Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10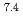 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
 U accumulations in
U accumulations in 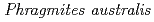 naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophores
naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophoresNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
Minerals (Internet), 11(12), p.1337_1 - 1337_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mine drainage is a vital water problem in the mining industry worldwide because of the heavy metal elements and low pH. Rhizofiltration using wetland plants is an appropriate method to remove heavy metals from the water via accumulation in the rhizosphere. 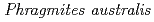 is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,
is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,  has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that
has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that  accumulated Fe, Mn, and
accumulated Fe, Mn, and  U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around
U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around  roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as
roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as 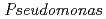 spp. and
spp. and 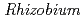 spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several
spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several 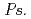 spp. and
spp. and 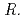 spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as
spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as 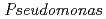 spp. and
spp. and 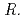 spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of
spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of  , might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in
, might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in  , and
, and 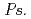 spp. and
spp. and 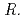 spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamaji, Keiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR 2019) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2019/05
To decommission the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP), it is necessary to estimate the current status of fuel debris and predicate the possible change under various condition. Some microorganisms may enter the plant due to the seawater injection after accident and future defueling activity. In this study, microbial influence on fuel debris under aerobic condition was experimentally investigated. By culturing some bacteria in the presence of simulant fuel debris in liquid medium, the microbial degradation of fuel debris was observed.
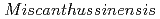 via increasing the aluminium detoxicants, chlorogenic acid and oosporein
via increasing the aluminium detoxicants, chlorogenic acid and oosporeinHaruma, Toshikatsu*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Ogawa, Kazuyoshi*; Masuya, Hayato*; Sekine, Yurina; Kozai, Naofumi
PLOS ONE (Internet), 14(2), p.e0212644_1 - e0212644_16, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:76.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Miscanthus sinensis Andersson is a pioneer plant species that grows naturally at mining sites. 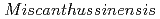 can detoxify aluminium (Al) by producing phytosiderophores. Root-endophytic Chaetomium cupreum, which produces microbial siderophores, enhances Al tolerance in M. sinensis. We identified the siderophore produced by C. cupreum as oosporein. It was revealed that oosporein could detoxify Al. Inoculation test of C. cupreum onto M. sinensis in acidic mine soil showed that C. cupreum promoted seedling growth, and enhanced Al tolerance.
can detoxify aluminium (Al) by producing phytosiderophores. Root-endophytic Chaetomium cupreum, which produces microbial siderophores, enhances Al tolerance in M. sinensis. We identified the siderophore produced by C. cupreum as oosporein. It was revealed that oosporein could detoxify Al. Inoculation test of C. cupreum onto M. sinensis in acidic mine soil showed that C. cupreum promoted seedling growth, and enhanced Al tolerance.
 Cs and Mn accumulator plant,
Cs and Mn accumulator plant, 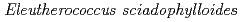 , increase
, increase  Cs and Mn desorption in the soil
Cs and Mn desorption in the soilYamaji, Keiko*; Nagata, Satoshi*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Kozaki, Tamotsu*; Watanabe, Naoko*; Namba, Kenji*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 153, p.112 - 119, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:56.65(Environmental Sciences)Of the 463 strains that we isolated, 107 (23.1%) produced the siderophores. We found  Cs and Mn desorption concomitant with Al and Fe desorption. These results suggest that root endophytes of
Cs and Mn desorption concomitant with Al and Fe desorption. These results suggest that root endophytes of  Cs accumulator plant produce siderophores, resulting in the desorption of
Cs accumulator plant produce siderophores, resulting in the desorption of  Cs from the contaminated soil collected at Fukushima, Japan.
Cs from the contaminated soil collected at Fukushima, Japan.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamaji, Keiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
no journal, ,
Fuel debris was formed in severe accident in nuclear power plant. After the confirmation of microorganisms in water in damaged plant, it is necessary to consider the element migration of fuel debris. Here, some widespread bacteria were applied. By cultivation with simulant fuel debris, the migration mechanism was estimated.
 U) and heavy metal (Fe, Mn) accumulation mechanism in phragmites australis influenced by root endophytic bacteria
U) and heavy metal (Fe, Mn) accumulation mechanism in phragmites australis influenced by root endophytic bacteriaNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Doyama, Kohei*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kazuya; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamaji, Keiko*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Nagayasu, Takaaki; Haruma, Toshikatsu; Tanaka, Kazuya; Masuya, Hayato*; Habe, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Tatsuki; Guido-Garcia, F.; Kozai, Naofumi; Zhang, S.*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Yu, Q.*; Grambow, B.
