Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ebihara, Mitsuru*; Shirai, Naoki*; Osawa, Takahito; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 389, p.200 - 210, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:96.61(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The 15 elements including most major elements of 12 carbonaceous chondrites collected in Antarctica were quantified using neutron-induced prompt gamma-ray analysis. While some of these samples were observed to share affinities with CI or CM chondrites, they do not exhibit the same characteristics as the known CI or CM chondrites. As a result, a new group named "CY" has been proposed for these meteorites. Common among the 12 meteorites is the depletion of volatile elements H and chlorine, showing a correlation and being depleted compared to non-Antarctic CI levels. Based on the abundance of moderately volatile elements Mn and S, the 12 meteorites can be divided into two groups: one with levels similar to non-Antarctic CI and the other with intermediate levels between CI and CM. These results suggest that CY chondrites originate from distinct parent bodies (materials), and considering two different parent bodies (materials) is necessary.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Nakayoshi, Akira; Arai, Yoichi; Sato, Takumi; Ohgi, Hiroshi; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Yamaguchi, Yukako; Morishita, Kazuki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-005, 418 Pages, 2023/12
For safe and steady decommissioning of Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings' Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), information concerning composition and physical/chemical properties of fuel debris generated in the reactors should be estimated and provided to other projects conducting the decommissioning work including the retrieval of fuel debris and the subsequent storage. For this purpose, in FY2021, samples of contaminants (the wiped smear samples and the deposits) obtained through the internal investigation of the 1F Unit 2 were analyzed to clarify the components and to characterize the micro-particles containing uranium originated from fuel (U-bearing particles) in detail. This report summarized the results of analyses performed in FY2021, including the microscopic analysis by SEM and TEM, radiation analysis, and elemental analysis by ICP-MS, as a database for evaluating the main features of each sample and the probable formation mechanism of the U-bearing particles.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 237(5), p.947 - 957, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.83(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. However, the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components are damaged is difficult to estimate if the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA based on event trees and fault trees. A methodology coupling thermal-hydraulic analysis with external event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID) is therefore proposed to overcome this limitation. A flood propagation model based on Bernoulli's theorem was applied to represent internal flooding in the turbine building of the pressurized water reactor. Uncertainties were also taken into account, including the flow rate of the floodwater source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. The simulated recovery actions included the operator isolating the floodwater source and using a drainage pump; these actions were modeled using several simplifications. Overall, the results indicate that combining isolation and drainage can reduce the conditional core damage probability upon the occurrence of flooding by approximately 90%.
Kubo, Kotaro; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.359 - 373, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:81.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is an essential approach to improving the safety of nuclear power plants. However, this method includes certain difficulties, such as modeling of combinations of multiple hazards. Seismic-induced flooding scenario includes several core damage sequences, i.e., core damage caused by earthquake, flooding, and combination of earthquake and flooding. The flooding fragility is time-dependent as the flooding water propagates from the water source such as a tank to compartments. Therefore, dynamic PRA should be used to perform a realistic risk analysis and quantification. This study analyzed the risk of seismic-induced flooding events by coupling seismic, flooding, and thermal-hydraulics simulations, considering the dependency between multiple hazards explicitly. For requirements of safety improvement, especially in light of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, sensitivity analysis was performed on the seismic capacity of systems, and the effectiveness of alternative steam generator injection by a portable pump was estimated. We demonstrate the use of this simulation-based dynamic PRA methodology to evaluate the risk induced by a combination of hazards.
