Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
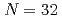
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58.81(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Takumi*; Hirai, Takamasa*; Yagi, Takashi*; Yamashita, Yuichiro*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 21(2), p.024039_1 - 024039_11, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied)Uchibori, Akihiro; Doda, Norihiro; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Sonehara, Masateru; Sogabe, Joji; Okano, Yasushi; Takata, Takashi*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Wakai, Takashi; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 413, p.112492_1 - 112492_10, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)The ARKAIDA has been developed to realize automatic optimization of plant design from safety evaluation for the advanced reactors represented by a sodium-cooled fast reactor. ARKADIA-Design offers functions to support design optimization both in normal operating conditions and design basis events. The multi-level simulation approach by the coupled analysis such as neutronics, core deformation, core thermal hydraulics was developed as one of the main technologies. On the other hand, ARKAIDA-Safety aims for safety evaluation considering severe accidents. As a key technology, the numerical methods for in- and ex-vessel coupled phenomena during severe accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors were tested through a hypothetical severe accident event. Improvement of the ex-vessel model and development of the AI technology to find best design solution have been started.
Louie, D. L. Y.*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Luxat, D. L.*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 407, p.112285_1 - 112285_5, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ito, Daichi*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Sakata, Shuhei*; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Koshi*; Imura, Takumi*; Motai, Satoko*; Ono, Takeshi*
Lithos, 440-441, p.107026_1 - 107026_14, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.82(Geochemistry & Geophysics)We propose a new method for elucidating zircon growth in granitic plutons, based on variations in three-dimensional 3D cathodoluminescence (CL) patterns, U-Pb ages, titanium concentration, and Th/U ratios. We focused on the zircon growth processes in the Okueyama granite (OKG) in central Kyushu, Japan, to obtain interpretations of magma chamber processes that result in the formation of granitic plutons. The OKG consists of three lithofacies: biotite granite (BG), hornblende granite (HG), and hornblende granodiorite (HGD). To determine the 3D internal structure and growth pattern of a zircon crystal, we performed CL observations for multi-sections of the samples. Simultaneously, we also determined the zircon U-Pb age and titanium concentration of the center sections of the samples. The 3D distribution of the oscillatory zoning can be used to determine the crystal nucleus. The simultaneous determination of zircon U-Pb ages and Ti concentrations of the granite samples indicates the time-temperature (t-T) history of granitic magma before its solidification. The t-T histories of the BG, HG, and HGD represented similar cooling behaviors within the magma chamber: rapid cooling from the zircon crystallization temperature to the closure temperature of the biotite K-Ar system between 16 Ma and 10 Ma. The variations in the Th/U ratios against temperature also demonstrate a different trend at the boundary of approximately 670  C. Fractional crystallization in the magma chamber progressed significantly at temperatures above 670
C. Fractional crystallization in the magma chamber progressed significantly at temperatures above 670  C; below 670
C; below 670  C, crystallization progressed slowly, indicating only minimal changes in the magma composition. The variations in the Th/U ratio against temperature in the BG, HG, and HGD portrayed common tendencies, indicating the same behavior in the progression of fractional crystallization among the three lithofacies, which in turn, represented the same behavior within the entire magma chamber.
C, crystallization progressed slowly, indicating only minimal changes in the magma composition. The variations in the Th/U ratio against temperature in the BG, HG, and HGD portrayed common tendencies, indicating the same behavior in the progression of fractional crystallization among the three lithofacies, which in turn, represented the same behavior within the entire magma chamber.
Louie, D. L. Y.*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Luxat, D. L.*
Proceedings of Technical Meeting on State-of-the-art Thermal Hydraulics of Fast Reactors (Internet), 6 Pages, 2022/09
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Sonehara, Masateru; Ishida, Shinya; Uchibori, Akihiro; Kawada, Kenichi; Okano, Yasushi; Takata, Takashi
Proceedings of Technical Meeting on State-of-the-art Thermal Hydraulics of Fast Reactors (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/09
 Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:67.20(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Uchibori, Akihiro; Sonehara, Masateru; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/04
A new computational code, SPECTRA, has been developed for integrated analysis of in- and ex-vessel phenomena during severe accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. The in-vessel thermal hydraulics module includes coupled analytical models for multidimensional multifluid model considering compressibility and relocation of a molten core. A lumped mass model is employed for computing behavior of ex-vessel compressible multicomponent gas including aerosols. This model is coupled with the models for ex-vessel phenomena such as sodium fire. Loss of reactor level event starting from leakage of sodium coolant was computed. Basic capability to evaluate severe accident progress was demonstrated through this analysis.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/03
Zhan, Y.*; Sun, G.*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 126, p.110402_1 - 110402_8, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:54.98(Thermodynamics)Takata, Takashi; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Sonehara, Masateru
IAEA-TECDOC-1972, p.224 - 234, 2021/08
Sodium fire is one of the key issues for plant safety of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) regardless of its size. In general, a concrete structure, which includes free and bonging water inside, is used in a reactor building. Accordingly, water vapor will release from the concrete during sodium fire incident due to temperature increase resulting in a hydrogengeneration even in a dry air condition. The probability of hydrogen generation will increase in accordance with a decrease of a dimension of compartment that corresponds to a small and medium sized or modular reactor (SMR). A numerical investigation of a small leakage sodium pool fire has been carried out by changing a dimension of compartment. Furthermore, numerical challenges to enhance a prediction accuracy of hydrogen generation during sodium fire has also been discussed in the paper.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111258_1 - 111258_11, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:31.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Louie, D. L. Y.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Luxat, D.*
