Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculations
muon spin relaxation method and first-principles calculationsTsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Matsuzaki, Teiichiro*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; et al.
Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 54(6), p.2374 - 2383, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Although hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high-strength Al alloys is recognized as a critical issue in the practical use of Al alloys, identifying the hydrogen trapping or distribution has been challenging. In the present study, an effective approach based on experiment and simulation is proposed to explore the potential trap sites in Al alloys. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments were carried out for Al-0.5%Mg, Al-0.2%Cu, Al-0.15%Ti, Al-0.011%Ti, Al-0.28%V, and Al-0.015%V (at.%) in the temperature range from 5 to 300 K. The temperature variations of the dipole field widths have revealed three peaks for Al-0.5%Mg, four peaks for Al-0.2%Cu, three peaks for Al-0.011%Ti and Al-0.015%V. Atomic configurations of the muon trapping sites corresponding to the observed  peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon
peaks are well assigned using the first-principles calculations for the trap energies of hydrogen around a solute and solute-vacancy pair. The extracted linear relationship between the muon  peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
peak temperature and the trap energy enables us to explore the potential alloying elements and their complex that have strong binding energies with hydrogen in Al alloys.
Hashimoto, Shunsuke*; Yamaguchi, Satoshi*; Harada, Masashi*; Nakajima, Kenji; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 638, p.475 - 486, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:66.51(Chemistry, Physical)Recently, it has been reported that anomalous improvement in the thermal conductivity of nanofluid composed of base liquids and dispersed solid nanoparticles, compared to the theoretically predicted value calculated from the particle fraction. Generally, the thermal conductivity values of gases and liquids are dominated by the mean free path of the molecules during translational motion. Herein, we present solid evidence showing the possible contribution of the vibrational behavior of liquid molecules around nanoparticles to increasing these thermal conductivities.
Yamaguchi, Akinori*; Yokotsuka, Muneyuki*; Furuta, Masayo*; Kubota, Kazuo*; Fujine, Sachio*; Mori, Kenji*; Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 21(4), p.173 - 182, 2022/09
Risk information obtained from probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of measures against severe accidents in nuclear facilities. The PRA methods used for reprocessing facilities are considered immature compared to those for nuclear power plants, and to make the methods mature, reducing the uncertainty of accident scenarios becomes crucial. In this paper, we summarized the results of literature survey on the event progression of evaporation to dryness caused by boiling of high-level liquid waste (HLLW) which is a severe accident in reprocessing facilities and migration behavior of associated radioactive materials. Since one of the important characteristics of Ru is its tendency to form volatile compounds over the course of the event progression, the migration behavior of Ru is categorized into four stages based on temperature. Although no Ru has been released in the waste in the high temperature region, other volatile elements such as Cs could be released. Sufficient experimental data, however, have not been obtained yet. It is, therefore, necessary to further clarify the migration behavior of radioactive materials that predominantly depends on temperature in this region.
Toda, Hiroyuki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*
Kagaku, 75(10), p.48 - 53, 2020/10
Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminum alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
 Si and Al
Si and Al FeCu
FeCu intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculations
intermetallic compounds in aluminum alloy; First-principles calculationsYamaguchi, Masatake; Tsuru, Tomohito; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Materials Transactions, 61(10), p.1907 - 1911, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:55.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Materials Science and Technology, 36(15), p.1621 - 1627, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable phases in aluminum alloys are the primary nano-scale precipitates which have the biggest contribution to the increase in the tangible mechanical properties. The continuous increase in hardness in the 7xxx aluminum alloys is associated with the phase transformation from clusters or GP-zones to the metastable  phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of
phase. The transformation which is structural and compositional should occur following the path of the lowest activation energy. This work is an attempt to gain insight into how the structural transformation may occur based on the shortest route of diffusion for the eventual structure to result in that of  phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
phase. However, for the compositional transformation to occur, the proposed mechanism may not stand, since it is a prerequisite for the atoms to be at very precise positions in the aluminum lattice, at the very beginning of structural transformation, which may completely differ from that of the GP-zones atomic arrangements.
 ladder
ladderUeda, Hiroshi*; Onoda, Shigeki*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Yoshizawa, Daichi*; Morioka, Toshiaki*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Hagihara, Masato*; Soda, Minoru*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(14), p.140408_1 - 140408_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tsuru, Tomohito; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Ebihara, Kenichi; Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.1998_1 - 1998_8, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:82.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Age-hardening has been one and only process to achieve high strength aluminum alloys since unlike iron and titanium, pure aluminum does not have other solid phases during heat treatment. Highly-concentrated precipitations play therefore dominant role in mechanical properties and hydrogen embrittlement of aluminium alloys. It has been considered that the coherent interface between matrix and precipitation does not contribute to the crack initiation and embrittlement due to its coherency. Here, we discovered the origin of unprecedented quasi-cleavage fracture mode. Hydrogen partitioning at various defect sites is investigated comprehensively combined with experiment, theory and first-principles calculations. We demonstrate that despite low excess free volume, the aluminum-precipitation interface is more preferable trap site than void and grain boundary. The cohesivity of the interface deteriorates significantly with increasing occupancy while hydrogen atoms are trapped stably up to extremely high occupancy equivalent to spontaneous cleavage.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Materials Characterization, 158, p.109958_1 - 109958_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:78.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Characterization of precipitates in Al-Zn-Mg alloys, using a combination of electron diffraction, bright field transmission electron microscopy and atomic scale scanning transmission electron microscopy imaging revealed the presence of an unreported 
 orientation relationship between the
orientation relationship between the  -MgZn
-MgZn phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
phase and the Al lattice with the following orientation relationship (0001)
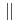 (120)
(120) and (
and (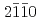 )
)
 (001)
(001)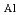 , plate on (120)
, plate on (120)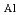 . The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90
. The precipitate interfaces were observed and analyzed along two projections 90 to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
to one-another. The precipitate coarsening was through the common thickening ledge mechanism. The ledges were significantly stepped along one lateral direction. An interface relaxation model using density functional theory was carried out to explain the precipitate behavior.
