Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nomura, Mitsuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nakayama, Takuya; Yaita, Yumi*; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Murata, Eiichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104396_1 - 104396_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)When dismantling centrifuges in uranium-enrichment facilities, decontamination techniques must be developed to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces of dismantled parts selectively. Dismantled uranium-contaminated parts can be disposed of as nonradioactive wastes or recycled after decontamination appropriate for clearance. previously, we developed a liquid decontamination technique using acidic electrolyzed water to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces. However, further developments are still needed for its actual application. Dismantled parts have various uranium-contaminated surface features due to varied operational conditions, inhomogeneous decontamination using iodine heptafluoride gas, and changes in long-term storage conditions after dismantling. Here, we performed liquid decontamination on specimens with varying uranium-contaminated surfaces cut from a centrifuge made of low-carbon steel. From the results, the liquid decontamination can effectively remove the uranium-contaminated surfaces, and radioactive concentrations fell below the target value within twenty minutes. Although the required time should also depend on dismantled parts' sizes and shapes in their actual application, we demonstrated that it could be an effective decontamination technique for uranium-contaminated steels of dismantled centrifuges.
Nakayama, Takuya; Nomura, Mitsuo; Mita, Yutaka; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Bunbai, Misako*; Yaita, Yumi*; Murata, Eiichi*; Hosaka, Katsumi*; Sugitsue, Noritake
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/05
Clearance of contaminated metal is important for recycling and volume reduction of radioactive waste. Among applicable decontamination technologies, immersion method with ultrasonic cleaning is considered to be effective for metal materials having various shapes. in this study is to demonstrate decontamination of carbon steel contaminated by uranium hexafluoride to the target level for clearance (less than 0.04 Bq/cm ), and minimize secondary waste. In this test, acidic electrolytic water, dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute sulfuric acid and ozone water with various pH and redox potential were used as decontamination solutions to be tested. We found that acidic electrolytic water is effective solution for decontamination of carbon steel contaminated by uranium hexafluoride. It could be decontaminate less than target level for clearance, and reduced secondary waste relatively.
), and minimize secondary waste. In this test, acidic electrolytic water, dilute hydrochloric acid, dilute sulfuric acid and ozone water with various pH and redox potential were used as decontamination solutions to be tested. We found that acidic electrolytic water is effective solution for decontamination of carbon steel contaminated by uranium hexafluoride. It could be decontaminate less than target level for clearance, and reduced secondary waste relatively.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 10, p.367 - 373, 2012/07
To apply organic thin films as new devices, it is important to immobilize organic molecules on oxide surfaces. In this study, we investigated the formation of organic self-assembled monolayer on the oxide surface. Decyl phosphonic acid (DPA) molecules were used as the adsorbed molecule on the surface. The DPA film was prepared by immersing the sapphire substrate in DPA ethanol solution. The sample was measured by XPS using synchrotron soft X-ray. For the P 1s XPS spectra of the DPA powder and the DPA film on the sapphire surface, a single peak was observed and the binding energies of the two samples were almost the same. And we measured the sample by the total reflection (TR) XPS, which is highly surface sensitive method. Compared with the normal XPS, the intensity of the C 1s peak in TR-XPS was enhanced. As a result, it was elucidated that the phosphonic acid of the DPA molecule was located at the lower side, while the alkyl chain was located at the upper side on the surface.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Applied Surface Science, 258(6), p.2034 - 2037, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.50(Chemistry, Physical)In order to apply the organic thin films to electric and optical devices, the immobilization of organic molecules on inorganic substrate is essential. Considering optical devices, it is important to immobilize organic molecules on oxide surfaces, because many of oxides have insulating and transparent properties. In this study, we have investigated the chemical states of the interface between organic molecules with silicon alkoxide and sapphire surfaces by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and near edge absorption fine structure (NEXAFS). Octadecyl-triethoxy-silane (ODTS) molecules which are terminated by silicon alkoxide were adsorbed on sapphire surfaces. On the basis of the Si 1s XPS spectra for monolayer, it is supposed that the chemical bond between silicon alkoxide and the surface is formed. For Si K-edge NEXAFS spectra, the polarization dependence was observed, which suggests that the Si-O bond in ODTS was located perpendicular to the surface.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Photon Factory Activity Report 2011, Part B, P. 94, 2012/00
Immobilization of organic molecules on oxide surface has been investigated using phosphonic acid as an anchor. The molecule investigated was decyl-phosphonic acid (DPA). The DPA film was formed by immersing the sapphire substrate in DPA ethanol solution. The results for X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) showed that the alkyl chain of the DPA molecules is located at the upper side, while the phosphonic acid is the lower side on the surface. The XPS and near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS) results indicated that the DPA film became homogeneous monolayer by heating at 250 C. It is concluded that the phosphonic acid is an excellent anchor that immobilizes the organic molecules on an oxide surface.
