Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ta
Ta O
O
Kimura, Kenta*; Yagi, Naoki*; Hasegawa, Shunsuke*; Hagihara, Masato; Miyake, Atsushi*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Cao, H.*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(20), p.15078 - 15084, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.45(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Nakayama, Masashi; Saiga, Atsushi; Kimura, Shun; Mochizuki, Akihito; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ono, Hirokazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Takeda, Masaki; Hayano, Akira; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2019-013, 276 Pages, 2020/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. The investigations will be conducted in three phases, namely "Phase 1: Surface based investigations", "Phase 2: Construction phase" (investigations during construction of the underground facilities) and "Phase 3: Operation phase" (research in the underground facilities). According to the research plan described in the 3rd Mid- and Long- term Plan of JAEA, "Near-field performance study", "Demonstration of repository design option", and "Verification of crustal-movement buffering capacity of sedimentary rocks" are important issues of the Horonobe URL Project, and schedule of future research and backfill plans of the project will be decided by the end of 2019 Fiscal Year. The present report summarizes the research and development activities of these 3 important issues carried out during 3rd Medium to Long-term Research Phase.
Motoshima, Takayuki*; Koike, Masashi*; Hagihara, Takeshi*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei
Dai-46-Kai Gamban Rikigaku Ni Kansuru Shimpojiumu Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.208 - 213, 2019/01
The short step construction method is the standard construction method for deep shaft excavation. However, considering the shaft construction in the sedimentary rock widely distributed in Japan, the support concrete stress can become excessive especially when there are bad conditions such as low rock strength, anisotropic initial stress, or high ground pressure. In this research, we introduced the dual support design to the short step construction method in order to reduce the support stress, and confirmed the validity by three dimensional numerical analysis. Validation analysis was conducted using the in-situ data in the Horonobe Underground Research Project conducted by Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Miyara, Nobukatsu; Ishii, Eiichi; Nakayama, Masashi; Kimura, Shun
Proceedings of 13th SEGJ International Symposium (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2018/11
The construction of underground facilities induces fractures in the rock mass around the underground voids due to the resultant stress redistribution. This has particular implications for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal projects, where fracture development creates an excavation damaged zone (EDZ) that increases the hydraulic conductivity of the surrounding rock mass and can provide a pathway for the migration of radionuclides from the storage facilities. It is therefore important to understand the long-term evolution of the EDZ and perform a comprehensive HLW disposal risk assessment. An in situ engineered barrier system experiment was conducted in the 350 m gallery at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Japan, to observe the near-field coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) process in situ and validate coupled THMC models. Here we investigate the evolution of the EDZ around the gallery and model a test pit that was excavated below the floor of the gallery using a series of seismic tomography surveys. There was a significant decrease in the seismic velocity field around the test pit due to its excavation, which became slightly more pronounced over time after the excavation. These seismic results, coupled with hydraulic tests and pore pressure measurements around the pit, indicate that fracture development and the decrease in saturation around the test pit resulted in a decrease in the seismic velocity field after the excavation of the test pit. Furthermore, the increase in saturation around the test pit is a key reason for the increase in the seismic velocity field after the heater test.
Sato, Toshinori; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Ishii, Eiichi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Fujita, Tomoo*; Tanai, Kenji; Nakayama, Masashi; Takeda, Masaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2016-025, 313 Pages, 2017/03
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formations at Horonobe, northern Hokkaido. This report summarizes the results of the Phase II investigations carried out from April 2005 to June 2014 to a depth of 350m. Integration of work from different disciplines into a "geosynthesis" ensures that the Phase II goals have been successfully achieved and identifies key issues that need to made to be addressed in the Phase II investigations Efforts are made to summarize as many lessons learnt from the Phase II investigations and other technical achievements as possible to form a "knowledge base" that will reinforce the technical basis for both implementation and the formulation of safety regulations.
Hama, Katsuhiro; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Takeda, Masaki; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; et al.
JAEA-Review 2016-014, 274 Pages, 2016/08
We synthesized the research results from the Mizunami/Horonobe Underground Research Laboratories (URLs) and geo-stability projects in the second midterm research phase. This report can be used as a technical basis for the Nuclear Waste Management Organization of Japan/Regulator at each decision point from siting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase).
