Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Kenji*; Yamada, Minami*; Shiro, Ayumi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Toyokawa, Hidenori*; Saji, Choji*
Zairyo, 71(4), p.347 - 353, 2022/04
We have already succeeded in the residual stress of aluminum alloys using the double exposure method (DEM) with 30 keV synchrotron radiation X-rays. However, the DEM has not be applied in the range of high-energy synchrotron X-rays. In this study, the stress measurements of a shrink-fitted ring using the DEM with synchrotron monochromatic X-rays beyond about 70 keV were performed. A CdTe pixel detector and a CCD camera were used as a detector. The shrink-fitted specimen of SUS304 was quasi-coarse grains of 43 micro-meters, and the diffraction rings were spotty. Despite quasi-coarse grains, it was possible to measure the stresses of the shrink-fitted specimen using the DEM. As a result, the DEM is excellent method to measures the stress for coarse grained materials. In addition, it is better to make the length between the detection positions longer to improve precision of the DEM. On the other hand, it was ineffective to increase the positions of detection.
 O
O
Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Ueda, Hiroaki*; Niitaka, Seiji*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kikuchi, Tatsuya; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nakajima, Kenji; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Physical Review Letters, 113(23), p.236402_1 - 236402_5, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:68.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Spin fluctuations were studied over a wide momentum (
 ) and energy (
) and energy ( ) space in the frustrated
) space in the frustrated 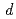 -electron heavy-fermion metal LiV
-electron heavy-fermion metal LiV O
O by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. We observed the overall
by time-of-flight inelastic neutron scattering. We observed the overall 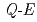 evolutions near the characteristic
evolutions near the characteristic 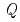 = 0.6
= 0.6 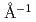 peak and found another weak broad magnetic peak around 2.4
peak and found another weak broad magnetic peak around 2.4 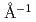 . The data are described by a simple response function, a partially delocalized magnetic form factor, and antiferromagnetic short-range spatial correlations, indicating that heavy-fermion formation is attributable to spin-orbit fluctuations with orbital hybridization.
. The data are described by a simple response function, a partially delocalized magnetic form factor, and antiferromagnetic short-range spatial correlations, indicating that heavy-fermion formation is attributable to spin-orbit fluctuations with orbital hybridization.
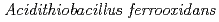
Kanao, Tadayoshi*; Kosaka, Megumi*; Yoshida, Kyoya*; Nakayama, Hisayuki*; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Yamada, Hidenori; Takada, Jun*; Kamimura, Kazuo*
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 69(6), p.692 - 694, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.28(Biochemical Research Methods)Tetrathionate hydrolase (4THase) from the iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacterium 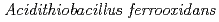 catalyses the disproportionate hydrolysis of tetrathionate to elemental sulfur, thiosulfate and sulfate. The gene encoding 4THase (
catalyses the disproportionate hydrolysis of tetrathionate to elemental sulfur, thiosulfate and sulfate. The gene encoding 4THase (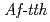 ) was expressed as inclusion bodies in recombinant
) was expressed as inclusion bodies in recombinant  . Recombinant
. Recombinant 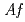 -Tth was activated by refolding under acidic conditions and was then purified to homogeneity. The recombinant protein was crystallized in 20 m
-Tth was activated by refolding under acidic conditions and was then purified to homogeneity. The recombinant protein was crystallized in 20 m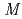 glycine buffer pH 10 containing 50 m
glycine buffer pH 10 containing 50 m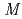 sodium chloride and 33%(
sodium chloride and 33%(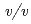 ) PEG 1000 using the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method. The crystal was a hexagonal cylinder with dimensions of 0.2
) PEG 1000 using the hanging-drop vapour-diffusion method. The crystal was a hexagonal cylinder with dimensions of 0.2  0.05
0.05  0.05 mm. X-ray crystallographic analysis showed that the crystal diffracted to 2.15
0.05 mm. X-ray crystallographic analysis showed that the crystal diffracted to 2.15  resolution and belongs to space group
resolution and belongs to space group  3
3 or
or  3
3 , with unit-cell parameters
, with unit-cell parameters  =
=  = 92.1,
= 92.1,  = 232.6
= 232.6  .
.