C. It is concluded that the phosphonic acid is an excellent anchor that immobilizes the organic molecules on an oxide surface.
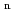 H
H (n
(n 2) molecules from adsorbed methane by low-energy ion irradiation
2) molecules from adsorbed methane by low-energy ion irradiationNarita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Hyomen Kagaku, 29(8), p.489 - 494, 2008/08
The formation of molecular ions and neutral molecules from adsorbed CH , CD
, CD and N
and N following 1 keV He
following 1 keV He ion irradiation has been investigated. The thickness of the adsorbed layer was precisely controlled. For mono-layered methane, only monomer ions (CH
ion irradiation has been investigated. The thickness of the adsorbed layer was precisely controlled. For mono-layered methane, only monomer ions (CH
 ) were desorbed, while a large number of heavy ions (C
) were desorbed, while a large number of heavy ions (C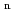 H
H
 ) up to n = 20 as well as heavy neutral molecules (C
) up to n = 20 as well as heavy neutral molecules (C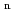 H
H ) were desorbed from multi-layered film. Among the desorbed ions and neutral molecules, molecules with C-C covalent bonds such as acetylene and ethylene were found. The results indicate that chemical bonds are newly formed by ion irradiation. Based on the results for thickness dependences of the mass spectra and calculation of He
) were desorbed from multi-layered film. Among the desorbed ions and neutral molecules, molecules with C-C covalent bonds such as acetylene and ethylene were found. The results indicate that chemical bonds are newly formed by ion irradiation. Based on the results for thickness dependences of the mass spectra and calculation of He energy loss process from TRIM-Code, it was elucidated that the monomer ions are desorbed from the top surface layer through single electron excitation. On the other hand, the cluster ions are formed mainly in the inside of the layers along the nuclear track due to phonon excitation, which is produced by nuclear collision between incident He
energy loss process from TRIM-Code, it was elucidated that the monomer ions are desorbed from the top surface layer through single electron excitation. On the other hand, the cluster ions are formed mainly in the inside of the layers along the nuclear track due to phonon excitation, which is produced by nuclear collision between incident He ions and adsorbed molecules.
ions and adsorbed molecules.
 ,
, -dialkyl carboxyamides
-dialkyl carboxyamidesSuzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Sugo, Yumi; Kimura, Takaumi
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1137 - 1141, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
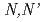 -dialkyl-2,6-pyridinedimethanaminium halide
-dialkyl-2,6-pyridinedimethanaminium halideKobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Sugo, Yumi; Suda, Hiroki*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Fujii, Yuki*; Nakano, Yoshiharu*
Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry, 43(3), p.549 - 557, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:13.16(Chemistry, Organic)Narita, Hirokazu*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Sato, Yumiko*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Solvent Extraction and Ion Exchange, 24(5), p.693 - 702, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:46.70(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The structure of the Ni(II) complex extracted with the commercial hydroxyoxime, LIX84I, and the effect of adding bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoricacid(D2EHPA) to LIX84I on the extraction rate and the coordination of Ni(II) were investigated by solvent extraction and XAFS methods. The XANES spectrum and the curve fit soft the EXAFS spectrum of the Ni-LIX84I complex showed that the complex is four-coordinate square-planar with a 1:2 stoichiometry. In the Ni(II)-D2EHPA-LIX84I system, the coordination geometry changes to six-coordinate octahedral with an increase in the D2EHPA concentration. Although the rate of Ni(II) extraction with LIX84I is significantly accelerated by adding as small amount of D2EHPA, most of the Ni(II) complexes extracted with this organic solution remain square-planar. This indicates that the effect of D2EHPA on the increase in the extraction rate would be attributed to a behavior of this ligand like catalysis.
