Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Akasaka, Naoaki; Sakaguchi, Norihito*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2017/06
The widths of void denuded zones (VDZs) which were formed near random grain boundaries by neutron irradiation were analyzed in order to perform quantitative evaluations for the irradiation-induced point defect behavior in the modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) having been developed by JAEA. Namely, the temperature dependence of VDZ width was investigated and vacancy migration energy of the PNC316 steel was estimated from the VDZ width analysis for the neutron-irradiated specimens. The obtained value of vacancy migration energy was estimated as 1.46 eV, which was consistent with that from the exiting method using electron in-situ examination. This indicates that VDZ analysis could be effective method to evaluate especially vacancy migration energy during irradiation, and this would be realized from not in-situ observation but post-irradiation examination in the case of neutron irradiation.
Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Inoue, Masaki; Maeda, Koji
Proceedings of 2014 Nuclear Plant Chemistry Conference (NPC 2014) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2014/10
In the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, seawater was temporarily injected into the spent fuel pools since water cooling and feeding functions were lost. For fuel assemblies which experienced seawater immersion, surface corrosion due to seawater constituents and the resultant degradation of mechanical property are of concern. Therefore, in order to assess the integrity of fuel assemblies (especially cladding tubes), the effects of seawater immersion on corrosion behavior and mechanical properties for as-recieved and irradiated Zircaloy-2 cladding tubes were investigated in the present study. As a result, no obvious surface corrosion and no significant degradation in the tensile strength property were observed after both artificial and natural seawater immersion tests for both steels. This suggests that the effects of seawater immersions on corrosion behavior and mechanical property (especially tensile property) for Zircaloy-2 cladding tubes are probably negligible.
Yamagata, Ichiro; Hayashi, Takehiro; Mashiko, Shinichi*; Sasaki, Shinji; Inoue, Masaki; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Maeda, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2013-004, 23 Pages, 2013/11
In the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant of Tokyo Electric Power Co. accompanying the Great East Japan Earthquake, fuel assemblies kept in the spent fuel pool of reactor units 1-4, were exposed to the inconceivable environment such as falling and mixing of rubble, especially seawater were injected into unit 2-4. In order to evaluate the integrity of the fuel assemblies in spent fuel pools, and in the long-term storage after transported to the common storage pool, the immersion tests were performed using zircaloy-2 fuel cladding tubes irradiated in the advanced thermal reactor Fugen. The immersion liquid was prepared with doubling dilution of artificial seawater, which temperature was 80  C and immersion time was about 336 hours, as assuming the situation of the pool. The results indicated zircaloy-2 cladding tubes had no significant corrosion and no influence on mechanical property by immersion tests with artificial seawater conditions of this work.
C and immersion time was about 336 hours, as assuming the situation of the pool. The results indicated zircaloy-2 cladding tubes had no significant corrosion and no influence on mechanical property by immersion tests with artificial seawater conditions of this work.
Yano, Yasuhide; Otsuka, Satoshi; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Sekine, Manabu; Endo, Toshiaki; Yamagata, Ichiro; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Tanno, Takashi; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-030, 57 Pages, 2013/11
It is necessary to develop the fast reactor core materials, which can achieve high-burnup operation improving safety and economical performance. Ferritic steels are expected to be good candidate core materials to achieve this objective because of their excellent void swelling resistance. Therefore, oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel and 11Cr-ferritic/martensitic steel (PNC-FMS) have been respectively developed for cladding and wrapper tube materials in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In this study, the effects of fast neutron irradiation on mechanical properties and microstructure of 9Cr-and 12Cr-ODS steel claddings for fast reactor were investigated. Specimens were irradiated in the experimental fast reactor Joyo using the CMIR-6 at temperatures between 420 and 835 C to fast neutron doses ranging from 16 to 33 dpa. The post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at irradiation temperatures.
C to fast neutron doses ranging from 16 to 33 dpa. The post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at irradiation temperatures.
Inoue, Toshihiko; Yamagata, Ichiro; Asaka, Takeo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 53(9), p.638 - 642, 2011/09
, 53(9), p.638 - 642, 2011/09
This paper presents the properties and the development of modified 316 steel. The core material is required to high-temperature strength caused by high power density and FP gas, swelling resistance caused by irradiation damage, and corrosion resistance caused by coolant sodium and FCCI. In the improvement of the modified 316 stainless steel, screening test conducted to improve high-temperature strength and swelling resistance. Optimizing a slight amount of addition element and cold working, the modified 316 steel was improved the high-temperature strength and swelling resistance in both. And under irradiated and FCCI conditions, these properties were tested. The modified 316 stainless steel uses 44,000 pins as fast reactor fuel pin in JOYO. These results show that the steel exhibits excellent characteristics in creep rupture strength and swelling resistance.