 Na
Na CuO
CuO Cl
Cl
Hanaguri, Tetsuo*; Kosaka, Yuki*; Davis, J. C.*; Lupien, C.*; Yamada, Ikuya*; Azuma, Masaki*; Takano, Mikio*; Oishi, Kazuki; Ono, Masaki*; Takagi, Hidenori*
Nature Physics, 3(12), p.865 - 871, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:148 Percentile:95.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Iwai, Yasunori; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Miura, Hidenori*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(12), p.1645 - 1651, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:14.50(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The confinement and removal of tritium are the key subjects for safety of ITER. The ITER buildings are confinement barriers of tritium. In a hot cell building, tritium is often released, as vapor and is in contact with the inner walls. Also those of an ITER tritium plant building will be exposed to tritium in an accident. However, the data are scarce, especially on the penetration of tritium into the concrete of the wall materials. The tritium released in the buildings is removed by the Atmosphere Detritiation Systems (ADS), where the tritium is oxidized by catalysts and is removed as water. Special gas of SF is used in ITER, and is expected to be released in an accident such as fire. Although the SF
is used in ITER, and is expected to be released in an accident such as fire. Although the SF gas has the potential as a catalyst poison, the performance of ADS with the existence of SF
gas has the potential as a catalyst poison, the performance of ADS with the existence of SF has not been confirmed yet. Tritiated water is produced in the regeneration process of ADS, and is subsequently processed by the ITER Water Detritiation System (WDS). One of the key components of WDS is an electrolysis cell. The electrolysis cell is made of organic compounds, and there is no data on the durability of the cell exposed to tritium. To overcome these issues in a global tritium confinement, a series of experimental studies have been carried out as an ITER R&D task: (1) tritium behavior in concrete; (2) effect of SF
has not been confirmed yet. Tritiated water is produced in the regeneration process of ADS, and is subsequently processed by the ITER Water Detritiation System (WDS). One of the key components of WDS is an electrolysis cell. The electrolysis cell is made of organic compounds, and there is no data on the durability of the cell exposed to tritium. To overcome these issues in a global tritium confinement, a series of experimental studies have been carried out as an ITER R&D task: (1) tritium behavior in concrete; (2) effect of SF on performance of ADS; and (3) tritium durability of electrolysis cell of ITER-WDS.
on performance of ADS; and (3) tritium durability of electrolysis cell of ITER-WDS.
Yonehara, Hidenori*; Ishimori, Yuu; Akiba, Suminori*; Iida, Takao*; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Kai, Michiaki*; Shimo, Michikuni*; Tokonami, Shinji*; Yamada, Yuji*; Yoshinaga, Shinji*; et al.
Hoken Butsuri, 42(3), p.201 - 213, 2007/09
The pooled analysis recently carried out in European countries and North American countries showed the excess relative risk of lung cancer increased by 10-20% per 100 Bqm increase in indoor radon concentration. The Scientific Committee on Indoor Radon Risk and Response to the Issue established by the Japan Health Physic Society reviewed the scientific evidence on the indoor radon risk obtained so far and evaluated the pooled analysis results from the viewpoint of estimating the risk coefficient in Japan. The committee concludes that the risk shown by the pooled analysis results has the consistency from miners risk analysis, and that it is probably not low in the reliability and validity, although the value may include the uncertainties caused from the correction of radon concentration measured, from the effect of thoron on measurement results, from the differences of environmental parameters in exposure, and so on.
increase in indoor radon concentration. The Scientific Committee on Indoor Radon Risk and Response to the Issue established by the Japan Health Physic Society reviewed the scientific evidence on the indoor radon risk obtained so far and evaluated the pooled analysis results from the viewpoint of estimating the risk coefficient in Japan. The committee concludes that the risk shown by the pooled analysis results has the consistency from miners risk analysis, and that it is probably not low in the reliability and validity, although the value may include the uncertainties caused from the correction of radon concentration measured, from the effect of thoron on measurement results, from the differences of environmental parameters in exposure, and so on.
 Na
Na CuO
CuO Cl
Cl
Hanaguri, Tetsuo*; Kosaka, Yuki*; Davis, J. C.*; Lupien, C.*; Yamada, Ikuya*; Azuma, Masaki*; Takano, Mikio*; Oishi, Kazuki; Takagi, Hidenori*
Physica C, 460-462, p.954 - 955, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.31(Physics, Applied)We performed high-resolution scanning tunneling microscopy/spectroscopy on an optimally-doped Ca Na
Na CuO
CuO Cl
Cl crystal. The so-called checkerboard local-density-of-state modulation manifests in the spectroscopic map of the optimally-doped sample. In addition, spatially-inhomogeneous energy gap is observed. The gap tends to be buried at elevated temperatures and correlates with the checkerboard modulation. These results suggest that the gap is related to superconductivity which coexists with the checkerboard modulation.
crystal. The so-called checkerboard local-density-of-state modulation manifests in the spectroscopic map of the optimally-doped sample. In addition, spatially-inhomogeneous energy gap is observed. The gap tends to be buried at elevated temperatures and correlates with the checkerboard modulation. These results suggest that the gap is related to superconductivity which coexists with the checkerboard modulation.
