Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 23(2), p.50 - 63, 2024/06
Selective separation of radioactive ions is essential for reducing or cleaning radioactive wastes. Among the radioisotopes to be removed,  Sr poses a major threat to human health and the environment. However, removal of
Sr poses a major threat to human health and the environment. However, removal of  Sr from environmental wastewater is still challenging due to the difficulty of separating
Sr from environmental wastewater is still challenging due to the difficulty of separating  Sr
Sr from Ca
from Ca . Here, we developed a series of isostructural lanthanide oxalate frameworks (LOFs) comprising oxalate and eight kinds of lanthanide (Ln) ions, i.e., from Samarium (Sm) to Thulium (Tm) for application to selective removal of
. Here, we developed a series of isostructural lanthanide oxalate frameworks (LOFs) comprising oxalate and eight kinds of lanthanide (Ln) ions, i.e., from Samarium (Sm) to Thulium (Tm) for application to selective removal of  Sr from wastewater using its tuned porous structure. The LOFs had ion exchangeable anionic pores, in which the size of the pores changed in a stepwise manner depending on the host Ln species. When Tb was the host Ln of the LOF, the LOF showed extremely high Sr
Sr from wastewater using its tuned porous structure. The LOFs had ion exchangeable anionic pores, in which the size of the pores changed in a stepwise manner depending on the host Ln species. When Tb was the host Ln of the LOF, the LOF showed extremely high Sr selectivity and was able to distinguish the subtle difference in ionic radius (0.2
selectivity and was able to distinguish the subtle difference in ionic radius (0.2  ) between Sr
) between Sr and Ca
and Ca . The Sr
. The Sr selectivity was higher than that of conventional adsorbents. The pore size tuning of the LOFs by selecting the constituent Ln species yielded a highly ion-selective adsorbent material. This novel strategy will be useful in developing custom porous materials that are easy to prepare and applicable across various fields.
selectivity was higher than that of conventional adsorbents. The pore size tuning of the LOFs by selecting the constituent Ln species yielded a highly ion-selective adsorbent material. This novel strategy will be useful in developing custom porous materials that are easy to prepare and applicable across various fields.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 95(5), p.825 - 829, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Advances in hazardous metal ion removal are essential for wastewater clean-up to tackle the global water shortage crisis. Here, we report a Pb-selective adsorbent using a Tb oxalate framework (TOF) synthesized by a one-pot hydrothermal method. The TOF has a two-dimensional sheet structure, in which the interlayer space functions as an ion exchangeable site. Sorption tests using a mixed-ion solution containing Pb , Cd
, Cd , Mn
, Mn , Co
, Co , Ni
, Ni , Cu
, Cu , Na
, Na , K
, K , Mg
, Mg , and Ca
, and Ca showed that the TOF has high selectivity for Pb
showed that the TOF has high selectivity for Pb among other metal ions. The saturated adsorption capacity of the TOF for Pb
among other metal ions. The saturated adsorption capacity of the TOF for Pb was 276 mg g
was 276 mg g , which is higher than that of conventional adsorbents. Furthermore, the TOF exhibited reversible Pb
, which is higher than that of conventional adsorbents. Furthermore, the TOF exhibited reversible Pb adsorption/desorption and could be used for at least three cycles. The results showed that TOF has excellent potential as an adsorbent for removing Pb
adsorption/desorption and could be used for at least three cycles. The results showed that TOF has excellent potential as an adsorbent for removing Pb , and because of its reusability, it is also a promising material for wastewater clean-up.