 Th nuclear clock isomer determined by absolute
Th nuclear clock isomer determined by absolute  -ray energy difference
-ray energy differenceYamaguchi, Atsushi*; Muramatsu, Haruka*; Hayashi, Tasuku*; Yuasa, Naoki*; Nakamura, Keisuke; Takimoto, Misaki; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Konashi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Makoto*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 123(22), p.222501_1 - 222501_6, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:89.11(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Matsuda, Kenji*; Yasumoto, Toru*; Bendo, A.*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Marioara, C. D.*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; et al.
Materials Transactions, 60(8), p.1688 - 1696, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:63.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Bendo, A.*; Maeda, Tomoyoshi*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lervik, A.*; Holmestad, R.*; Marioara, C. D.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Nunomura, Norio*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; et al.
Philosophical Magazine, 99(21), p.2619 - 2635, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:82.72(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lee, S.*; Nunomura, Norio*; Shimano, Tomoki*; Bendo, A.*; Watanabe, Katsumi*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 774, p.405 - 409, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.96(Chemistry, Physical) hydrogen partitioning control
hydrogen partitioning controlToda, Hiroyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Matsuda, Kenji*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Su, H.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 105(2), p.240 - 253, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 156, p.368 - 375, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:78.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The segregation of multiple hydrogen atoms along aluminum (Al) grain boundaries (GBs) and fracture surfaces (FSs) was investigated through first-principles calculations considering the characteristics of GBs. The results indicate that hydrogen segregation is difficult along low-energy GBs. The segregation energy of multiple hydrogen atoms along GBs and FSs and the cohesive energy was obtained for three types of high-energy Al GBs. With increasing hydrogen segregation along the GBs, the cohesive energy of the GB decreases and approaches zero with no decrease in GB segregation energy. The GB cohesive energy decreases in parallel with the volume expansion of the region of low electron density along the GB.
Bendo, A.*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Lee, S.*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake
Materialia, 3, p.50 - 56, 2018/11
 precipitate in Al-Mg-Zn alloys
precipitate in Al-Mg-Zn alloysTsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Computational Materials Science, 148, p.301 - 306, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:82.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of high strength 7xxx series Al alloys has been recognized as the critical issues in the practical use of Al alloys. Focusing on the interface between MgZn precipitates and an Al matrix, which is considered as one of the important segregation sites in these alloys, we investigated the stable
precipitates and an Al matrix, which is considered as one of the important segregation sites in these alloys, we investigated the stable  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al interface, and the possible hydrogen trap sites in MgZn
-Al interface, and the possible hydrogen trap sites in MgZn and at the
and at the  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al interface via first-principles calculation. Most of the interstitial sites inside the MgZn
-Al interface via first-principles calculation. Most of the interstitial sites inside the MgZn crystal were not possible trap sites because their energy is relatively higher than that of other trap sites. The trap energy of the most favorable site at the
crystal were not possible trap sites because their energy is relatively higher than that of other trap sites. The trap energy of the most favorable site at the  -MgZn
-MgZn -Al is approximately -0.3 eV/H, which is more stable that of the interstitial site at the grain boundary. The interface between MgZn
-Al is approximately -0.3 eV/H, which is more stable that of the interstitial site at the grain boundary. The interface between MgZn and Al is likely to be a possible trap site in Al alloys.
and Al is likely to be a possible trap site in Al alloys.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Nishihara, Kenji; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inoue, Akira; Sugawara, Takanori; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Sasa, Toshinobu; Obayashi, Hironari; Yamaguchi, Kazushi; Kikuchi, Masashi*
JAEA-Technology 2015-051, 47 Pages, 2016/03
This report summarizes fabrication and test results of a testing equipment for fuel cooling that is a component of the testing equipment for remote-handling of highly-radioactive MA fuels in the transmutation physics experimental facility (TEF-P) planned in the J-PARC. Evaluation formula of pressure drop and temperature increase used in the design of TEF-P was validated by the test, and, feasibility of cooling concept was confirmed.
 O
O thin films on Si (100) by ion beam sputter deposition
thin films on Si (100) by ion beam sputter depositionMao, W.*; Fujita, Masaya*; Chikada, Takumi*; Yamaguchi, Kenji; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*; Matsuzaki, Hiroyuki*
Surface & Coatings Technology, 283, p.241 - 246, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.89(Materials Science, Coatings & Films)Single-phase nanocrystalline thin films of Er O
O (440) has been first prepared using Si (100) substrates by ion beam sputter deposition at 973 K at a pressure of
(440) has been first prepared using Si (100) substrates by ion beam sputter deposition at 973 K at a pressure of  10
10 Pa and
Pa and 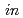 -
-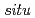 annealing at 1023 K at a pressure of
annealing at 1023 K at a pressure of  10
10 Pa. Er silicides formed during the deposition are eliminated via the annealing, which results in the single phase and the smooth surface of the Er
Pa. Er silicides formed during the deposition are eliminated via the annealing, which results in the single phase and the smooth surface of the Er O
O thin films. The epitaxial relationship between Si (100) and Er
thin films. The epitaxial relationship between Si (100) and Er O
O (110) is clarified by X-ray diffraction and reflection high energy electron diffraction.
(110) is clarified by X-ray diffraction and reflection high energy electron diffraction.