Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Itazu, Toru; Inagaki, Manabu; Kato, Tomoko; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Ebashi, Takeshi; Kawamura, Makoto; Ebina, Takanori*; Miyahara, Kaname
JAEA-Review 2009-015, 59 Pages, 2009/07
The project of high-level radioactive waste disposal is in the stage of site selection in Japan, and the site-specific performance assessment using the methodology of site-generic study has been developed after the publication of the second progress report (H12). In the same way, biosphere assessment using the behavior of radionuclides, which depends on the site-specific condition, has been started. In this paper, the following issues have been addressed. (1) Survey of the foreign literature relating to the surface and near- surface hydrology for biosphere assessments. (2) Survey of the domestic literature of flow and transport in subsurface systems valuable for biosphere assessments. (3) Trial of transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment of the model site. (4) The setting and boundary conditions of model used for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis. About the fist issue, from literature of Sweden, we studied the calculation of the dose with account to radionuclides migration in the Quaternary. Concerning the second item, collecting and compiling the useful information for the surface and near-surface hydrological analysis from literature related to groundwater flow and pollution survey in Japan, we learned about the environmental tracer method and so on. Concerning the third point, transport analysis in surface and near-surface environment using site-specific data for sensitivity analysis after this has been carried out to check out the influence of some parameters on transport phenomena, and the relative high sensitivity of the difference of the source positions were shown. Concerning the fourth item, we examined the setting and the boundary conditions of model whose outputs include groundwater flow and transport rate into river, lake, sea. These outputs are used as inputs of biosphere assessment model.
Yamada, Hiroshi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kamada, Yutaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1418 - 1424, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)High densities exceeding the Greenwald limit by a factor of 1.7 have been obtained in discharges with high internal inductances of 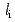 as high as 2.8 in JT-60U L-mode plasmas. The internal inductance, which is an index of the edge magnetic shear, is controlled by ramping down the plasma current. In addition to the extension of the operational regime, confinement performance remains as good as an H89PL factor of 1.5 even above the Greenwald limit. While the earlier work of a high
as high as 2.8 in JT-60U L-mode plasmas. The internal inductance, which is an index of the edge magnetic shear, is controlled by ramping down the plasma current. In addition to the extension of the operational regime, confinement performance remains as good as an H89PL factor of 1.5 even above the Greenwald limit. While the earlier work of a high 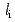 study has indicated that core confinement improvement, the additional improvement of the tolerance against the high density is turned out to be correlated with high edge temperature. The normalized density when the detachment characterized by the decrease in a D
study has indicated that core confinement improvement, the additional improvement of the tolerance against the high density is turned out to be correlated with high edge temperature. The normalized density when the detachment characterized by the decrease in a D signal at the divertor occurs is even higher in the case with no disruption than the case with a disruption. These comparisons have indicated that the improvement in thermal and particle transport does exist in the periphery and the edge in the high
signal at the divertor occurs is even higher in the case with no disruption than the case with a disruption. These comparisons have indicated that the improvement in thermal and particle transport does exist in the periphery and the edge in the high 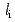 plasmas, and mitigation of the density limit is observed coincidently. Although the high
plasmas, and mitigation of the density limit is observed coincidently. Although the high 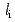 discharge studied here lies outside of the usual parameter space for a steady-state operation of tokamak, demonstration of a stable discharge with good confinement beyond the Greenwald limit suggest the magnetic shear at the edge is one key parameter to uncover physical element of the operational density limit.
discharge studied here lies outside of the usual parameter space for a steady-state operation of tokamak, demonstration of a stable discharge with good confinement beyond the Greenwald limit suggest the magnetic shear at the edge is one key parameter to uncover physical element of the operational density limit.
Inagaki, Manabu; Kato, Tomoko; Yoshida, Hideji*; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Fukaya, Yukiko*; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oi, Takao
JAEA-Research 2007-029, 81 Pages, 2007/03
The project of high-level radioactive waste disposal is in activity for the site selection of HLW disposal facility and the performance assessment should be more site-specific rather than site-generic, where the applicability of the achievement of site-generic study such as second progress report (H12) to the site specific is to be clarified. In the same way, it is necessary for biosphere assessment to incorporate the site specific condition to the model. The exposure pathway or concentration of the radio nuclides should be determined according to the site specific geological condition, for example. In this paper, following topics have been selected to start the study to reflect specific geological condition to the biosphere modeling. (1) The literature survey of international and national approaches and issues relating to the treatment of GBIs within biosphere assessments, (2) To develop methodology to estimate the release point of the deep groundwater to the shallow accessible groundwater. (3) To prepare information to estimate water balance this is, in turn, necessary to assess the dilution and/or dispersion of the radionuclides in the shallow accessible groundwater body.
Yamada, Hiroshi*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kamada, Yutaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Tsuda, Takashi; Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kawano, Yasunori; Kusama, Yoshinori; Mase, Atsushi*; Sasao, Mamiko*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Fujita, Takaaki; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 83(2), p.195 - 198, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Oi, Takao; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Inagaki, Manabu; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*; Sone, Tomoyuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Ebashi, Takeshi; Nakajima, Kunihiko*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.985, p.129 - 134, 2007/00
A comprehensive sensitivity analysis method has been developed with the aim of providing quantitative information in an efficient manner. This methodology is composed of the following two components: (1) a statistical method with random sampling of independent parameters, which identifies important parameters and extracts threshold values of parameters and/or combinations yielding a "successful condition" where maximum dose does not exceed a target value, (2) A nuclide migration model that as far as possible incorporates a comprehensive set of phenomena occurring within the repository. This approach was applied as part of a safety assessment of the geological disposal of TRU waste in Japan (TRU-2). It was shown that the concept of TRU waste disposal is robust from the point of view of safety.