Ishimori, Kenichiro*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Kimura, Takaumi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Yamada, Takashi*; Kataoka, Yumiko*; Shinoda, Satoshi*; Tsukube, Hiroshi*
Chemistry Letters, 34(8), p.1112 - 1113, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:45.83(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Stereochemical substitution on tripod ligand significantly offered efficient separation of trivalent actinides from trivalent lanthanides. Liquid-liquid extraction using chiral tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine ligands as an extractant exhibited high efficiency and selectivity for trivalent actinides. A combination of chiral ligand and 2-bromodecanoic acid further enhanced extraction performance for trivalent actinides.
Yaita, Yumi*; Ohira, Shigeru; Okuno, Kenji
Fusion Technology, 28(3), p.1294 - 1298, 1995/10
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Photon or electron irradiation breaks chemical bond and induces desorption of fragment. However, formation of chemical bond from adsorbed light molecules, such as methane, by high energy radiation has scarcely been reported. This process is important in space, because organic molecules can be formed through these reactions. In this report, we have investigated formation of molecular ions and neutral molecules with covalent bond from frozen methane by He+ ion irradiation. It was found that acetylene ion(C2H2+), and ethylene ion(C2H4+) with covalent bond were formed by He+ ion irradiation. These results were compared with Monte-Carlo simulation for energy-loss processes of He+ ions in solid methane. As a result, it was elucidated that molecular ions are formed inside of frozen methane by high-density excitation due to nuclear collision. On the other hand, neutral molecules are formed by rapid evaporation due to temperature increase along the nuclear track.
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Organic thin films have advantages over currently used Si-devises, and they can have new functions that Si-devices don't have. However, there are several problems to be solved such as chemical states of organic-inorganic interfaces and molecular orientations. In this study, we investigated chemical states of the interface between mercapto-propyl-trimetoxy-silane (MPTS) and aluminum oxide using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and near edge X-ray absorption fine structure (NEXAFS). For the XP spectra, it was elucidated that MPTS molecules and aluminum oxide surface made the chemical bond through silicon alkoxide. Moreover, the NEXAFS spectra at the silicon K-edge show a polarization dependence. From these results, we concluded that MPTS molecules locate perpendicular direction to the aluminum oxide surface.
Suzuki, Shinichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Sugo, Yumi; Kimura, Takaumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie*; Baba, Yuji; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi*; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie*; Baba, Yuji; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Narita, Ayumi; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
It is difficult to immobilize organic molecules on an inorganic material, because the lattice constants of organic crystals are larger than those of inorganic ones. Especially, there are few reports about the immobilization of organic molecules on oxide. In this study, we have investigated that the immobilization of alkane molecules on oxide surfaces. Octadecyl-triethoxy-silane (ODTS) molecules were adsorbed on a sapphire single crystal, and the chemical states of the interfaces were measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) using synchrotron radiation. The Si 1s XPS spectrum of ODTS monolayer on sapphire suggested that silicon alokoxides of ODTS formed chemical bond with the surface. For Si-K edge XAFS spectra of ODTS monolayer, the polarization dependence was observed. On the basis of the angle dependence, it was elucidated that one of the Si-O bonds in the ODTS molecule is perpendicular to the surface.