Takaya, Shigeru; Yamagata, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shoichi; Nagae, Yuji; Aoto, Kazumi
International Journal of Applied Electromagnetics and Mechanics, 33(3-4), p.1335 - 1342, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:44.78(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We newly developed a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) for neutron irradiated materials to investigate the relationship between neutron irradiation damage and magnetic property. The magnetization curves of type 316 stainless steels irradiated in a fast reactor JOYO, a light water reactor JRR-3M or both of them were measured. The ranges of dose and He content were about 0.1-1.8 dpa and 0.5-35 appm, respectively. As the result, it was revealed that the magnetization at 5 kOe increases monotonously with dose regardless of He content. This result shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of dose of structural materials by VSM measurement of surveillance samples.
Yamagata, Ichiro; Akasaka, Naoaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 47(10), p.898 - 907, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)The swelling behaviors in wrapping wire and duct were investigated for a fuel assembly made of modified type 316 austenitic stainless steel irradiated in a fast breeder reactor. The temperature dependence of swelling varied because the peak temperatures of swelling in the wrapping wire and the duct were different. The void distribution in the material was observed by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy and it was confirmed that the voids grew within an area of about 100  m from the surface. This phenomenon seemed to be caused by a surface effect on the neutron-irradiated materials.
m from the surface. This phenomenon seemed to be caused by a surface effect on the neutron-irradiated materials.
Takaya, Shigeru; Yamagata, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shoichi; Nagae, Yuji; Wakai, Eiichi; Aoto, Kazumi
Hozengaku, 9(1), p.51 - 56, 2010/04
The remote operated vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) for neutron irradiated samples has been developed. The maximum range of applied magnetic field is more than  0.5/
0.5/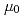 A/m, and the resolution of magnetization is higher than 5
A/m, and the resolution of magnetization is higher than 5 10
10 A
A m
m . The hysteresis loops of neutron irradiated samples were measured by this VSM, and the relationships between dose, which is one of representative irradiation parameter, and magnetic properties such as magnetic coercive force were examined. As result, it was revealed that there are good correlations between them. This fact shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of irradiation damage by using VSM.
. The hysteresis loops of neutron irradiated samples were measured by this VSM, and the relationships between dose, which is one of representative irradiation parameter, and magnetic properties such as magnetic coercive force were examined. As result, it was revealed that there are good correlations between them. This fact shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of irradiation damage by using VSM.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Yamagata, Ichiro; Akasaka, Naoaki; Ukai, Shigeharu
Materia, 42(12), 878 Pages, 2003/00
Focusing on the cover layer materials (as the Radon Barrier Materials), which could have the effect to restrain the radon from scattering into the air and the effect of the radiation shielding, we produced the radon barrier materials with crude bentonite on an experimental basis, using the rotary type comprehensive unit for grinding and mixing, through which we carried out the evaluation of the characteristics thereof.
Donomae, Takako; Akasaka, Naoaki; Yamagata, Ichiro
JNC TN9400 2001-092, 44 Pages, 2001/03
None
Akasaka, Naoaki; Yamagata, Ichiro;
20th Symposium on Effects of Radiation on Materials, p.443 - 456, 2001/00
None
; Yamagata, Ichiro; Donomae, Takako; Akasaka, Naoaki
JNC TN9400 2000-046, 24 Pages, 2000/02
lt is well known that solute atoms are segregated on surface, grain boundary, etc. and composition changed partially in irradiated austenitic stainless steel. For understanding radiation induced segregation (RIS), we adopt a Fe-15Cr-20Ni-x (x: Si, Mo) which is basically alloy system in PNC1520, and size of Si, Mo are different from matrix atoms to investigate RIS behaviors. The specimens were irradiated by "Joyo" fast reactor that irradiation condition is 3.5  10
10 n/m
n/m (E>0.1Mev) at 476
(E>0.1Mev) at 476 C. After irradiation, the specimen were observed and analyzed with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope) of 400kV TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The behavior of RIS depends on size of solute atoms of alloy. For example, oversized atoms are decreased and undersized atoms are increased in sink. RIS of voids are as same as or more than grain boundaries and smaller than precipitates. The void denuded zone was existed nearby G.B. in case of combinations between the grains from G.B.0ne of the reasons in this, the voids swepted by moving G.B. in radiation induced G.B. migration.
C. After irradiation, the specimen were observed and analyzed with EDS (Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscope) of 400kV TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The behavior of RIS depends on size of solute atoms of alloy. For example, oversized atoms are decreased and undersized atoms are increased in sink. RIS of voids are as same as or more than grain boundaries and smaller than precipitates. The void denuded zone was existed nearby G.B. in case of combinations between the grains from G.B.0ne of the reasons in this, the voids swepted by moving G.B. in radiation induced G.B. migration.