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Nakano, Tomohide; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Iio, Shunji*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Ono, Yasushi*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 82(7), p.448 - 450, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Mase, Atsushi*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(2), p.128 - 130, 2005/02
no abstracts in English

Fujino, Takeo*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Yamada, Kota*; Okazaki, Manabu*; Fukuda, Kosaku; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Shiratori, Tetsuo*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 289(3), p.270 - 280, 2001/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Itazu, Toru; Kato, Tomoko; Inagaki, Manabu; Maekawa, Keisuke; Suzuki, Yuji*; Oyamada, Kiyoshi*
no journal, ,
On the performance assessment of HLW Geological Disposal, we must evaluate the human impact of radionuclides delivered to the ground surface by groundwater flow, which evaluation requires the setting of pathways of the radionuclides and the estimation of dilution effect. In this presentation, for development of methodology for biosphere assessment modeling including the dilution effect with the site-specific information in the stage of site selection, we show the examination of the methodology through trial of groundwater flow analysis in surface and near-surface environment of Horonobe by using existing literature.
Matoba, Shiro; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Koizumi, Tetsuo*; Takahashi, Karin*; Ishikawa, Manabu*; Moriya, Sosuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Matoba, Shiro; Narumi, Kazumasa; Saito, Yuichi; Yamada, Keisuke; Chiba, Atsuya; Koizumi, Tetsuo*; Takahashi, Karin*; Ishikawa, Manabu*; Shiromaru, Haruo*; Kato, Ryoya*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogata, Manabu; King, G.*; Herman, F.*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yamada, Ryuji*; Omura, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogata, Manabu; King, G. E.*; Herman, F.*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yamada, Ryuji*; Omura, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ogata, Manabu; King, G. E.*; Herman, F.*; Yamada, Ryuji*; Omura, Kentaro*; Sueoka, Shigeru
no journal, ,
Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) thermochronometry is a tool for constraining cooling histories in low-temperature domains (several tens of degree Celsius) during the past 10-100 kyr. This method is currently applied only to rapidly denuded regions (about 5 mm/yr), because luminescence signals in slowly denuded regions saturate before the rocks are exhumated to the surface. However, cooling histories in slowly denuded regions may be constrained if unsaturated samples are obtained from deep boreholes. We applied multi-OSL-thermochronometry to the deep borehole core drilled at the Rokko Mountains, Japan, where slow denudation rates (0.1-1.0 mm/yr) are expected from previous studies. We used the Kabutoyama core collected by National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience. The total length of Kabutoyama core is 1,313 m and we collected the samples at 408, 642, 818 and 1048 m for OSL-thermochronometry. We found that the sample temperatures remained around the present ambient temperature at each depth for the last 0.1 Myr, indicating that the Rokko Mountains is topographically stable, which was consistent with previous findings. Thus, the thermal denudation history of slowly denuded regions may be constrained by multi-OSL-thermochronometry using samples from deep borehole cores. However, the denudation rates in the Rokko Mountains were too low and could not be determined by this method.
Takir, D.*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; et al.
no journal, ,
JAXA spacecraft and sample return mission Hayabusa2 has arrived at the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, which is classified a primitive carbonaceous object. Here we report recent results of near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. The observations provide direct measurements of the surface composition of Ryugu and context for the returned samples. NIRS3 has detected a weak and narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micrometer across entire observed surface. This absorption feature is attributed to the presence of OH-bearing minerals. The NIRS3 observations also revealed that Ryugu is the darkest object to be observed up-close by a visiting spacecraft. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are consistent with thermally-and/or shock-metamorphosed, and/or carbon-rich space-weathered primitive and hydrated carbonaceous chondrites.
Ogata, Manabu; King, G. E.*; Herman, F.*; Yamada, Ryuji*; Omura, Kentaro*; Sueoka, Shigeru
no journal, ,
Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL)-thermometry can be used to reconstruct the thermal structure in slowly denuded regions where infrared stimulated luminescence (IRSL) signals of samples obtained from deep boreholes are measured and evaluated with depth. Only one study had explored this approach, using a target mineral of Na-feldspar. We applied multi-OSL-thermometry to K-feldspar obtained from deep borehole core samples drilled at the Tono (MIZ-1) and Rokko regions (Kabutoyama), which are well-documented thermally stable crustal environment. For the K-feldspar obtained from the MIZ-1 core, the inverted temperatures for the IRSL50  C of the samples at a depth of
C of the samples at a depth of  1 km (
1 km ( 40
40  C) were consistent with the in-situ temperatures. The results suggest that the application of OSL-thermometry to K-feldspar in a borehole is useful to reconstruct the palaeothermal condition. In this presentation, we will also show the results of the Kabutoyama core to draw more comprehensive conclusions.
C) were consistent with the in-situ temperatures. The results suggest that the application of OSL-thermometry to K-feldspar in a borehole is useful to reconstruct the palaeothermal condition. In this presentation, we will also show the results of the Kabutoyama core to draw more comprehensive conclusions.