Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:184 Percentile:99.44(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.7(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Ichimura, Makoto*; Higaki, Hiroyuki*; Kakimoto, Shingo*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Nemoto, Tatsuki*; Katano, Makoto*; Ishikawa, Masao; Moriyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Takahiro
Nuclear Fusion, 48(3), p.035012_1 - 035012_7, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:83.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In this paper, experimental observations of spontaneously excited waves in the ion cyclotron range of frequency (ICRF) on JT-60U are described. The fluctuations in ICRF are driven by the presence of non-thermal ion distribution in magnetic confinement plasmas. Two types of magnetic fluctuations are detected: one is due to high energy D ions from neutral beam injections and the other is due to fusion products (FPs) of  He and T ions. These fluctuations have been reported as ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) in the burning plasma experiments on large tokamaks. This paper describes the first measurement of the spatial structures of the excited modes in the poloidal and toroidal directions. It is confirmed by using ICRF antennas as magnetic probes that all modes excited spontaneously have magnetic components and couple to the antenna straps. The modes due to D ions have small toroidal wave number
He and T ions. These fluctuations have been reported as ion cyclotron emissions (ICEs) in the burning plasma experiments on large tokamaks. This paper describes the first measurement of the spatial structures of the excited modes in the poloidal and toroidal directions. It is confirmed by using ICRF antennas as magnetic probes that all modes excited spontaneously have magnetic components and couple to the antenna straps. The modes due to D ions have small toroidal wave number 
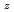 and will behave as electrostatic waves. On the while, the measurement of finite
and will behave as electrostatic waves. On the while, the measurement of finite 
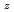 in the modes due to FP ions supports the excitation of the Alfv
in the modes due to FP ions supports the excitation of the Alfv n waves is the possible origin of FP-ICEs. It is also confirmed that the excited modes due to FP ions have different wave structures and are suggested to be in the different branch of the Alfv
n waves is the possible origin of FP-ICEs. It is also confirmed that the excited modes due to FP ions have different wave structures and are suggested to be in the different branch of the Alfv n waves, that is, the fast Alfv
n waves, that is, the fast Alfv n wave and the slow Alfv
n wave and the slow Alfv n wave. Frequency peaks due to FP ions are sometimes split into doublet shape as observed in JET experiments. The phase differences of both peaks are measured and indicate that two waves are traveling in both toroidal directions. Both beam-driven ICEs and FP-ICEs are observed and those spatial structures are obtained on JT-60U.
n wave. Frequency peaks due to FP ions are sometimes split into doublet shape as observed in JET experiments. The phase differences of both peaks are measured and indicate that two waves are traveling in both toroidal directions. Both beam-driven ICEs and FP-ICEs are observed and those spatial structures are obtained on JT-60U.
Yamasaki, Chisato*; Murakami, Katsuhiko*; Fujii, Yasuyuki*; Sato, Yoshiharu*; Harada, Erimi*; Takeda, Junichi*; Taniya, Takayuki*; Sakate, Ryuichi*; Kikugawa, Shingo*; Shimada, Makoto*; et al.
Nucleic Acids Research, 36(Database), p.D793 - D799, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:71.25(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Here we report the new features and improvements in our latest release of the H-Invitational Database, a comprehensive annotation resource for human genes and transcripts. H-InvDB, originally developed as an integrated database of the human transcriptome based on extensive annotation of large sets of fulllength cDNA (FLcDNA) clones, now provides annotation for 120 558 human mRNAs extracted from the International Nucleotide Sequence Databases (INSD), in addition to 54 978 human FLcDNAs, in the latest release H-InvDB. We mapped those human transcripts onto the human genome sequences (NCBI build 36.1) and determined 34 699 human gene clusters, which could define 34 057 protein-coding and 642 non-protein-coding loci; 858 transcribed loci overlapped with predicted pseudogenes.
