Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Science of the Total Environment, 964, p.178585_1 - 178585_13, 2025/02
There are many unresolved issues in the adsorption reactions of clay minerals. One of the reasons is the existence of multiple adsorption sites. It is known that the contribution of each adsorption site depends on the concentration of adsorbed ions, and there is a challenge in comprehensively correlate the results of atomic-level simulations that employ limited number of atoms and inevitably deal high-concentration samples with actual environmental samples where concentrations are orders of magnitude lower. In this study, we combined experiments using synchrotron radiation and first-principles calculations to comprehensively elucidate the systematic changes in the local structure of adsorption sites and adsorbed ions based on the adsorption concentration at the atomic level, and demonstrated that the interaction between adsorbed ions and clay minerals involves ionic bonding.
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Yomogida, Takumi
Treatise on Geochemistry, 3rd edition, Vol.6, p.105 - 150, 2025/00
With the recent development of measurement techniques, new approaches to the environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been applied for various research targets. In this review article, several topics within the last 10-15 years in the field of environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been discussed. In particular, this article mainly focused on two topics, (i) studies on the migration of radionuclides emitted by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident in 2011 and (ii) the development of X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy and its application to the geochemical processes of radionuclides.
Nagasawa, Makoto*; Shimizu, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Tokunaga, Kohei; Mukai, Hiroki*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemical Geology, 670, p.122431_1 - 122431_25, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.42(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Yamaguchi, Akiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Okumura, Masahiko
Isotope News, (796), p.21 - 23, 2024/12
Clay minerals are abundant in soils and control the environmental behavior of various elements because they adsorb many cations. Since the strength of adsorption of clay minerals depends on the adsorption structure at the molecular level, a systematic understanding of what determines the adsorption structure at the molecular level is important. In this study, we systematically elucidated the adsorption structures of many cations, including radium, using extensive X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements and first-principles simulations. The results show that the size and hydration enthalpy of adsorbed ions are important in determining the adsorption structure.
Oguri, Kaori; Hagura, Naoto*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Aoki, Katsumi; Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165516_1 - 165516_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ningyo-toge is the uranium mine that has been operated in Japan. Various radioactive elements such as Uranium (U), and Radium (Ra) are still present in the mine ground water with very small amount, and behavior of those elements is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the composition of metal oxides and clay minerals in a soil of slag deposit at the mine, and systematics of adsorption structure of various ions were examined. Identifying the composition and chemical forms of minerals present in the soil of slag can provide useful information for the safety assessment and evaluation of influence on the surrounding environment.
Uno, Koichiro*; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakao, Atsushi*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Yanai, Junta*
Science of the Total Environment, 949, p.175012_1 - 175012_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Frayed edge sites (FES), formed by the partial weathering of mica minerals, selectively adsorb Cs ions. However, the detailed mechanism of this adsorption has not been fully clarified. In this study, cation extraction and Cs adsorption experiments were conducted on mica. It was found that potassium-adsorbed mica adsorbed more Cs than rubidium-adsorbed mica. To elucidate the cause of this, the stability of Cs, rubidium, and potassium adsorbed on FES was evaluated using first-principles calculations. It was determined that the presence of potassium as the cation species prior to Cs adsorption is important for the stability of Cs on the FES.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10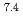 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.77(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Isotope News, (789), p.20 - 23, 2023/10
Radium is a radioactive element produced from uranium and thorium and is important for environmental contamination issues around uranium mines and for geological disposal. In addition, radium is used in radiometric dating and cancer therapy, making it important not only in environmental chemistry but also in many other fields, including geochemistry and nuclear medicine. However, because radium is a radioactive element with no stable isotopes, spectroscopic measurement of radium is difficult, and little information at the molecular level has been obtained so far. In this study, we have clarified the molecular-level information of hydrated radium for the first time in the world by combining extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) measurements and first-principles molecular dynamics simulations.

 values calculated from radiocesium interception potential
values calculated from radiocesium interception potentialUno, Koichiro*; Nakao, Atsushi*; Okumura, Masahiko; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Yanai, Junta*
Nihon Dojo Hiryo Gaku Zasshi, 94(5), p.376 - 384, 2023/10
Radiocesium interception potential (RIP) has been widely used as a quantitative indicator of cesium (Cs) adsorption capacity of soil, but it has been found that RIP does not always correlate with the distribution coefficient (
 ) of Cs in the actual environment. In order to clarify the cause of this discrepancy, we measured Kd using more realistic solutions, compared it with RIP, and evaluated the mineral structure. As a result, it was found that the concentration of competing cations, such as potassium and ammonium ions, and the structural change of the mineral itself are important.
) of Cs in the actual environment. In order to clarify the cause of this discrepancy, we measured Kd using more realistic solutions, compared it with RIP, and evaluated the mineral structure. As a result, it was found that the concentration of competing cations, such as potassium and ammonium ions, and the structural change of the mineral itself are important.
Yamaguchi, Akiko
Hosha Kagaku, (48), p.56 - 59, 2023/09
The adsorption reaction on clay minerals is an important chemical reaction that controls the environmental behaviors of various ions at the Earth's surface, but the details are unknown due to the complexity of the reaction, such as the diversity of clay mineral compositions and the existence of multiple adsorption sites. In this study, we focused on the adsorption structure on clay minerals at the atomic level, and clarified it in detail by combining X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) methods and first-principles calculations. In particular, XAFS measurements of radium, which has the largest ionic radius among alkaline earth metals and has been difficult to measure at the atomic level, were successfully performed, and new knowledge was obtained by comparing the results with those of other elements.
Yamaguchi, Akiko
Hosha Kagaku, (47), p.41 - 42, 2023/03
Radium (Ra) is essential for various fields, such as environmental chemistry and nuclear medicine. However, even the hydration structure of Ra remains unclear due to the difficulty in the Ra treatment, caused by the fact that Ra has no stable isotopes and forms radon, noble gas. This study measured the extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) of Ra to investigate its hydration structure and adsorption structures on clay minerals. The EXAFS results were consistent with our environmental analysis of core samples in a uranium mine.
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:66.73(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Keita; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Applied Clay Science, 228, p.106596_1 - 106596_11, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:73.45(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ion
molecular dynamics simulations reveal the hydration structure of the radium(II) ionYamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Kobayashi, Keita; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Shimojo, Kojiro; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
iScience (Internet), 25(8), p.104763_1 - 104763_12, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:68.06(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kobayashi, Keita; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Tanida, Hajime; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Kaneta, Yui; Matsuda, Shohei; et al.
Hosha Kagaku, (45), p.28 - 30, 2022/03
no abstracts in English
 molecular dynamics simulations using the SCAN meta-GGA density functional and EXAFS spectroscopy studies
molecular dynamics simulations using the SCAN meta-GGA density functional and EXAFS spectroscopy studiesYamaguchi, Akiko; Kobayashi, Keita; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Chemical Physics Letters, 780, p.138945_1 - 138945_5, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:65.52(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 -edge for the determination of oxidation state for trace amount of Eu in natural samples by bragg-type crystal analyzer system
-edge for the determination of oxidation state for trace amount of Eu in natural samples by bragg-type crystal analyzer systemKonagaya, Rimi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemistry Letters, 50(8), p.1570 - 1572, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.46(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:96.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kobayashi, Keita; Nakamura, Hiroki; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko
Computational Materials Science, 188, p.110173_1 - 110173_14, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:76.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English