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/08
Sonehara, Masateru; Uchibori, Akihiro; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Kawada, Kenichi; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Dai-25-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2021/07
In sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), it has been pointed out that molten fuel may be discharged from the core during a severe accident (SA) accompanied by core damage, and may solidify into debri particles with diameters ranging from several millimeters to several hundred micrometers due to interaction with the sodium coolant and accumulate at the bottom of the reactor vessel. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the behavior of such debri particles appropriately to evaluate the SA event progression. To meet these requirements, a molten fuel behavior analysis code using dissipative particle dynamics (DPD), a kind of particle method, has been developed as a part of the SPECTRA code, tool for consistent analysis of in-vessel and ex-vessel events in sodium fast reactor accidents. In this study, it was found that the new analyses code can reproduce sedimentation behavior of particles by adding a new stress term in the shear direction.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Yagi, Koshi*; Sasao, Eiji; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Heliyon (Internet), 7(4), p.e06750_1 - e06750_9, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.18(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Our methodology and interpretations provide new insight for K-Ar geochronology in hydrothermal microcline within altered plagioclase in a granitic pluton. Our methodology employs a two-step separation process consisting of (1) plagioclase extraction from the rock sample and (2) separation of the hydrothermal microcline from the plagioclase, giving precise determination of microcline powders in K-Ar geochronology. This tighter constraint should provide the ability to better unravel thermal and age histories in granite subject to multi-step alteration processes and complex thermal histories.
Zhan, Y.*; Kuwata, Yusuke*; Okawa, Tomio*; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi
Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 120, p.110249_1 - 110249_12, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:74.00(Thermodynamics)Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ishibashi, Kozue*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ito, Daichi*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yagi, Koshi*; Ono, Takeshi*
Lithos, 372-373, p.105682_1 - 105682_9, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:41.51(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Simultaneous determination of zircon U-Pb age and titanium concentration for a single analysis spot gives both the crystallization age and temperature. The crystallization age and temperature pairs in granitic zircons map the time-temperature ( ) path of granitic magma before its solidification. In laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) analysis, it is challenging to quantitatively analyse a low level of titanium concentration. This study employed two approaches using a Quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with a collision/reaction cell (CRC). The methods were applied to zircon samples of the Kurobegawa granite (KRG), the Okueyama granite (OKG), the Toki granite (TKG), and the Tono plutonic complex (TPC) and provided U-Pb ages and titanium concentrations consistent with previous studies. The crystallization ages and temperatures collected from individual analysis spots of zircon samples in the KRG, OKG, TKG, and TPC are plotted in the
) path of granitic magma before its solidification. In laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) analysis, it is challenging to quantitatively analyse a low level of titanium concentration. This study employed two approaches using a Quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with a collision/reaction cell (CRC). The methods were applied to zircon samples of the Kurobegawa granite (KRG), the Okueyama granite (OKG), the Toki granite (TKG), and the Tono plutonic complex (TPC) and provided U-Pb ages and titanium concentrations consistent with previous studies. The crystallization ages and temperatures collected from individual analysis spots of zircon samples in the KRG, OKG, TKG, and TPC are plotted in the  diagrams and enable us to characterize the rapid cooling paths at thermal conditions of zircon crystallization at the sampling sites.
diagrams and enable us to characterize the rapid cooling paths at thermal conditions of zircon crystallization at the sampling sites.
Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Louie, D. L. Y.*; Clark, A. J.*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2020/08
The Sodium Chemistry (NAC) package in MELCOR has been developed to enhance application to sodium cooled fast reactors. The models in the NAC package have been assessed through benchmark analyses of the F7-1 pool fire experiment. This study assesses the capability of the pool fire model in MELCOR and provides recommendations for future model improvements. The MELCOR analysis yields lower values than the experimental data in pool combustion rate and pool, catch pan, and gas temperature during early time. The current heat transfer model for the catch pan is the primary cause of the difference. After sodium discharge stopping, the pool combustion rate and temperature become higher than experimental data. This is caused by absence of a model for pool fire suppression due to the oxide layer buildup on the pool surface. Based on these results, recommendations for future works are needed, such as heat transfer modification for the catch pan and consideration of the effects of the oxide layer.
Uchibori, Akihiro; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2020/08
The multi-scenario simulation system named SPECTRA has been developed for integrated analysis of in- and ex-vessel phenomena during a severe accident in sodium-cooled fast reactors. The base module computing ex-vessel compressible gas behavior by a lumped mass model and a sodium-concrete interaction module were verified through the basic analyses individually. A validity of the system including the base module and the individual physical module such as the sodium-concrete interaction module was confirmed through the analysis assuming sodium leakage from a reactor vessel and a primary cooling loop.