Yamada, Hidenori*; Tamada, Taro; Kosaka, Megumi*; Miyata, Kohei*; Fujiki, Shinya*; Tano, Masaru*; Moriya, Masayuki*; Yamanishi, Mamoru*; Honjo, Eijiro; Tada, Horiko*; et al.
Protein Science, 16(7), p.1389 - 1397, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:60.18(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)In an attempt to control protein incorporation in a crystal lattice, a leucine zipper-like hydrophobic interface (comprising four leucine residues) was introduced into a helical region (helix 2) of the human pancreatic ribonuclease 1 (RNase 1) that was predicted to form a suitable crystallization interface. Although crystallization of wild type RNase 1 has not yet been reported, the RNase 1 mutant having four leucines (4L-RNase 1) was successfully crystallized under several different conditions. The crystal structures were subsequently determined by X-ray crystallography by molecular replacement using the structure of bovine RNase A. The overall structure of 4L-RNase 1 is quite similar to that of the bovine RNase A, and the introduced leucine residues formed the designed crystal interface. To further characterize the role of the introduced leucine residues in crystallization of RNase 1, the number of leucines was reduced to three or two (3L- and 2L-RNase 1, respectively). Both mutants crystallized and a similar hydrophobic interface as in 4L-RNase 1 was observed. A related approach to engineer crystal contacts at helix 3 of RNase 1 (N4L-RNase 1) was also evaluated. N4L-RNase 1 also successfully crystallized, and formed the expected hydrophobic packing interface. These results suggest that appropriate introduction of a leucine zipper-like hydrophobic interface can promote intra molecular symmetry for more efficient protein crystallization in crystal lattice engineering efforts.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Iwai, Yasunori; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Miura, Hidenori*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Shaaban, N.*; Masuda, Fukuzo*; Nasif, H.*; Yamada, Masao*; Sawamura, Hidenori*; Morota, Hidetsugu*; Sato, Satoshi; Iida, Hiromasa; Nishitani, Takeo
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-14) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Nose, Tadao*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Yoshida, Fumiyo*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Matsushita, Akira*; Nakai, Kei*; Yamada, Takashi*; et al.
UTRCN-G-29, p.114 - 123, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Matsushita, Akira*; Nakai, K.*; Yamada, Takashi*; Takano, Shingo*; Mizutani, Taro*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer, p.29 - 30, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Kosaka, Megumi*; Kanao, Tadayoshi*; Nakayama, Hisayuki*; Yoshida, Kyoya*; Kamimura, Kazuo*; Takada, Jun*; Yamada, Hidenori; Tamada, Taro; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Onishi, Yuki*; Ostermann, A.*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Honjo, Eijiro; Kuroki, Ryota; Futami, Junichiro*; Yamada, Hidenori*
no journal, ,
Our goal is to develop new methods for determining macromolecular crystal structures  from neutron diffraction data and to validate these methods by making applications to several proteins. The proposed methods, which have the potential to be more powerful than X-ray ones, exploit perfectly isomorphous pairs of crystals that differ by replacement of D atoms with H atoms in selected amino-acid residues. This research involves collaboration among teams on three continents that have expertise in different aspects of neutron crystallography. The Japanese team measures high-resolution neutron diffraction data from protein crystals to answer questions about H bonding, protonation, hydration, and enzyme mechanisms. The team will focus on fundamental and simple proteins such as myoglobin, insulin, and RNase A at the first stage and then on rubredoxin, aldose reductase and other samples from the French team. In the meeting the research plan of the Japanese team will be reported.
from neutron diffraction data and to validate these methods by making applications to several proteins. The proposed methods, which have the potential to be more powerful than X-ray ones, exploit perfectly isomorphous pairs of crystals that differ by replacement of D atoms with H atoms in selected amino-acid residues. This research involves collaboration among teams on three continents that have expertise in different aspects of neutron crystallography. The Japanese team measures high-resolution neutron diffraction data from protein crystals to answer questions about H bonding, protonation, hydration, and enzyme mechanisms. The team will focus on fundamental and simple proteins such as myoglobin, insulin, and RNase A at the first stage and then on rubredoxin, aldose reductase and other samples from the French team. In the meeting the research plan of the Japanese team will be reported.