Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamagishi, Isao; Hato, Shinji*; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Sagawa, Yusuke*
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-002, 63 Pages, 2024/07
Adsorption columns filled with zeolite are used to treat contaminated water containing radioactive cesium generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. As the contaminated water treatment progresses, the radioactive cesium in the adsorption column becomes highly concentrated, and the adsorption column becomes a high radiation source. To evaluate the radiation effects such as decay heat and radiolytic hydrogen production in the adsorption column, the concentration of radioactive cesium in the adsorption column is necessary, but since it is difficult to evaluate the concentration by measurement, it is estimated by simulation. In this research, a zeolite column adsorption dynamics simulation (Zeolite Adsorption Column: ZAC) code was developed to calculate the concentration of radioactive materials such as radioactive cesium in a zeolite filled adsorption column when they are injected into the column. The code was validated through comparison of calculation results with existing codes and experimental results of small column tests. This report presents the details of the model, the handling of the code, and the validity of the results for the developed code.
Cantarel, V.; Chupin, F.; Ortega-Charlot, M.*; Yamagishi, Isao; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 592, p.154969_1 - 154969_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kato, Tomoaki; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Technology 2023-018, 53 Pages, 2023/11
In the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, radioactive carbonate slurry waste was generated using the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS) pretreatment and temporarily stored in a high integrity container (HIC). In 2015, overflow of supernatant from HIC estimate as bubble retention in the carbonate slurry was discovered, increasing the need for a safety assessment of the carbonate slurry stored the HIC (HIC slurry). In this study, a carbonate slurry (simulated slurry) was prepared according to the Mg/Ca mass ratio in the ALPS inlet water of the HIC slurry which overflew the HIC. The effects of reaction time during the pretreatment process, suspended solids concentration (SS concentration), and settling time on the particle composition, morphology and rheological properties of the slurry were investigated. Evaluating the effect of reaction time and concentration process on chemical properties in slurry production, the effect of the reaction time was not confirmed in the simulated slurry that had undergone the concentration process, and slurry prepared at SS concentration of 150 g/L was composed of formless particles have a particle diameter of 0.4  m or less. We also investigate the effect of SS concentration on sedimentability, decrease in SS concentration by dilution with processing solution contributed to an increase in the initial slurry settling velocity. Furthermore, two different flow characteristics were observed depending on the settling time, suggesting that the slurry at the initial settling time has non-Bingham flow properties, whereas it changes to Bingham flow properties as the settling time becomes longer. In addition, yield stress was increased with settling time, and this yield stress was found to be exponentially proportional to the density of the slurry. These results provide knowledge to estimate the current state of HIC slurry and are expected to contribute to the safety assessment.
m or less. We also investigate the effect of SS concentration on sedimentability, decrease in SS concentration by dilution with processing solution contributed to an increase in the initial slurry settling velocity. Furthermore, two different flow characteristics were observed depending on the settling time, suggesting that the slurry at the initial settling time has non-Bingham flow properties, whereas it changes to Bingham flow properties as the settling time becomes longer. In addition, yield stress was increased with settling time, and this yield stress was found to be exponentially proportional to the density of the slurry. These results provide knowledge to estimate the current state of HIC slurry and are expected to contribute to the safety assessment.
Cantarel, V.; Yamagishi, Isao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.888 - 897, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kato, Chiaki; Yamagishi, Isao; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.441 - 447, 2021/12
Zeolite particles have been used in a Cs adsorption vessel for purification of contaminated water in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). The used Cs adsorption vessels were kept in storage space on 1F site. The risk of localized corrosion of stainless steel used in the vessel was worried. To evaluate the risk of localized corrosion, using specially designed electrochemical testing apparatus was used under gamma-ray irradiation test. And, real size mock-up test conducted. The results showed the potential change caused by creation of H O
O by water radiolysis decreased by zeolite particles and the enrichment of chloride ion concentration in the vessel do not propagate during dry up procedure of Cs adsorption vessel. These data indicate the risk of localized corrosion of Cs adsorption vessel may stay at considerably low level.
by water radiolysis decreased by zeolite particles and the enrichment of chloride ion concentration in the vessel do not propagate during dry up procedure of Cs adsorption vessel. These data indicate the risk of localized corrosion of Cs adsorption vessel may stay at considerably low level.
