Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ito, Kenichi*; Miyahara, Hidetaka*; Ujiie, Toru*; Takeshima, Toshikatsu*; Yokoyama, Shingo*; Nakata, Kotaro*; Nagano, Tetsushi; Sato, Tsutomu*; Hatta, Tamao*; Yamada, Hirohisa*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(4), p.255 - 271, 2012/04
no abstracts in English
 pulse generation in an X-ray tube with a plasma cathode induced by a femtosecond laser pulse
pulse generation in an X-ray tube with a plasma cathode induced by a femtosecond laser pulseYamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi; Shimada, Yukihiro
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(6), p.375 - 379, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.92(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi; Shimada, Yukihiro
Hyomen Kagaku, 29(7), p.413 - 417, 2008/07
A femtosecond-laser-driven X-ray source and an X-ray focusing system have been developed for the time-resolved X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. The X-ray source, in which a plasma cathode induced by a 10 -W/cm
-W/cm laser pulse serves as an electron source of an X-ray tube, provides 10
laser pulse serves as an electron source of an X-ray tube, provides 10 Cu K
Cu K photons in 4
photons in 4 sr per pulse. The X-ray pulse duration is measured to be about two hundred nanoseconds. Emission analysis of the plasma cathode indicates that the temporal characteristics of the X-ray pulse are determined by the dynamics of the plasma particles under the electrostatic shielding against the applied voltage in the X-ray tube. As for the X-ray focusing system, a focal spot size by a polycapillary lens is measured and the enhancement of X-ray fluorescence intensity due to the lens is demonstrated.
sr per pulse. The X-ray pulse duration is measured to be about two hundred nanoseconds. Emission analysis of the plasma cathode indicates that the temporal characteristics of the X-ray pulse are determined by the dynamics of the plasma particles under the electrostatic shielding against the applied voltage in the X-ray tube. As for the X-ray focusing system, a focal spot size by a polycapillary lens is measured and the enhancement of X-ray fluorescence intensity due to the lens is demonstrated.
Sugita, Akihiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yamada, Hidetaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Aoyama, Makoto; Yamakawa, Koichi
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 46(1), p.226 - 228, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:29.39(Physics, Applied)Generation of broadband mid-infrared (MIR) laser pulses by difference frequency mixing (DFM) is reported. Two-color femtosecond pulses from a Ti: Sapphire laser system is mixed in an AgGaS crystal utilizing a noncollinear phase matching scheme. The relative bandwidth of the generated MIR pulse has been measured to be 23 % to the central frequency, the broadest in DFM-based MIR sources reported so far. It is found that the type-I crystal can give broader phase matching range of spectrum than the type-II crystal within this scheme.
crystal utilizing a noncollinear phase matching scheme. The relative bandwidth of the generated MIR pulse has been measured to be 23 % to the central frequency, the broadest in DFM-based MIR sources reported so far. It is found that the type-I crystal can give broader phase matching range of spectrum than the type-II crystal within this scheme.

 ) and Cs(7
) and Cs(7
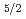 ) by femtosecond laser pulses
) by femtosecond laser pulsesYamada, Hidetaka; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Teranishi, Yoshiaki*; Sugita, Akihiro; Shirai, Toshizo*; Aoyama, Makoto; Akahane, Yutaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki*; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Physical Review A, 72(6), p.063404_1 - 063404_5, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:30.83(Optics)A demonstration of coherent quantum control for ultrafast precise selection of closely-lying states is reported. A phase-locked pair of femtosecond laser pulses is generated through a pulse shaper to excite the ground-state cesium atom to the Cs(7
 ) and Cs(7
) and Cs(7
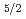 ) states by two-photon absorption. The excited state population is measured by detecting fluorescence from each spin-orbit state. By controlling the phase-difference of the pulse pair, an ultrafast precise selection is accomplished. The contrast ratio of the maximal to minimal selection ratio exceeds 10
) states by two-photon absorption. The excited state population is measured by detecting fluorescence from each spin-orbit state. By controlling the phase-difference of the pulse pair, an ultrafast precise selection is accomplished. The contrast ratio of the maximal to minimal selection ratio exceeds 10 with the delay less than 400 fs.
with the delay less than 400 fs.
