Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 109, p.1421 - 1436, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:93.94(Chemistry, Physical)Our preceding investigation revealed that multiple hydrogen traps at coherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn
precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn
through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn
interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn
interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Nishijima, Masahiko*; Kamada, Yasuhiro*
Corrosion, 79(8), p.818 - 830, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:52.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)7xxx aluminum alloys are representative high-strength aluminum alloys; however, mechanical property degradation due to hydrogen hinders further strengthening. We propose the dispersion of Mn-based second-phase particles as a novel technique for preventing 7xxx aluminum alloy hydrogen embrittlement. In this study, the deformation and fracture behaviors of high hydrogen 7xxx alloys containing 0.0% Mn and 0.6% Mn are observed in situ using synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography. The obtained macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement is quantitatively analyzed based on hydrogen partitioning in alloys. Adding 0.6% Mn, generating second-phase particles with high hydrogen trapping abilities, significantly suppresses hydrogen-induced quasicleavage fracture.
 hydrogen partitioning control
hydrogen partitioning controlToda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Su, H.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 105(2), p.240 - 253, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Kubo, Shinji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ioka, Ikuo; Onuki, Kaoru; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38(16), p.6577 - 6585, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:54.05(Chemistry, Physical)Very harsh environments exist in the iodine-sulfur process for hydrogen production. Structural materials for sulfuric acid vaporizers and concentrators are exposed to high-temperature corrosive environments. Immersion tests were carried out to evaluate the corrosion resistance of ceramics and to evaluate corrosion-resistant metals exposed to environments of aqueous sulfuric acids at temperatures of 320, 380, and 460 C, and pressure of 2 MPa. The aqueous sulfuric acid concentrations for the temperatures were 75, 85, and 95 wt%, respectively. Ceramic specimens of silicon carbides (SiC), silicon impregnated silicon carbides (Si-SiC), and silicon nitrides (Si
C, and pressure of 2 MPa. The aqueous sulfuric acid concentrations for the temperatures were 75, 85, and 95 wt%, respectively. Ceramic specimens of silicon carbides (SiC), silicon impregnated silicon carbides (Si-SiC), and silicon nitrides (Si N
N ) showed excellent corrosion resistance from weight loss measurements after exposure to 75, 85, and 95 wt% sulfuric acid. High-silicon irons with silicon content of 20 wt% showed a fair measure of corrosion resistance. However, evidence of crack formation was detected via microscopy. Silicon enriched steels severely suffered from uniform corrosion with a corrosion rate in 95 wt% sulfuric acid of approximately 1 gm
) showed excellent corrosion resistance from weight loss measurements after exposure to 75, 85, and 95 wt% sulfuric acid. High-silicon irons with silicon content of 20 wt% showed a fair measure of corrosion resistance. However, evidence of crack formation was detected via microscopy. Silicon enriched steels severely suffered from uniform corrosion with a corrosion rate in 95 wt% sulfuric acid of approximately 1 gm h
h . Among the tested materials, the ceramics SiC, Si-SiC, and Si
. Among the tested materials, the ceramics SiC, Si-SiC, and Si N
N were found to be suitable candidates for structural materials in direct contact with the considered environments.
were found to be suitable candidates for structural materials in direct contact with the considered environments.