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Ogawa, Toru
Insights Concerning the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident, Vol.4; Endeavors by Scientists, p.37 - 45, 2021/10
Zeolite adsorbents are to be used for decontamination of radioactive water in Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station. Evaluation of hydrogen production by water radiolysis during decontamination is important for safe operation. Thus hydrogen production from the mixture of zeolite adsorbents and seawater was studied because seawater was urgently used as a coolant for the fuels. The hydrogen yield from the mixture decreased at a high weight fraction of zeolites. However, the measured yield was higher than the yield expected from the direct radiolysis of seawater in the mixture, which would decrease proportional to the weight fraction of seawater. The result suggests that the radiation energy deposited to zeolites was involved in the hydrogen formation. From the results, the hydrogen production rate was evaluated to be 3.6 mL/h per ton of radioactive water before decontamination. After the process, it was evaluated to be 1.5 L/h per ton of waste adsorbents due to the high dose rate.
Horita, Takuma; Yamagishi, Isao; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kashiwaya, Ryunosuke*
JAEA-Technology 2021-012, 34 Pages, 2021/07
Waste mainly consisting of carbonate precipitates (carbonate slurry) from the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS) and the improved ALPS at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station of Tokyo Electric Power Holdings, Inc. have been storing in the High Integrity Container (HIC). The supernatant solution of carbonate slurry contained in some of HICs were overflowed in April of 2015. The all of level of liquid in the HICs were investigated; however, almost of the HICs were under the level of overflow. The mechanism of overflow suggested to be depending on the difference of the properties of the carbonate slurry such as the retention/release characteristics of the bubbles. Therefore, in order to clarify the mechanism of leakage, the repeatability experiment was carried out by using simulated carbonate slurry. The simulated carbonate slurry was perpetrated by using the same cross-flow filter system of the actual ALPS. Moreover, the preparative conditions for the simulated carbonate slurry were the same as Mg/Ca concentration ratio in inlet water of the ALPS (raw water) and the ALPS operating conditions. The chemical characteristics of simulated carbonate slurries were revealed by ICP-AES, pH meter, etc. The density of the settled slurry layer tended to increase depending on the calcium concentration in the raw water. The bubble injection test was conducted in order to investigate the bubble retention/release behavior in the simulated carbonate slurry layer. The simulated carbonate slurry with high settling density, which was generated by high calcium concentration solution was revealed to retain the injected bubbles. Since the ratio of concentration calcium and magnesium during the carbonate slurry generation is assumed to affect the retention of bubbles in the slurry layer, the information on the composition of raw water is one of important factor for overflow of HICs.
Cantarel, V.; Lambertin, D.*; Labed, V.*; Yamagishi, Isao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.62 - 71, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)The gas production of wasteforms is a major safety concern for encapsulating active nuclear wastes. For geopolymers and cements, the H produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the gas composition evolution around geopolymers was monitored on line under
produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the gas composition evolution around geopolymers was monitored on line under  Co gamma irradiation. Transient evolution of the hydrogen production yield was measured for samples with different formulations. The rate of its evolution and the final values are consistent with the presence of a chemical reaction of the pseudo-first order consuming hydrogen in the samples. The results show this phenomenon can significantly reduce the hydrogen source term of geopolymer wasteform provided their diffusion constant remains low. Lower hydrogen production rates and faster kinetics were observed with geopolymers formulations in which pore water pH was higher. Besides hydrogen production, a steady oxygen consumption was observed for all geopolymers samples. The oxygen consumption rates are proportional to the diffusion constants estimated in the modelization of hydrogen recombination by a pseudo first order reaction.
Co gamma irradiation. Transient evolution of the hydrogen production yield was measured for samples with different formulations. The rate of its evolution and the final values are consistent with the presence of a chemical reaction of the pseudo-first order consuming hydrogen in the samples. The results show this phenomenon can significantly reduce the hydrogen source term of geopolymer wasteform provided their diffusion constant remains low. Lower hydrogen production rates and faster kinetics were observed with geopolymers formulations in which pore water pH was higher. Besides hydrogen production, a steady oxygen consumption was observed for all geopolymers samples. The oxygen consumption rates are proportional to the diffusion constants estimated in the modelization of hydrogen recombination by a pseudo first order reaction.