Ichimura, Makoto*; Higaki, Hiroyuki*; Kakimoto, Shingo*; Yamaguchi, Yusuke*; Nemoto, Kenju*; Katano, Makoto*; Kozawa, Isao*; Muro, Taishi*; Ishikawa, Masao; Moriyama, Shinichi; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 51(2T), p.150 - 153, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)In magnetically confined plasmas, fluctuations in the ion cyclotron range of frequency (ICRF) will be driven by the presence of non-thermal ion energy distribution. In strong ICRF heating experiments on the GAMMA 10 tandem mirror, plasmas with a strong temperature anisotropy have been formed. Alfven-ion-cyclotron (AIC) modes are spontaneously excited due to strong temperature anisotropy. High-energy ions are trapped in the local mirror and will form the velocity distribution with the strong anisotropy. To study the relation among the AIC modes, ICEs and beam-driven electrostatic instabilities with non-thermal energy distribution is the main purpose of this work. When the NBs are injected, the magnetic fluctuations due to injected beams and FP ions are detected by ICRF antennas used as pickup loops on JT-60U. The wave excitation near ion cyclotron and its higer harmonic frequencies are studied experimentally and theoretically in plasmas with non-thermal ion energy distribution.
Akai, Masanobu; Ito, Nobuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Tanaka, Tadao; Iida, Yoshihisa; Nakayama, Shinichi; Inagaki, Shingo*
JAERI-Tech 2004-058, 47 Pages, 2004/09
Geochemistry Research Equipment for TRU Waste Elements has been installed in Back-end Cycle Key Elements Research Facility (BECKY) of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Safety Engineering Research Facility (NUCEF). This equipment is designed to study geochemical behavior of TRU elements and other radionuclides contained in TRU waste (TRU waste elements) and to acquire data for safety assessments of radioactive wastes disposal. The equipment consists of anaerobic glove box systems, aerobic glove box systems equipped with built-in barrier performance testing apparatus, and analytical instruments. This report describes principles, structure, performance and safety designs of each component of the equipment, and results of research performed in the equipment.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Negishi, Kumi; Ebashi, Katsuhiro; Inagaki, Shingo*; Shibata, Mitsunobu*; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
JAERI-Conf 2004-011, p.139 - 140, 2004/07
Uncertainties should be quantitatively assessed in a long-term assessment of radioactive waste disposal. We focus our experimental efforts on parameters that induce major uncertainties in the radionuclide migration analysis and that have not been quantitatively understood. Solubility of radionuclides, diffusion in bentonite buffer material and sorption on rocks were investigated to quantify the uncertainties associated with the parameters and to minimize the uncertainties.
Honda, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Shingo*
JNC TJ8400 2003-059, 55 Pages, 2004/01
In general, it is difficult to evaluate non-destructively the corroded states of iron-based archaeological remains, as they are fully covered by thick rust formed under ground during a long period over a hundred years. The purpose of this study is to estimate the corrosion amounts of such remains with using X-ray CT and summarize the longevity of iron in soil. It has been clarified that rust and residual metallic iron can be quantitatively divided by this technique. Therefore, it is supposed that the amounts of corrosion can be figured out on the basis of thickness and density of rust. Eight remains dug out at seven relics were analyzed. The burial periods in soil were estimated to be from 1000 to 1500 years. Metallic iron remained in six remains, and the corrosion amounts were figured out to be from 0.5 to 3 mm in these periods. In addition, the soil environments of relics were analyzed, and the relation between corrosion behaviors and environmental factors was discussed. The rust was composed of outer goethite and inner magnetite layers in normally oxidizing conditions. On the other hand, a few samples were buried in slightly oxidizing environments, and these were covered by magnetite single layers. The corrosion amount of remains in such an environment was small compared to the others.