, and because of its reusability, it is also a promising material for wastewater clean-up.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Takeguchi, Masaki*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Shimoyama, Iwao; Kozai, Naofumi; Morooka, Satoshi
Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(2), p.105114_1 - 105114_12, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:43.75(Engineering, Environmental)Remediating toxic ion contamination is crucial for protecting human health and the environment. This study aimed to provide a powerful strategy for effectively utilizing bone waste from the food production and preparation industries for removal of toxic ions. Here, we show that immersing pig bone in NaHCO solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr
solution produced a carbonated nanohydroxyapatites (C-NHAP). The C-NHAP exhibited high adsorptivity for Sr , Cd
, Cd , Pb
, Pb , and Cu
, and Cu . The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
. The strontium adsorptivity was about 250 and 4,500 times higher than that of normal bone and synthetic HAP, respectively. The C-NHAP is an eco-friendly, high-performance material that is simple to prepare and should be useful for tackling problems of food waste disposal and environmental pollution.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Yunoki, Shunji*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Teppei*
ACS Applied Polymer Materials (Internet), 2(12), p.5482 - 5491, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:94.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We developed a cross-linking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize a new type of carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel with high compressive strength ( 80 MPa) and high compressive recoverability. The hydrogels were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure that reflected the ice crystal structure. Their cross-linked structure has a high stability to compressive stress. Bentonite was immobilized on a CMCF hydrogel by adding bentonite to the CMCF sol before freeze cross-linking. The CMCF-bentonite hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for chemical dyes. The physically cross-linked CMCF hydrogels are non-toxic, metal-free, and simple to prepare, and thus they may be useful as sustainable materials in various fields.
80 MPa) and high compressive recoverability. The hydrogels were prepared by adding an aqueous solution of citric acid (CA) to a frozen CMCF sol and then thawing the sol. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated CMCF and CA created a rigid porous structure that reflected the ice crystal structure. Their cross-linked structure has a high stability to compressive stress. Bentonite was immobilized on a CMCF hydrogel by adding bentonite to the CMCF sol before freeze cross-linking. The CMCF-bentonite hydrogel showed high adsorptivity for chemical dyes. The physically cross-linked CMCF hydrogels are non-toxic, metal-free, and simple to prepare, and thus they may be useful as sustainable materials in various fields.
Hashimoto, Makoto*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Okusawa, Makoto*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Kakeshita, Teruhisa*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Uchida, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 79(14), p.140502_1 - 140502_4, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:52.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr CuO
CuO and La
and La CuO
CuO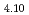
Hashimoto, Makoto*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Okusawa, Makoto*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Kakeshita, Teruhisa*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Uchida, Shinichi*
Physica C, 460-462(2), p.884 - 885, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.09(Physics, Applied)In the high-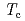 research, relationship between the pseudogap and the superconducting gap has been an important issue. We have performed a detailed temperature-dependent angle-integrated photoemission study of lightly-doped to heavily-overdoped La
research, relationship between the pseudogap and the superconducting gap has been an important issue. We have performed a detailed temperature-dependent angle-integrated photoemission study of lightly-doped to heavily-overdoped La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO and oxygen-doped La
and oxygen-doped La CuO
CuO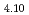 . We found that, while the magnitude of the pseudogap increased with decreasing doping, that of the superconducting gap did not increase. This behavior can be explained if the superconducting gap opens only on the Fermi arc around the node (0,0)-(
. We found that, while the magnitude of the pseudogap increased with decreasing doping, that of the superconducting gap did not increase. This behavior can be explained if the superconducting gap opens only on the Fermi arc around the node (0,0)-( ,
, ) whereas the pseudogap opens primarily around (
) whereas the pseudogap opens primarily around ( ,0).
,0).
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO cuprate superconductors
cuprate superconductorsHashimoto, Makoto*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Fujimori, Atsushi*; Okusawa, Makoto*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*; Kakeshita, Teruhisa*; Eisaki, Hiroshi*; Uchida, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 75(14), p.140503_1 - 140503_4, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:88.22(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have performed a temperature-dependent angle-integrated photoemission study of La Sr
Sr CuO
CuO covering from lightly doped to heavily overdoped regions and oxygen -doped La
covering from lightly doped to heavily overdoped regions and oxygen -doped La CuO
CuO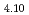 . The superconducting gap energy
. The superconducting gap energy 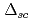 was found to remain small for decreasing hole concentration while the pseudogap energy
was found to remain small for decreasing hole concentration while the pseudogap energy 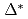 and temperature
and temperature 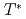 increase. The different behaviors of the superconducting gap and the pseudogap can be explained if the superconducting gap opens only on the Fermi arc around the nodal (0,0)-
increase. The different behaviors of the superconducting gap and the pseudogap can be explained if the superconducting gap opens only on the Fermi arc around the nodal (0,0)-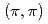 direction while the pseudogap opens around
direction while the pseudogap opens around 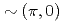 . The results suggest that the pseudogap and the superconducting gap have different microscopic origins.