Yokoyama, Keiichi; Teranishi, Yoshiaki; Toya, Yukio; Shirai, Toshizo; Fukuda, Yuji; Aoyama, Makoto; Akahane, Yutaka; Inoue, Norihiro*; Ueda, Hideki; Yamakawa, Koichi; et al.
Journal of Chemical Physics, 120(20), p.9446 - 9449, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.29(Chemistry, Physical)Optimal laser control for ultrafast selection of closely-lying excited states, whose energy separation is smaller than the laser bandwidth, is reported on the two-photon transition of atomic cesium; Cs(6S  7D
7D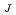 , J = 5/2 and 3/2). Selective excitation was carried out by pulse shaping of ultrashort laser pulses which were adaptively modulated in a closed-loop learning system handling eight parameters representing the electric field. Two-color fluorescence from the respective excited states was monitored to measure the selectivity. The fitness used in the learning algorithm was evaluated from the ratio of the fluorescence yield. After fifty generations, a pair of nearly transform-limitted pulses were obtained as an optimal pulse shape, proving the effectiveness of "Ramsey fringes" mechanism. The contrast of the selection ratio was improved by
, J = 5/2 and 3/2). Selective excitation was carried out by pulse shaping of ultrashort laser pulses which were adaptively modulated in a closed-loop learning system handling eight parameters representing the electric field. Two-color fluorescence from the respective excited states was monitored to measure the selectivity. The fitness used in the learning algorithm was evaluated from the ratio of the fluorescence yield. After fifty generations, a pair of nearly transform-limitted pulses were obtained as an optimal pulse shape, proving the effectiveness of "Ramsey fringes" mechanism. The contrast of the selection ratio was improved by  30 % from the simple "Ramsey fringes" experiment.
30 % from the simple "Ramsey fringes" experiment.
Yamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi; Shimada, Yukihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi; Shimada, Yukihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sugita, Akihiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Itakura, Ryuji; Yamada, Hidetaka
no journal, ,
Selective excitation to the closely lying state of potassiium atoms were examined as a fundamental research of a new laser-isotope-separation technique. Using time-resolved photon counting to measure the fluorescence intensity, the scatterd light from the pump beam and the fluorescence of interest were perfectly distinguished. Owing to this experimental setup, a high contrast more than 1000 was obtained for the selectivity. In addition, the excitation behavior when the laser intensity increased was recorded through the laser power dependence of the fluorescence intensity. As a result, it is found that the destructive interference between two excited states becomes incomplete with increasing laser power. Moreover, the relative population of the two states exhibit the power dependence expected by a computer simulation, indicating that the laser power required for the selective complete excitation is achieved.
Akamatsu, Ken; Murakami, Hiroshi; Yamada, Hidetaka*
no journal, ,
We have investigated DNA strand breaks induced by 266-nm femtosecond (fs) laser pulses in the solid state. The amounts of open-circular (oc) and linear (L) forms produced from closed circular plasmid DNA (pUC18, 2686 base pairs) are quantified as a function of the laser intensity. The amount of L-form produced per pulse is proportional to the square of the intensity within 100  102 GW/cm
102 GW/cm region, while that of oc-form is almost proportional to the intensity. This indicates that the direct double strand break (DSB) formation occurs by the two-photon absorption corresponding to one-photon absorption in a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) range (133 nm, 9.4 eV). The mechanism of the strand break is discussed on the basis of the ionization potential of DNA.
region, while that of oc-form is almost proportional to the intensity. This indicates that the direct double strand break (DSB) formation occurs by the two-photon absorption corresponding to one-photon absorption in a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) range (133 nm, 9.4 eV). The mechanism of the strand break is discussed on the basis of the ionization potential of DNA.
Yamada, Hidetaka; Murakami, Hiroshi; Shimada, Yukihiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English