Kubo, Shinji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Onuki, Kaoru; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*
Corrosion Engineering, 62(3), p.104 - 111, 2013/03
The iodine-sulfur thermochemical cycle for hydrogen production takes place in very harsh environments. Structural metallic materials for the hydrogen iodide decomposition are exposed in a high temperature halogen corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement environment. To evaluate adaptability of the materials, the corrosion rates and mechanical properties (the yield strength, the tensile strength, and the elongation) were measured. Prepared test specimens were exposed to ambient gas consisting of HI, I , H
, H O, and H
O, and H (molar fraction of 1:1:6:0.16) at 450
(molar fraction of 1:1:6:0.16) at 450 C for 1000 h at atmospheric pressure. After the exposure, the corrosion rates were obtained by the weight loss of each specimen. Nickel-based alloys (Hastelloy C-276, MAT21, Inconel 625) exhibited appropriate corrosion resistance (
C for 1000 h at atmospheric pressure. After the exposure, the corrosion rates were obtained by the weight loss of each specimen. Nickel-based alloys (Hastelloy C-276, MAT21, Inconel 625) exhibited appropriate corrosion resistance ( 0.03 g m
0.03 g m h
h . In addition, no degradations of the mechanical properties for the MAT21 and the Inconel 625 were observed. The specimens of tantalum and titanium showed hydrogen embrittlement; the specimens of zirconium and niobium exhibited poor corrosion resistance. The specimens of molybdenum (Mo) exhibited good corrosion resistance; however, the strength degradation of Mo is cause for concern. As the results show, the nickel-based alloys are well suited for the structural materials within this environment from the viewpoint of the corrosion resistance. MAT21 among them is an outstanding material with an eye to its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
. In addition, no degradations of the mechanical properties for the MAT21 and the Inconel 625 were observed. The specimens of tantalum and titanium showed hydrogen embrittlement; the specimens of zirconium and niobium exhibited poor corrosion resistance. The specimens of molybdenum (Mo) exhibited good corrosion resistance; however, the strength degradation of Mo is cause for concern. As the results show, the nickel-based alloys are well suited for the structural materials within this environment from the viewpoint of the corrosion resistance. MAT21 among them is an outstanding material with an eye to its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Kubo, Shinji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Onuki, Kaoru; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 62(3), p.122 - 128, 2013/03
The iodine-sulfur thermochemical cycle for hydrogen production takes place in very harsh environments. Structural metallic materials for the hydrogen-iodide decomposition are exposed in the high-temperature halogen corrosion and the hydrogen embrittlement environment. To evaluate adaptability of the materials, corrosion rates and mechanical properties (the yield strength, the tensile strength, and the elongation) were measured. Prepared test specimens were exposed to ambient gas consisting of HI, I , H
, H O and H
O and H (molarfraction, 1:1:6:0.16) at 450
(molarfraction, 1:1:6:0.16) at 450 C for 1000 hours at the atmospheric pressure. After the exposure, the corrosion rates were obtained by the weight loss of each specimen. Nickel-based alloys (Hastelly C-276, MAT21, Inconel 625) exhibited appropriate corrosion resistance (
C for 1000 hours at the atmospheric pressure. After the exposure, the corrosion rates were obtained by the weight loss of each specimen. Nickel-based alloys (Hastelly C-276, MAT21, Inconel 625) exhibited appropriate corrosion resistance ( 0.03 g m
0.03 g m h
h ). In addition, no degradations of the mechanical properties for the MAT21 and the Inconel 625 were observed. The specimens of tantalum and titanium showed the hydrogen embrittlement; the specimens of zirconium and niobium exhibited poor corrosion resistance. The specimens of molybdenum (Mo) exhibited good corrosion resistance, however strength degradation of Mo is causing concern. As the results, the nickel-based alloys are well suited for the structural materials within this environment from the viewpoint of the corrosion resistance. MAT21 among them is the outstanding material with an eye to its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
). In addition, no degradations of the mechanical properties for the MAT21 and the Inconel 625 were observed. The specimens of tantalum and titanium showed the hydrogen embrittlement; the specimens of zirconium and niobium exhibited poor corrosion resistance. The specimens of molybdenum (Mo) exhibited good corrosion resistance, however strength degradation of Mo is causing concern. As the results, the nickel-based alloys are well suited for the structural materials within this environment from the viewpoint of the corrosion resistance. MAT21 among them is the outstanding material with an eye to its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Sasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sai, Akihisa*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Kamiya, Itaru*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Journal of Crystal Growth, 323(1), p.13 - 16, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:82.31(Crystallography)Growth temperature dependence of strain relaxation during In![$$_{0.12}]$$](/search/images/ERPXWMBOGEZH0XJE.gif) Ga
Ga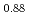 As/GaAs(001) molecular beam epitaxy was studied by in situ X-ray reciprocal space mapping. Evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality for the InGaAs film was obtained as a function of film thickness at growth temperatures of 420, 445 and 477
As/GaAs(001) molecular beam epitaxy was studied by in situ X-ray reciprocal space mapping. Evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality for the InGaAs film was obtained as a function of film thickness at growth temperatures of 420, 445 and 477  C. In the early stages of strain relaxation, it was found that evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality was dependent on the growth temperature. In order to discuss this observation quantitatively, the strain relaxation model was proposed based on the Dodson-Tsao kinetic model, and its validity was demonstrated by good agreement with the experimental residual strain. Additionally, rate coefficients reflecting dislocation motions during strain relaxation were obtained as a function of growth temperature and strain relaxation was discussed in terms of the thermally active dislocation motion.