. The results suggest that the pseudogap and the superconducting gap have different microscopic origins.
Watanabe, Masayuki; Nankawa, Takuya*; Yamada, Teppei*; Kimura, Takaumi; Namiki, Kosuke*; Murata, Masaki*; Nishihara, Hiroshi*; Tachimori, Shoichi
Inorganic Chemistry, 42(22), p.6977 - 6979, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:74.65(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)A tripodal ligand, tris(2-pyridyl)carbinol affords a novel tetradentate coordination mode in homodinuclear lanthanide complexes, which exhibit remarkably short distance between the metal ions. Strong fluorescence of Eu(III) and Tb(III) complexes with the ligand demonstrate that the ligand has a suitable excited state for energy transfer from the ligand to Eu(III) and Tb(III) center.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
no journal, ,
Among the radioisotopes to be removed,  Sr, which has a radioactive half-life of 28.8 years, poses a major threat to human health and the environment because of its uptake and retention in biological systems. However, removal of
Sr, which has a radioactive half-life of 28.8 years, poses a major threat to human health and the environment because of its uptake and retention in biological systems. However, removal of  Sr from wastewater is still challenging due to the difficulty of separating Sr
Sr from wastewater is still challenging due to the difficulty of separating Sr from Ca
from Ca . Ca
. Ca has a similar properties and ionic radius to
has a similar properties and ionic radius to  Sr
Sr . Indeed, the difference in their ionic radii is only 0.2
. Indeed, the difference in their ionic radii is only 0.2  . Furthermore, the concentration of Ca
. Furthermore, the concentration of Ca in actual nuclear wastewater is usually much higher than that of
in actual nuclear wastewater is usually much higher than that of  Sr, which limits the efficient removal of
Sr, which limits the efficient removal of  Sr. Here, we developed a series of isostructural lanthanide oxalate frameworks (LOFs) comprising oxalate and eight kinds of lanthanide (Ln) ions, i.e., from Sm to Tm, for application to selective removal of
Sr. Here, we developed a series of isostructural lanthanide oxalate frameworks (LOFs) comprising oxalate and eight kinds of lanthanide (Ln) ions, i.e., from Sm to Tm, for application to selective removal of  Sr from wastewater using its tuned porous structure. When Tb was the host Ln of the LOF, the LOF showed extremely high Sr
Sr from wastewater using its tuned porous structure. When Tb was the host Ln of the LOF, the LOF showed extremely high Sr selectivity and was able to distinguish the subtle difference in ionic radius between Sr
selectivity and was able to distinguish the subtle difference in ionic radius between Sr and Ca
and Ca . This novel pore size tuning strategy will be useful in developing custom porous materials that are easy to prepare and applicable across various fields.
. This novel pore size tuning strategy will be useful in developing custom porous materials that are easy to prepare and applicable across various fields.
Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Ogoshi, Yurie; Kuwahara, Akira; Alexandros, K.*; David, S.*; Marco, Z.*; Jansat, S.*; Troy, D. M.*; Matthew, J. R.*
no journal, ,
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
no journal, ,
Clean water resources are becoming increasingly limited and advances in toxic ion or radioactive ion removal technology are essential for dealing with the global water shortage crisis. Sorption using adsorbent materials, such as activated carbon, zeolites have been used to remove toxic ions from water. However, the ion selectivity and recovery of adsorbed ions still need to be improved to clean up water more effectively and sustainably. In this study, we synthesized metal-organic-frameworks (MOFs) with a jungle gym structure composed of ligands and metals, which enables fine adjustment of the pore size at the nano level. We also tested selective removal and recovery of metal ions by using the size controlled pores of MOFs.