Kubo, Kotaro; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.357 - 367, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA), which handles epistemic and aleatory uncertainties by coupling the thermal-hydraulics simulation and probabilistic sampling, enables a more realistic and detailed analysis than conventional PRA. However, enormous calculation costs are incurred by these improvements. One solution is to select an appropriate sampling method. In this paper, we applied the Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube, grid-point, and quasi-Monte Carlo sampling methods to the dynamic PRA of a station blackout sequence in a boiling water reactor and compared each method. The result indicated that quasi-Monte Carlo sampling method handles the uncertainties most effectively in the assumed scenario.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Nagae, Daisuke*; Abe, Yasushi*; Okada, Shunsuke*; Omika, Shuichiro*; Wakayama, Kiyoshi*; Hosoi, Shun*; Suzuki, Shinji*; Moriguchi, Tetsuro*; Amano, Masamichi*; Kamioka, Daiki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 986, p.164713_1 - 164713_7, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:71.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of 30th European Safety and Reliability Conference and 15th Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management Conference (ESREL 2020 and PSAM-15) (Internet), p.2279 - 2286, 2020/11
Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is one of the methods used to assess the risks associated with large and complex systems. When the risk of an external event is evaluated using conventional PRA, a particular limitation is the difficulty in considering the timing at which nuclear power plant structures, systems, and components fail. To overcome this limitation, we coupled thermal-hydraulic and external-event simulations using Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID). Internal flooding was chosen as the representative external event, and a pressurized water reactor plant model was used. Equations based on Bernoulli's theorem were applied to flooding propagation in the turbine building. In the analysis, uncertainties were taken into account, including the flow rate of the flood water source and the failure criteria for the mitigation systems. In terms of recovery action, isolation of the flood water source by the operator and drainage using a pump were modeled based on several assumptions. The results indicate that the isolation action became more effective when combined with drainage.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Ishikawa, Jun; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2020 (ASRAM 2020) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2020/11
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) enables a more realistic and detailed analysis than classical PRA. However, the trade-off for these improvements is the enormous computational cost associated with performing a large number of thermal-hydraulic (TH) analyses. In this study, based on machine learning (ML), we aim to reduce these costs by skipping the TH analysis. For the ML algorithm, we selected a support vector machine; we built it using a high-fidelity/high-cost detailed model and low-fidelity/low-cost simplified model. As a result, the computational costs could be reduced by approximately 80% without significantly decreasing the accuracy under the assumed conditions.
Kubo, Kotaro; Zheng, X.; Tanaka, Yoichi; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Jang, S.*; Takata, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Akira*
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.308 - 315, 2020/10
Dynamic probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is a method for improving the realism and completeness of conventional PRA. However, enormous calculation costs are incurred by these improvements. One solution is to select an appropriate sampling method. In this paper, we applied the Monte Carlo, Latin hypercube, grid-point, and quasi-Monte Carlo sampling methods to the dynamic PRA of a simplified accident sequence and compared the results for each method. Quasi-Monte Carlo sampling was found to be the most effective method in this case.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:303 Percentile:99.67(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Li, J.*; Jang, S.*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Takata, Takashi; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 11th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-11) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2018/11
The sodium-water reaction model is developed in particle methods. Two chemical reaction model, called surface reaction model and gas-phase reaction model are developed in the particle method. Validation on the case of vapor injection into liquid water is conducted and good consistency of jet velocity evolution along jet trajectory is obtained. Finally, sodium-water chemical reaction in a configuration of multiple tube bundles is simulated. Jet velocity, water vapor fraction and temperature are investigated and reasonable results are observed, which presents promising future of this methodology.
 TiBi
TiBi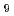
Motoyama, Gaku*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Kawasaki, Ikuto*; Sumiyama, Akihiko*; Yamamura, Tomoo*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.157 - 160, 2018/11
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management (PSAM-14) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2018/09
Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 331, p.147 - 152, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.46(Nuclear Science & Technology) Ge
Ge in the normal state
in the normal stateNakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Mori, Takeo*; Tsuruta, Atsushi*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Yasui, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(11), p.115160_1 - 115160_7, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.25(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Narukawa, Takafumi; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Jang, S.*; Amaya, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 499, p.528 - 538, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:60.52(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Matsuoka, Moe*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Osawa, Takahito; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Abe, Masanao*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Arai, Takehiko*; Komatsu, Mutsumi*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 69(1), p.120_1 - 120_12, 2017/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.45(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)We have conducted ground-based performance evaluation tests of the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) onboard Hayabusa2 spacecraft and established a method for evaluating its measured reflectance spectra. Reflectance spectra of nine powdered carbonaceous chondrite samples were measured by both NIRS3 and a FT-IR spectrometer. Since raw data obtained by NIRS3 had considerable spectral distortion caused by systematic offsets in sensitivity of individual pixels, we have established two methods for correcting the NIRS3 data by comparing them with the corresponding FT-IR data. In order to characterize the absorption bands in NIRS3 spectra, the depth of each band component D is defined for each wavelength
is defined for each wavelength  (
( m). Reflectance spectra of asteroid Ryugu, the target asteroid of Hayabusa2, to be recorded by the NIRS3 are expected to reveal the characteristics of the surface materials by using the evaluation technique.
m). Reflectance spectra of asteroid Ryugu, the target asteroid of Hayabusa2, to be recorded by the NIRS3 are expected to reveal the characteristics of the surface materials by using the evaluation technique.