Honda, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Shingo*
JNC TJ8400 2003-012, 89 Pages, 2003/01
The corrosion behaviors of iron-based archaeological remains, which were dug out in six relics in Aomori-ken and Izumotalsya-keidai-iseki, were analyzed mainly with using X-ray CT. Several samples were cut and investigated on the details of metals and oxide films. The soils were also analyzed on redox-potential, resistance, chemical contents, and others. The results indicate that metal remains in 7/14 samples. The corrosion amounts of objects of Aomori-ken were estimated to be from 1 to 4mm during 400 - 1000 years. The environments were supposed to be oxidizing. On the other hands, it is supposed that two objects in Izumotaisya-keidai-iseki were in a reducing condition. The corrosion amounts were 0.5 - 2 mm. Furthermore, the corrosion behavior of the cast gas-pipe, which had been buried for about 130 years, were evaluated. By analyzing analysis data of soil, the environment is estimated to be weak oxidizing, and the maximum graphitic corrosion depth was about 7mm.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Ueno, Kenichi; Honda, Takashi*; Yamaguchi, Shingo*; Yui, Mikazu
9th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM '03), 0 Pages, 2003/00
None
*; Tanigawa, Shingo*; *; Yamaguchi, Katsuhisa; *; *; *
PNC TN9410 88-141, 159 Pages, 1988/09
The structural analyses of the core support plate have been applied to study thermal transfomation behaviors and the differences of the movement by changing analytical model, under anticipated transient without scram (ATWS) conditions of FBR. The analyses have been performed for 1000 MWe class loop type fast breeder reactor using a structural analysis code FINAS. The thermal-hydraulic results, which have been performed to ATWS conditions using a plant system code, were used as the thermal boundary conditions to the calculation. The scope of the analyses included a whole section of reactor vessel and the dead load of core assemblies was also considered. Following results were obtained from these studies. (1)The thermal transformation of a upper core support plate can be evaluated according to the free expansion behavior owing to the temperature change of core support plate itself. (2)The radial restriction due to core subassemblies has much influence on the axial bend of the core support plate. (3)There are some differences to the transformation results between by the whole model and by the one dimensional model during the thermal transient is large. Another analysis will be needed, however, about the reactivity change according to the displacement of the core structure.
*; Haraguchi, Tetsuharu*; *; Tanigawa, Shingo*; Yamaguchi, Katsuhisa
PNC TN9410 88-107, 121 Pages, 1988/09
In the studies using PLANDTL, it would be planned to valid the thermal-hydraulic analysis codes which were developed each for whole system, plenum and subassembly, and also to evaluate the reactor plant in the future using these codes. SSC-L is to be as the main code in these studies and is used for design analysis through test analysis. In the first step of this study, model development and modification of SSC-L has been achieved for PLANDTL and predictive analyses have been applied as to validate the models and examine the design of PLANDTL. The estimated transient curves have been obtained about flow rate and temperatures at subassembly and loop of PLANDTL. As a result, the design conditions have been given to be able to perform the programmed tests. It have been validated that the conditions of tests would be within the design value, and the characteristics of PLANDTL and operational conditions have been obtained from the predictive analyses using design data of the plant. The modification and validation of SSC-L will be applied using the results of various kinds of functional tests, and test analyses will be performed in future.
Motoki, Chika*; Furuta, Koya*; Yamaguchi, Kazuya*; Saito, Shingo*; Fujiwara, Hideki*; Shibano, Koya; Sumi, Mika; Kageyama, Tomio
no journal, ,
Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) of uranium and plutonium are necessary to perform Isotope Dilution Mass Spectrometry (IDMS) for nuclear material accountancy. Qualified Pu standard Material is a highly precious resource on a global scale. Therefore domestic securement of the material is strongly desired. JNFL entrust the development of preparation technique of Pu standard material to JAEA. Recently, purified Pu nitrate solution from MOX powder stored at JAEA was characterized. The framework for certification is presented in this brief.
Shibano, Koya; Okazaki, Hiro; Sumi, Mika; Kayano, Masashi; Matsuyama, Kazutomi; Kageyama, Tomio; Fujiwara, Hideki*; Furuta, Koya*; Yamaguchi, Kazuya*; Saito, Shingo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tomiyama, Shingo*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Odashiro, Kana*; Yamaguchi, Kohei*; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takir, D.*; Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; et al.
no journal, ,
JAXA spacecraft and sample return mission Hayabusa2 has arrived at the near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, which is classified a primitive carbonaceous object. Here we report recent results of near-infrared spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. The observations provide direct measurements of the surface composition of Ryugu and context for the returned samples. NIRS3 has detected a weak and narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micrometer across entire observed surface. This absorption feature is attributed to the presence of OH-bearing minerals. The NIRS3 observations also revealed that Ryugu is the darkest object to be observed up-close by a visiting spacecraft. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are consistent with thermally-and/or shock-metamorphosed, and/or carbon-rich space-weathered primitive and hydrated carbonaceous chondrites.