Nankawa, Takuya; Sekine, Yurina; Yamada, Teppei*
no journal, ,
Clean water resources are becoming increasingly limited and advances in toxic ion removal technology are essential. Sorption using adsorbent materials have been used to remove toxic ions from water. However, the ion selectivity and absorption capacity of these materials still need to be improved to clean up water more effectively and sustainably. In this study, we synthesized a metal organic frameworks consisting of terbium and oxalate (TOF) and the ion absorptivity of the TOF was investigated by sorption tests. The crystal structure of the TOF before and after ion adsorption provided useful insights into the ion selectivity of the adsorbent.
Miura, Daisuke; Nankawa, Takuya; Yamada, Teppei*; Sekine, Yurina
no journal, ,
We developed a crosslinking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize a carboxymethyl cellulose nanofiber (CMCF) hydrogel with high compressive strength and high formability. The reaction between freeze-concentrated CMCF and organic acids created a rigid porous structure. In this study, we found that the structure of the freeze-concentrated CMCF could be fixed by organic acids in presence of ice, and the fixed structure contributed the mechanical properties of the hydrogel. We will give a presentation on the gelation mechanism of the CMCF hydrogel.
Sekine, Yurina; Nankawa, Takuya; Miura, Daisuke*; Yunoki, Shunji*; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamada, Teppei*
no journal, ,
We developed a crosslinking method using freeze concentration and used it to synthesize a cellulose nanofiber hydrogel with high compressive strength. The reaction between the freeze-concentrated cellulose nanofiber and citric acid created a rigid porous structure. Without the freeze crosslinking method, the complex of the cellulose nanofiber sol and citric acid produced hydrogels, which easily collapsed under compressive stress. We will give a presentation on the crosslinking method and the chemical and physical properties of the hydrogel.
Nankawa, Takuya; Ogoshi, Yurie; Kuwahara, Akira; Yamada, Teppei*; Zanella, M.*; Jansat, S.*; Manning, T.*; Rosseinsky, M.*
no journal, ,
Radioactive Cesium(Cs) and Strontium(Sr) in liquid waste can be separated by porous materials such as zeolite. The pore sizes of these materials seems to identify metal ion radius or hydrated ion radius of Cs or Sr. But since it is very difficult to change the pore sizes of these materials, we cannot investigate the relationship between the pore sizes and Cs or Sr uptake behavior of these materials. And since the frameworks of these materials are rigid, it is very hard to recover Cs or Sr absorbed in the materials and we have to dispose Cs or Sr containing material as nuclear waste. But if Cs and Sr can be recovered from the materials, we can make use of these radioactive nuclides as radiation or heat source. On the other hand, metal-organic-frameworks (MOF) have attracted much interest in this two decades because of its fascinating characters such as gas absorption, catalytic or optical properties. The advantages of MOF over zeolites or other porous materials are a highly-ordered structure composed of metal ions and organic ligands, and highly controllable pore sizes that can be controlled by the length of ligand and ionic radii of metal ions. Moreover, structures of MOF can easily be influenced by solution phase. So, it becomes easy to recover guest ions from MOF. In this study, we synthesized a novel series of MOF, (NH )[Ln(C
)[Ln(C O
O )
) (H
(H O)]. The structure is shown in Fig.1. All the structures the MOF are isostructural. The cell lengths and pore sizes tend to be decreased with the increase of atomic number in response to the decrease of ionic radius known as lanthanide contraction. And we investigated the behavior of Cs or Sr uptake by changing lanthanide ions in the MOF. Moreover, we found that Cs can be recovered from the MOF and we can reuse the MOF again. According to these results, we found a new material to recover Cs from radioactive liquid waste to decrease the amount of waste and make use of Cs as radiation source.
O)]. The structure is shown in Fig.1. All the structures the MOF are isostructural. The cell lengths and pore sizes tend to be decreased with the increase of atomic number in response to the decrease of ionic radius known as lanthanide contraction. And we investigated the behavior of Cs or Sr uptake by changing lanthanide ions in the MOF. Moreover, we found that Cs can be recovered from the MOF and we can reuse the MOF again. According to these results, we found a new material to recover Cs from radioactive liquid waste to decrease the amount of waste and make use of Cs as radiation source.