C. In the early stages of strain relaxation, it was found that evolution of the residual strain and crystal quality was dependent on the growth temperature. In order to discuss this observation quantitatively, the strain relaxation model was proposed based on the Dodson-Tsao kinetic model, and its validity was demonstrated by good agreement with the experimental residual strain. Additionally, rate coefficients reflecting dislocation motions during strain relaxation were obtained as a function of growth temperature and strain relaxation was discussed in terms of the thermally active dislocation motion.
Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sasaki, Takuo*; Sai, Akihisa*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Kamiya, Itaru*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji
Applied Physics Letters, 97(4), p.041906_1 - 041906_3, 2010/07
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:73.76(Physics, Applied)Sasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sai, Akihisa*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1268, 6 Pages, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) real-time X-Ray reciprocal space mapping during InGaAs/GaAs growth for understanding strain relaxation mechanisms
real-time X-Ray reciprocal space mapping during InGaAs/GaAs growth for understanding strain relaxation mechanismsSasaki, Takuo*; Suzuki, Hidetoshi*; Sai, Akihisa*; Lee, J.-H.*; Takahashi, Masamitsu; Fujikawa, Seiji; Arafune, Koji*; Kamiya, Itaru*; Oshita, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Masafumi*
Applied Physics Express, 2, p.085501_1 - 085501_3, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:75.58(Physics, Applied)Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Onuki, Kaoru; Shimizu, Saburo; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 55(7), p.320 - 324, 2006/07
Exposure tests of candidate materials were carried out up to 1000 hr in the sulfuric acid environments of thermochemical hydrogen production IS process, focusing on the corrosion of welded portion and of crevice area. In the gas phase sulfuric acid decomposition condition at 850 C, welded samples of Alloy 800 and of Alloy 600 showed the same good corrosion resistance as the bare materials. Also, in the boiling condition of 95wt% sulfuric acid solution, negligible corrosion was observed in crevice corrosion test sample of SiC.
C, welded samples of Alloy 800 and of Alloy 600 showed the same good corrosion resistance as the bare materials. Also, in the boiling condition of 95wt% sulfuric acid solution, negligible corrosion was observed in crevice corrosion test sample of SiC.
Kubo, Shinji; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*; Tsukada, Ryuji*; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2006 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '06) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2006/06
no abstracts in English
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kubo, Shinji; Wakui, Takashi*; Onuki, Kaoru; Shimizu, Saburo; Yamaguchi, Akihisa*
Jikken Rikigaku, 3(2), p.109 - 114, 2003/06
Micro-indentation technique was applied to evaluate the mechanical properties of corroded surface layers of Ni-alloy, 316SS, Ti and Ta, which were exposed into the corrosive gaseous environment consisting of HI+I +H
+H O+H
O+H . The corrosion condition was chosen so as to simulate one of the environments in the thermochemical hydrogen production, IS process, where the degradation due to the corrosion attack by HI and the hydrogen embrittlement is a key issue from the viewpoint of material integrity. The micro-indentation tests using a spherical indenter and the inverse analysis with Kalman filter were performed to quantitatively estimate material constants of corroded surface layer. Ni-alloy exhibited good corrosion resistance and Ta was remarkably influenced by the hydrogen embrittlement.
. The corrosion condition was chosen so as to simulate one of the environments in the thermochemical hydrogen production, IS process, where the degradation due to the corrosion attack by HI and the hydrogen embrittlement is a key issue from the viewpoint of material integrity. The micro-indentation tests using a spherical indenter and the inverse analysis with Kalman filter were performed to quantitatively estimate material constants of corroded surface layer. Ni-alloy exhibited good corrosion resistance and Ta was remarkably influenced by the hydrogen embrittlement.