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi; Nakayama, Masashi; Fujita, Tomoo
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-65-Ki Tsujo Sokai, Gakujutsu Koenkai Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), p.19 - 20, 2016/05
no abstracts in English
Hama, Katsuhiro; Mizuno, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Sato, Toshinori; Fujita, Tomoo; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Yokota, Hideharu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2015-007, 269 Pages, 2015/08
We have synthesised the research results from Mizunami/Horonobe URLs and geo-stability projects in the second mid-term research phase. It could be used as technical bases for NUMO/Regulator in each decision point from sitting to beginning of disposal (Principal Investigation to Detailed Investigation Phase). High quality construction techniques and field investigation methods have been developed and implemented and these will be directly applicable to the National Disposal Program (along with general assessments of hazardous natural events and processes). It will be crucial to acquire technical knowledge on decisions of partial backfilling and final closure by actual field experiments in Mizunami/Horonobe URLs as main themes for the next phases.
Motoshima, Takayuki*; Yabuki, Yoshio*; Minamide, Masashi*; Nago, Makito*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei
Tonneru Kogaku Hokokushu (CD-ROM), 24, p.I_10_1 - I_10_5, 2014/12
Economic tunnel support design for Horonobe underground research laboratory was obtained according to the relationship in the direction of the initial stress and the direction of excavation. The authors compared between the in situ convergence results and calculated results in order to investigate the validity of initial stress measurements. As a result, a positive correlation was observed between the in situ convergence results and calculated results, and the difference between the two was able to be explained by the difference between the assumed deformation coefficient and the measured coefficient. From these results, the measurement results of the initial stress performed in the surface based investigation has been confirmed almost reasonable.
 C and
C and  O nuclei by low-energy proton beams
O nuclei by low-energy proton beamsAkagi, Takashi*; Yagi, Masashi*; Yamashita, Tomohiro*; Murakami, Masao*; Yamakawa, Yoshiyuki*; Kitamura, Keiji*; Ogura, Koichi; Kondo, Kiminori; Kawanishi, Shunichi*
Radiation Measurements, 59, p.262 - 269, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:76.68(Nuclear Science & Technology)In proton therapy, positron emitters are induced from  C and
C and O nuclei by protons on the beam path in the patient. Many studies for monitoring positron emitters with beam-induced PET technique have been performed by various groups to verify the proton beam range and the dose in the patient for quality assurance. The aim of this study was to develop a method for measuring the production cross sections of positron emitters using standard equipment for proton therapy. The time-activity curve was then obtained with a high-sensitivity PET scanner to extract the number of positron emitters produced in the target. The production cross sections for four reaction channels:
O nuclei by protons on the beam path in the patient. Many studies for monitoring positron emitters with beam-induced PET technique have been performed by various groups to verify the proton beam range and the dose in the patient for quality assurance. The aim of this study was to develop a method for measuring the production cross sections of positron emitters using standard equipment for proton therapy. The time-activity curve was then obtained with a high-sensitivity PET scanner to extract the number of positron emitters produced in the target. The production cross sections for four reaction channels:  O(p,pn)
O(p,pn) O,
O,  O(p,3p3n)
O(p,3p3n) C,
C,  O(p,2p2n)
O(p,2p2n) N, and
N, and  C(p,pn)
C(p,pn) C were then measured. The cross sections for the
C were then measured. The cross sections for the  O(p,pn)
O(p,pn) O reaction channel were consistent with data of previous experiments within the uncertainties, while those of
O reaction channel were consistent with data of previous experiments within the uncertainties, while those of  C(p,pn)
C(p,pn) C were generally lower than data of previous experiments.
C were generally lower than data of previous experiments.
Awaji, Satoshi*; Namba, Masashi*; Watanabe, Kazuo*; Ito, Shun*; Aoyagi, Eiji*; Kai, Hideki*; Mukaida, Masashi*; Okayasu, Satoru
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 21(3), p.3192 - 3195, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.75(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The flux pinning behaviors for the heavy ion irradiated Er123 films are investigated based on the detailed 
 (
( ,
,  ,
,  ) properties. The double peaks of
) properties. The double peaks of 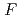
 curves for
curves for  //c appear in case of the matching field of 0.3 T along
//c appear in case of the matching field of 0.3 T along  -axis and 1.7 T tilted from
-axis and 1.7 T tilted from  -axis. In addition, the peaks on
-axis. In addition, the peaks on 
 (
( ) at
) at  = 0
= 0 (B//c), which originate from the columnar defects, decrease with increasing magnetic field but increase again near the irreversibility field. We found that the cooperation model of the
(B//c), which originate from the columnar defects, decrease with increasing magnetic field but increase again near the irreversibility field. We found that the cooperation model of the  -axis correlated and random pinning centers can describe the observed double peak behavior of
-axis correlated and random pinning centers can describe the observed double peak behavior of 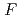
 (B) and the angular dependence of
(B) and the angular dependence of 
 related to the correlated pinning.
related to the correlated pinning.