Cantarel, V.; Arisaka, Makoto; Yamagishi, Isao
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 102(12), p.7553 - 7563, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:52.00(Materials Science, Ceramics)The hydrogen gas (H ) production of wasteforms is a major safety concern for encapsulating nuclear wastes. For geopolymers, the H
) production of wasteforms is a major safety concern for encapsulating nuclear wastes. For geopolymers, the H produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the hydrogen production was measured under
produced by radiolytic processes is a key factor because of the large amount of water present in their porous structure. Herein, the hydrogen production was measured under  Co gamma irradiation. The effect of water saturation and sample size were studied for pure geopolymers, or using zeolites as an example waste. When geopolymer monolithic samples were large and saturated by water, the hydrogen released was measured up to two orders of magnitude lower with a 40 cm long cylinder samples (1.9
Co gamma irradiation. The effect of water saturation and sample size were studied for pure geopolymers, or using zeolites as an example waste. When geopolymer monolithic samples were large and saturated by water, the hydrogen released was measured up to two orders of magnitude lower with a 40 cm long cylinder samples (1.9 10
10 mol/J) than a sample in powder form (2.2
mol/J) than a sample in powder form (2.2 10
10 mol/J). To interpret results, a simple model was used, considering only hydrogen production, a potential recombination and its diffusion in the geopolymer matrix. Knowing the diffusion constant of the matrix, the model was able to reproduce the evolution of the hydrogen release as a function of the water saturation level and predict the evolution when sample size is increased up to 40 cm.
mol/J). To interpret results, a simple model was used, considering only hydrogen production, a potential recombination and its diffusion in the geopolymer matrix. Knowing the diffusion constant of the matrix, the model was able to reproduce the evolution of the hydrogen release as a function of the water saturation level and predict the evolution when sample size is increased up to 40 cm.
Cantarel, V.; Arisaka, Makoto; Yamagishi, Isao
Proceedings of 3rd International Symposium on Cement-based Materials for Nuclear Wastes (NUWCEM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2018/10
Geopolymers were successfully synthesized with different water content and loading of zeolites (0 to 40%wt). Zeolite A, geopolymer and their composites were then irradiated by a  Co source (1.5 to 2.5 kGy/h) up to 10 kGy. The hydrogen was measured by GC after irradiation. Yields of radiolitic hydrogen were obtained for individual components. Obtained yields suggested a recombination process during irradiation. The system was then modelled to explain the observed behavior and predict the hydrogen production under
Co source (1.5 to 2.5 kGy/h) up to 10 kGy. The hydrogen was measured by GC after irradiation. Yields of radiolitic hydrogen were obtained for individual components. Obtained yields suggested a recombination process during irradiation. The system was then modelled to explain the observed behavior and predict the hydrogen production under  ray irradiation of larger samples.
ray irradiation of larger samples.
Cantarel, V.; Motooka, Takafumi; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Review 2017-014, 36 Pages, 2017/06
After a necessary decay time, the zeolites used for the water decontamination will eventually be conditioned for their long-term storage. Geopolymer is considered as a potential matrix to manage radioactive cesium and strontium containing waste. For such applications, a correct comprehension of the binder structure, its macroscopic properties, its interactions with the waste and the physico-chemical phenomena occurring in the waste form is needed to be able to judge of the soundness and viability of the material. Although the geopolymer is a young binder, a lot of research has been carried out over the last fifty years and our understanding of this matrix and its potential applications is progressing fast. This review aims at gathering the actual knowledge on geopolymer studies about geopolymer composites, geopolymer as a confinement matrix for nuclear wastes and geopolymer under irradiation. This information will finally provide guidance for the future studies and experiments.
