi model with fully three-dimensional geometry. The most stable structure and the equation of state of matter with and without WS cell approximation and the energy difference between fcc and bcc for droplet are compared.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 67(10), p.685 - 689, 2012/10
Coherent phonon is the macroscopic coherent oscillation of atoms in a solid state generating under the ultrafast laser pulse which is shorter than the frequency of the phonon. Some physical processes for the coherent phonon have been proposed. We are studying the computational method describing the dynamics of the electron and atom employing the time-dependent density functional theory. Our computational results show the origine of the coherent phonon in Si quantitatively.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Iwata, Junichi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 137(22), p.22A527_1 - 22A527_8, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:67.85(Chemistry, Physical)The time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) is the leading computationally feasible theory to treat excitations by strong electromagnetic fields. Here the theory is applied to coherent optical phonon generation. We examine the process in the crystalline semimetal antimony (Sb), where nonadiabatic coupling and optical phonon of different symmetries can be observed. The TDDFT is able to account for a number of qualitative features of the observed coherent phonon.
Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Sugiyama, Takeshi*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 85(4), p.045134_1 - 045134_11, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:187 Percentile:97.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We apply the coupled dynamics of time-dependent density functional theory and Maxwell equations to the interaction of intense laser pulses with crystalline silicon. As a function of electromagnetic field intensity, we see several regions in the response. At the lowest intensities, the pulse is reflected and transmitted in accord with the dielectric response, and the characteristics of the energy deposition is consistent with two-photon absorption. The absorption process begins to deviate from that at laser intensities  10
10 W/cm
W/cm , where the energy deposited is of the order of 1 eV per atom. Changes in the reflectivity are seen as a function of intensity. When it passes a threshold of about
, where the energy deposited is of the order of 1 eV per atom. Changes in the reflectivity are seen as a function of intensity. When it passes a threshold of about 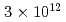 W/cm
W/cm , there is a small decrease. At higher intensities, above 2
, there is a small decrease. At higher intensities, above 2 10
10 W/cm
W/cm , the reflectivity increases strongly. This behavior can be understood qualitatively in a model treating the excited electron-hole pairs as a plasma.
, the reflectivity increases strongly. This behavior can be understood qualitatively in a model treating the excited electron-hole pairs as a plasma.
Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Iwata, Junichi*; Bertsch, G. F.*
Procedia Computer Science, 4, p.852 - 859, 2011/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:60.86(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)We report a first-principle computational method to describe many-electron dynamics in crystalline solid. The method is based on the time-dependent density functional theory, solving time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation in real-time and real-space. The calculation is efficiently parallelized by distributing computations of different  -point among processors. To illustrate usefulness of the method and efficiency of the parallel computation, we show calculations of electron dynamics in bulk Si induced by intense and ultrafast laser pulse.
-point among processors. To illustrate usefulness of the method and efficiency of the parallel computation, we show calculations of electron dynamics in bulk Si induced by intense and ultrafast laser pulse.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Kawashita, Yosuke*; Iwata, Junichi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 82(15), p.155110_1 - 155110_10, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:88.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We apply the adiabatic time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) to the generation of coherent optical phonons in Si crystals by intense laser pulses. The theory reproduces the main phenomena observed experimentally: dependence on polarization, strong growth at the direct band gap, and the change in phase from below to above the band gap. Both show that two mechanisms invoked in phenomenological theory, namely, impulsively stimulated Raman scattering and displacive excitation, are present in the TDDFT. The calculated phase of the coherent phonon is in qualitative agreement with experiment and with phenomenological modeling in the vicinity of the direct band gap. At higher laser frequencies, the TDDFT predicts additional structure not present in the modeling.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Kawashita, Yosuke*; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 22(38), p.384212_1 - 384212_4, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:50.83(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report a first-principle description for coherent phonon generation in diamond based on the time-dependent density functional theory. The time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation is solved in real-time to calculate the electron dynamics in periodic solid under an ultrashort laser pulse. We find the calculated forces acting on ions are consistent with measurements in selection rule and in dependence on laser intensity.
Otobe, Tomohito; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Iwata, Junichi*
Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 6(12), p.2545 - 2549, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:33.2(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The nonlinear electron dynamics in the diamond crystal under the intense laser field is considered. We employ the time-dependent density-functional theory solving the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation in real time and real space. We found the high harmonic generation from diamond up to 11th order with the laser intensity 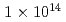 W/cm
W/cm and the induced field from surface charge suppress the harmonic generation strongly.
and the induced field from surface charge suppress the harmonic generation strongly.

Otobe, Tomohito; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Iwata, Junichi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 21(6), p.064224_1 - 064224_5, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:83.39(Physics, Condensed Matter)We present the first-principles description for electron dynamics in crystalline SiO induced by a spatially uniform external electric field. We rely upon the time-dependent density-functional theory with the adiabatic local-density approximation and a real-space and real-time method is employed to solve the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation. The calculations are achieved for both weak and intense regimes. The response to the weak field provides us with the information on dielectric function, while the response to the intense field shows optical dielectric breakdown. We discuss the critical threshold for the dielectric breakdown of crystalline SiO
induced by a spatially uniform external electric field. We rely upon the time-dependent density-functional theory with the adiabatic local-density approximation and a real-space and real-time method is employed to solve the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation. The calculations are achieved for both weak and intense regimes. The response to the weak field provides us with the information on dielectric function, while the response to the intense field shows optical dielectric breakdown. We discuss the critical threshold for the dielectric breakdown of crystalline SiO , in comparison with the results for diamond.
, in comparison with the results for diamond.
Otobe, Tomohito; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Nakatsukasa, Takashi*; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 77(16), p.165104_1 - 165104_5, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:154 Percentile:96.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a first-principle calculation for optical dielectric breakdown induced by an intense laser field. We employ the time-dependent density-functional theory, solving the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation in real time and real space. The calculation shows a qualitative change of electron dynamics as the laser intensity increase, above 7 10
10 W/cm
W/cm . Following the pulse, the excited electron exhibit a coherent plasma oscillation.
. Following the pulse, the excited electron exhibit a coherent plasma oscillation.
Otobe, Tomohito; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Nakatsukasa, Takashi*; Bertsch, G. F.*
RIKEN Accelerator Progress Report, Vol.41, P. 185, 2008/00
We simulate the optical breakdown process of dielectrics under the intense laser field employing the first-principle method. Our result for the diamond, which is typical dielectrics, shows the saturation of the energy absorption and electron excitation. We found also the induced field by the surface charge becomes out of phase to the applied field.
Otobe, Tomohito; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review A, 75(6), p.062507_1 - 062507_8, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:69.38(Optics)The tunnel ionization rate under a static intense electric field is calculated for some hydrocarbon molecules, acetylene, ethylene and benzene, employing the ab-initio density functional theory. The ionization rate is found to reflect the properties of the highest occupied molecular orbital, in agreement with the description of the molecular Ammosov-Delone-Krainov theory. Many-electron correlation effects beyond a single-electron approximation are discussed. The screening effect on the ionization rate is quantitatively evaluated.
Otobe, Tomohito; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Iwata, Junichi*; Nakatsukasa, Takashi*; Bertsch, G. F.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matsuyama, Hiroaki*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English