 Fe
Fe Nx
NxKasatani, Hirofumi*; Omura, Masashi*; Yokoyama, Katsumi*; Kobayashi, Kurima*; Nishihata, Yasuo; Yagi, Kenichiro*; Terauchi, Hikaru*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 38(Suppl.38-1), p.433 - 435, 1999/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.87(Physics, Applied)High energy XAFS studies of Sm: K-edge in Sm2Fe17Nx with x = 0.0, <= 0.1, 0.5, 2.0 and 3.0 were carried out at room temperature in order to clarify the relation between the local structure around the Sm-atom and the change of the magnetic property due to the absorption of nitrogen atom. In the XANES region, we firstly found the change of Sm electron state by nitriding because of the change of the shape in the absorption edge junp. In the result of the EXAFS spectra, we confirmed that the Sm-Fe distance was expanded monotonously due to the absorption of N-atom.
Utsumi, Wataru; Abe, Jun; Hattori, Takanori; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Igawa, Naoki; Kagi, Hiroyuki; Arima, Hiroshi*; Arakawa, Masashi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Abe, Jun; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi; Arakawa, Masashi*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Kagi, Hiroyuki; Yagi, Takehiko*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have examined the feasibility of in situ neutron powder diffraction under high pressure with the Engineering Materials Diffractometer "TAKUMI", which has been constructed at BL19 in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) of J-PARC. We have tested two types of high pressure devices at TAKUMI, a Paris-Edinburgh press and a Palm cubic anvil cell. Neutron poder diffraction profiles of Pb placed in the high pressure devices as a standard material were collected. As results, diffraction peaks of Pb were clearly observed. In this study, it has been confirmed that in situ neutron powder diffraction under high pressure can be made with a combination of the high pressure devices and the TAKUMI at J-PARC.
Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi; Sano, Asami; Abe, Jun; Honda, Mitsunori; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Utsumi, Wataru; Okuchi, Takuo*; Ono, Yoshiki*; Sasaki, Shigeo*; et al.
no journal, ,
The high-pressure neutron experiments above 10 GPa are limited so far due to the small neutron flux, which is insufficient for tiny high-pressure sample. Recent construction of the intense pulsed neutron source around the world has changed the situation. Inspired by the new Japanese pulsed neutron source JSNS at J-PARC, we started the high-P neutron experiments at the already operated beamlines (TAKUMI, NOVA) and the construction of the new beamline dedicated for high-pressure use (PLANET). This talk introduces these activities.
Inagaki, Daisuke; Tsusaka, Kimikazu; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Hagihara, Takeshi*; Nago, Makito*; Minamide, Masashi*; Ijiri, Yuji*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Aoyagi, Noboru
no journal, ,
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been employed as a powerful tool to understand the coordination bonds of actinide complexes. Our previous works have indicated that a valid choice of DFT method benchmarked with experimental spectroscopic parameters leads to an accurate prediction of the separation of minor-actinides from lanthanides. The present study aims to improve DFT method for the bond estimation of actinide complexes and focuses on UV-Vis absorption spectroscopic study for tetravalent halides, UX in tetrahydrofuran (thf) solution. We modeled tetravalent uranium complex as [UX
in tetrahydrofuran (thf) solution. We modeled tetravalent uranium complex as [UX (thf)
(thf) ] (X = F, Cl, Br and I) by referring single crystal X-ray diffraction data of [UI
] (X = F, Cl, Br and I) by referring single crystal X-ray diffraction data of [UI (1,4-dioxane)
(1,4-dioxane) ] and calculated the transition energies and transition probabilities using time-dependent DFT. As the result, the corresponding peak maxima were given at 168, 217, 249 and 305 nm for the complexes with X = F, Cl, Br and I, respectively. This tendency correlated to the experimental result for X = Br and I. The transition energy analysis of the peak for X = I indicated the plausible assignment as a ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) transition by molecular orbital analysis.
] and calculated the transition energies and transition probabilities using time-dependent DFT. As the result, the corresponding peak maxima were given at 168, 217, 249 and 305 nm for the complexes with X = F, Cl, Br and I, respectively. This tendency correlated to the experimental result for X = Br and I. The transition energy analysis of the peak for X = I indicated the plausible assignment as a ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) transition by molecular orbital analysis.