Morita, Yasuji; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Research 2017-006, 27 Pages, 2017/06
Separation of Pd by extraction with 5,8-diethyl-7-hydroxy-6-dodecanone oxime (DEHDO) was examined by batch and continuous tests for the purpose of developing Pd separation process. Batch extraction tests using n-dodecane solution of DEHDO revealed that Pd, Zr and Mo were extracted from simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) and other elements were not, and also showed that the extraction rate was a little slow and a white precipitate appeared in the aqueous phase but its formation could be avoided by raising temperature. The extracted Pd was found to be back-extracted with sodium nitrite. In the continuous extraction tests with simulated HLLW without Zr and Mo, about 98% of Pd were extracted with DEHDO-n-dodecane and 95% of the extracted Pd were back-extracted with sodium nitrite and nitric acid. Continuous extraction test with simulated HLLW with Zr and Mo showed the possibility of the simultaneous separation of Pd and Mo by DEHDO extraction.
Motooka, Takafumi; Yamagishi, Isao
JAEA-Review 2017-004, 157 Pages, 2017/03
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) is responsible to promote international cooperation in the R&D activities on the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and to develop the necessary human resources. CLADS held the Research Conference on Post-accident Waste Management Safety (RCWM2016) was held on November 7th, 2016 and the Technical Seminar on Safety Research for Radioactive Waste Storage was held on November 8th, 2016. This report compiles the abstracts and the presentation materials in the above conference and seminar.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationMotooka, Takafumi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamagishi, Isao
QST-M-2; QST Takasaki Annual Report 2015, P. 95, 2017/03
We conducted  ray irradiation test using simulated carbonate slurry to investigate the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container (HIC). This test was performed at Co-60 irradiation facility in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute. We observed a rise in water level, air bubbles in the slurry, a supernatant when the carbonate slurry with 95 g/L density was irradiated by
ray irradiation test using simulated carbonate slurry to investigate the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container (HIC). This test was performed at Co-60 irradiation facility in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute. We observed a rise in water level, air bubbles in the slurry, a supernatant when the carbonate slurry with 95 g/L density was irradiated by  ray at a dose rate of 8.5 kGy/h. The cause of the rise in water level was regarded as the volume expansion by the gas retention of the carbonate slurry. It was suggested that the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container might be the volume expansion by the gas retention.
ray at a dose rate of 8.5 kGy/h. The cause of the rise in water level was regarded as the volume expansion by the gas retention of the carbonate slurry. It was suggested that the cause of stagnant water over the high integrity container might be the volume expansion by the gas retention.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Motooka, Takafumi; Yamagishi, Isao
Proceedings of 2016 EFCOG Nuclear & Facility Safety Workshop (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/09
Overflow of water from waste storage tanks of High Integrity Containers (HIC) in the multi-nuclide removal equipment (ALPS) was discovered at Fukushima Daiichi NPS in April of last year. The mechanism of overflow was not understood very much at that time. To elucidate that for chemical safety in the waste storage, irradiation experiments of simulated carbonate slurry by Co-60  -rays have been conducted in CLADS, JAEA in cooperation with TEPCO, TOSHIBA and KURITA. Hydrogen molecule was the main radiolytic gas product in the slurry, and its amount was enhanced by dissolved species of not only halide ions as seawater components but also carbonate ion as an additive for co-precipitation at a basic condition. The bubbles of molecules were further formed and almost held in the slurry without stirred. These sequentially led to the expansion of slurry, and then to its separation into the shrunk one and supernatant water, which was little accumulated without irradiated.
-rays have been conducted in CLADS, JAEA in cooperation with TEPCO, TOSHIBA and KURITA. Hydrogen molecule was the main radiolytic gas product in the slurry, and its amount was enhanced by dissolved species of not only halide ions as seawater components but also carbonate ion as an additive for co-precipitation at a basic condition. The bubbles of molecules were further formed and almost held in the slurry without stirred. These sequentially led to the expansion of slurry, and then to its separation into the shrunk one and supernatant water, which was little accumulated without irradiated.
Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1357 - 1374, 2016/05
With respect to the long-term storage of the zeolite-containing spent Cs adsorption vessels used at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the corrosion of the vessel material is one of the most important issues. In this study, we performed electrochemical tests on stainless steel specimens in zeolite-containing artificial seawater under gamma-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ESP and critical pitting potential VC of the type 316L steel in systems in contact with various zeolites were measured in order to evaluate the corrosion resistance of the steel. In addition, the water sample was analyzed after being irradiated, in order to determine the concentrations of various dissolved oxidants such as oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which can accelerate the corrosion process. The steady-state rest potential increased with an increase in the dose rate; however, the increase was suppressed in contact with the zeolites. The VC value of the steel when in contact with the zeolites was slightly smaller than the VC value in bulk water; however, the choice of the zeolite used as herschelite, IE96 and IE911 hardly affect the VC value. The concentration of H O
O in the bulk water under irradiation also increased with the increase in the dose rate. This increase was suppressed in the systems in contact with the zeolites, owing to the decomposition of the H
in the bulk water under irradiation also increased with the increase in the dose rate. This increase was suppressed in the systems in contact with the zeolites, owing to the decomposition of the H O
O by the zeolites. A clear relationship was observed between ESP and the H
by the zeolites. A clear relationship was observed between ESP and the H O
O concentration. As contact with the zeolites caused the increase in ESP under irradiation to be suppressed, it can be concluded that the presence of zeolites in the spent Cs adsorption vessels can reduce the probability of the localized corrosion of the stainless steel in the vessels.
concentration. As contact with the zeolites caused the increase in ESP under irradiation to be suppressed, it can be concluded that the presence of zeolites in the spent Cs adsorption vessels can reduce the probability of the localized corrosion of the stainless steel in the vessels.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationKato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(3), p.181 - 188, 2015/09
In relation to the consideration for long-term storage of spent Cs adsorption vessels containing zeolites in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of the vessel material in the spent Cs adsorption vessel is one of important issues. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (SUS 316L) in the zeolites containing artificial seawater under  -ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential (
-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ( ) and critical pitting potential (
) and critical pitting potential (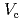 ), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after
), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after  -ray irradiation. The
-ray irradiation. The  , defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing
, defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing  was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H
was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H O
O in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H
in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H O
O . There was good relationship between
. There was good relationship between  and the concentration of H
and the concentration of H O
O . The
. The 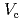 of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl
of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the
ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the 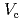 in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing
in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing  under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
Yamagishi, Isao; Odakura, Makoto; Ichige, Yoshiaki; Kuroha, Mitsuhiko; Takano, Masahide; Akabori, Mitsuo; Yoshioka, Masahiro*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference & Exhibition; Nuclear Fuel Cycle for a Low-Carbon Future (GLOBAL 2015) (USB Flash Drive), p.1113 - 1119, 2015/09
The characteristics of insoluble residues in fine suspension at the Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant were analyzed. The insoluble residues were washed with oxalic acid solution to dissolve zirconium molybdate residues. XRD profiles of unwashed residues showed the presence of a noble metal alloy, zirconium molybdate, and zirconia, but zirconium molybdate was not found after washing. More than 50% of the Sb-125 and Pu in thee residues was washed out as well. The noble metal alloy composed of Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, and Pd occupied more than 90% of the total weight of 12 elements (Ca, Cr, Fe, Ni, Zr, Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, Pd, Te, and U) found in the residues. In consideration of the chemical forms of 12 elements, the alloy-to-residue weight ratio was evaluated to be 64% and 78% with and without 18% of an unknown component, respectively.
Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo 2015 Koenshu (CD-ROM), p.83 - 86, 2015/05
In relation to the consideration for long-term storage of spent Cs adsorption vessels containing zeolites in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of the vessel material in the spent Cs adsorption vessel is one of important issues. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (SUS 316L) in the zeolites containing artificial seawater under gamma-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential (ESP) and critical pitting potential (VC), of SUS316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after gamma-ray irradiation. The ESP, defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing ESP was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H O
O in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H
in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H O
O . There was good relationship between ESP and the concentration of H
. There was good relationship between ESP and the concentration of H O
O . The VC of SUS316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl
. The VC of SUS316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the VC in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing ESP under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolites can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS316L.
ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the VC in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing ESP under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolites can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS316L.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.301 - 307, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:79.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the severe accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant, large amounts of contaminated stagnant water have accumulated in turbine buildings and their surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of the radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. This evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011. The release ratios of tritium, iodine, and cesium were several tens of percent, whereas those of strontium and barium were smaller by one or two orders of magnitude. The release ratios in the Fukushima accident were equivalent to those in the TMI-2 accident.