Donomae, Takako; ; ; Akasaka, Naoaki; Yamagata, Ichiro; ;
JNC TN9400 2000-075, 374 Pages, 1999/08
The irradiation test of the Monju-type fuel subassembly, MEA-1, was conducted at FFTF as a Joint Research Program of Fuels and Materials between DOE and PNC. MFA-1 subassembly is consisted of cladding tube, wrapper tube, wrapping wire which are all made of PNC316, as well as 85% low density pellet. The pellet peak burnup and maximum fast neutron fluence reached 147.1GWd/t and 21.4 10
10 n/m
n/m , respectively. Based on the results of Post-irradiation examination, Subassembly and fuel elements behaviors have been evaluated, and the following results were obtained. (1)The wrapper tube elongation and dilation are relatively small, and the fuel pin diameter changes were measured to be about 4% in maximum. The Bundle-Duct lnteraction (BDI) was confirmed not to be severe condition in Monju-type fuel assembly up to the fast neutron fluence of 21.4
, respectively. Based on the results of Post-irradiation examination, Subassembly and fuel elements behaviors have been evaluated, and the following results were obtained. (1)The wrapper tube elongation and dilation are relatively small, and the fuel pin diameter changes were measured to be about 4% in maximum. The Bundle-Duct lnteraction (BDI) was confirmed not to be severe condition in Monju-type fuel assembly up to the fast neutron fluence of 21.4 10
10 n/m
n/m . (2)In the claddings with the sand-brusted treatment to shave the flaw on the inner surface, the enhanced sweIling was measured, compared with PNC316 claddings manufactured by the usual process. lt is considered that this swelling enhancement in sand-brusted claddings attributed to relatively higher level of residual stress and lower cold-worked. (3)The deferent temperature dependency in swelling was evaluated for cladding and wrapping wire: the peak swelling temperature to be 495
. (2)In the claddings with the sand-brusted treatment to shave the flaw on the inner surface, the enhanced sweIling was measured, compared with PNC316 claddings manufactured by the usual process. lt is considered that this swelling enhancement in sand-brusted claddings attributed to relatively higher level of residual stress and lower cold-worked. (3)The deferent temperature dependency in swelling was evaluated for cladding and wrapping wire: the peak swelling temperature to be 495 C for cladding and 475
C for cladding and 475 C for wrapping wire. 0n the contrary, the swelling-temperature dependency for wrapper tube was not able to be determined.
C for wrapping wire. 0n the contrary, the swelling-temperature dependency for wrapper tube was not able to be determined.
Akasaka, Naoaki; Yamagata, Ichiro;
9th International Conference on Fusion Reactor Materials, 192 Pages, 1999/00
None
Yamagata, Ichiro; Hayashi, Takehiro; Sasaki, Shinji; Mashiko, Shinichi; Inoue, Masaki; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Maeda, Koji
no journal, ,
In the accident on Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, the spent fuel pool was cooled by sea water. To investigate soundness evaluation of fuel assemblies in the pool, immersion tests were conducted for irradiated zircaloy-2 cladding tubes and the results were reported in 2012 Fall Meeting of Atomic Energy Society of Japan. In this report, the same tests were performed in the more corrosive conditions of artificial sea water concentration and extended immersion time, and the influence of artificial sea water concentration on corrosion behavior and tensile properties of zircaloy-2 cladding tubes were evaluated.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Ichise, Kenichi; Usami, Koji; Endo, Shinya; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Yonekawa, Minoru; Ito, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Masaya; Soga, Tomonori; et al.
no journal, ,
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from 2006 fiscal year in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupling irradiations or single irradiations by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 fission reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are the very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we will present about the overall plan, work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Konno, Shotaro; Takaya, Shigeru; Nagae, Yuji; Yamagata, Ichiro; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Akasaka, Naoaki; Nishinoiri, Kenji
no journal, ,
We are developing a method for evaluation of irradiation damage on structural materials in nuclear plants by using change in magnetic flux density due to irradiation damage. In this study, the magnetic flux density measurement technique has been improved by introducing a new magnetizer which enables local magnetizing by contacting the sample surface, and the calibration method of the flux gate sensor for the magnetic flux density. We can magnetize samples, especially ferromagnetic samples, more precisely compared to the existing method. Furthermore, the new method can remove many limitations for the application to real plants.
Fukumoto, Kenichi*; Matsui, Hideki*; Akasaka, Naoaki; Yamagata, Ichiro
no journal, ,
The relationship between the addition of minor element and the swelling behavior was investigated using nine heats of Fe-15Cr-20Ni austenitic model alloys, Fe-15Cr-xNi(x = 20, 25 and 30) and a PNC1520 steel irradiated at 480, 570, 620 and 700  C in the Joyo to doses of 20-56 dpa. Phosphorus and boron suppressed the appearance of swelling for these experimental irradiation conditions. Additions of titanium and niobium were effective for suppression of swelling at low temperature, below 570
C in the Joyo to doses of 20-56 dpa. Phosphorus and boron suppressed the appearance of swelling for these experimental irradiation conditions. Additions of titanium and niobium were effective for suppression of swelling at low temperature, below 570  C. Complicated microstructural dependence of nickel contents for Fe-15Cr-xNi alloys could be seen.
C. Complicated microstructural dependence of nickel contents for Fe-15Cr-xNi alloys could be seen.