no journal, ,
To understand bacterial ability to dissolve clay minerals, we isolated siderophore-producing bacteria from white clover roots grown in south Osaka, Japan. The ability to produce siderophores was evaluated by CAS plate method. llite, biotite, vermiculite and nontronite were used for testing as clay minerals. Three different bacteria strains were cultivated. Bacteria cells were centrifuged and washed before inoculation tests. Fifty mg dry weight of bacteria were inoculated into 100 mL modified Balland media and 100 mg of each clay mineral added. The suspension was sampled and new media was added. The concentrations of iron, aluminium and silicon were determined by ICP-OES. The presence of organic molecules was determined by SEC-ICP-OES. The peaks of siderophores were determined using the 405 nm absorbance. As a result, siderophore producing bacteria are able to dissolve clay. This suggests that the effect of siderophore on cesium dissolution is an indirectly process.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Grambow, B.
no journal, ,
Radium-226, a descendant nuclide of  U, is of serious concern in Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center because its radioactive concentration in mining wastewater exceeds the effluent standard. In this study, we examined Ba and Sr adsorption on biogenic Mn oxide as a preliminary surrogate for Ra adsorption. Both Ba and Sr show the dependence of adsorption on NaCl concentration. Overall, Ba gave an order of magnitude higher Kd values than Sr. Adsorption behavior of Ra would be similar to that of Ba in terms of ionic radius. Barium showed Kd value greater than 10
U, is of serious concern in Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center because its radioactive concentration in mining wastewater exceeds the effluent standard. In this study, we examined Ba and Sr adsorption on biogenic Mn oxide as a preliminary surrogate for Ra adsorption. Both Ba and Sr show the dependence of adsorption on NaCl concentration. Overall, Ba gave an order of magnitude higher Kd values than Sr. Adsorption behavior of Ra would be similar to that of Ba in terms of ionic radius. Barium showed Kd value greater than 10 in 10 mM NaCl solution, similar to the ionic strength of the fresh water system in the Ningyo-toge center. Therefore, it is expected that the biogenic Mn can work effectively for removal of Ra from mining wastewater.
in 10 mM NaCl solution, similar to the ionic strength of the fresh water system in the Ningyo-toge center. Therefore, it is expected that the biogenic Mn can work effectively for removal of Ra from mining wastewater.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Grambow, B.
no journal, ,
Radium-226 is of serious concern in Ningyo-toge Environmental Engineering Center because its radioactive concentration in mining wastewater exceeds the effluent standard. In this study, we examined Ba and Sr adsorption on biogenic Mn oxide as a preliminary surrogate for Ra adsorption. Both Ba and Sr show the dependence of adsorption on NaCl concentration. Overall, Ba gave an order of magnitude higher Kd values than Sr. Adsorption behavior of Ra would be similar to that of Ba in terms of ionic radius. Barium showed Kd value greater than 10 mL/g in 10 mM NaCl solution, similar to the ionic strength of the fresh water system in the Ningyo-toge center. Therefore, it is expected that the biogenic Mn can work effectively for removal of Ra from mining wastewater.
mL/g in 10 mM NaCl solution, similar to the ionic strength of the fresh water system in the Ningyo-toge center. Therefore, it is expected that the biogenic Mn can work effectively for removal of Ra from mining wastewater.
Guido-Garcia, F.; Kimura, Tatsuki*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; David, K.*; Grambow, B.*; Haruma, Toshikatsu; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
Mushrooms (fungi) accumulate radiocesium from soil and believed to control Cs circulation in forest. To elucidate mechanism of fungi-involving radiocesium circulation in forest, we investigated dissolution of mineral by a fungus mycelia (Phlebiopsis gigantean) and local concentration ratios of cesium to potassium, Cs/K, in fruit body of Lentinula edodes (shiitake). The tested fungus has higher ability than a siderophore-producing bacterium to dissolve minerals. Most of the Fe dissolved from minerals were found to be not stable complexes with organic substances. Cs/K values were almost constant in same fruit body specimen of shiitake, revealing that cesium is stored in proportion to potassium at any locations of a shiitake fruit body and there is no specific binding site for cesium in shiitake.
Habe, Hiroshi*; Inaba, Tomohiro*; Aoyagi, Tomo*; Aizawa, Hidenobu*; Sato, Yuya*; Hori, Tomoyuki*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Cai, H.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Jiang, X.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Haruma, Toshikatsu; Takahashi, Junko*; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Jiang, Q.*; Tamura, Kenji*; Asano, Maki*; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Takahashi, Junko*; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
In the former open-pit mining area of Ningyo-toge mine, 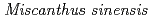 is the dominant in its vegetation and the vegetation succession has been suspended for 2 decades. The present work was conducted to understand the soil micromorphological characteristics on this unusual area. We set two sampling sites (site A and site B) at the former open-pit mining area. Site A is in
is the dominant in its vegetation and the vegetation succession has been suspended for 2 decades. The present work was conducted to understand the soil micromorphological characteristics on this unusual area. We set two sampling sites (site A and site B) at the former open-pit mining area. Site A is in 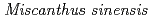 dominant vegetation, and site B is in
dominant vegetation, and site B is in  dominant vegetation. Soil samples were taken from each horizon of the soil profiles for chemical analysis at the sites, and thin sections were obtained from the soil core samples (0-5 cm, 10-15 cm, 30-35 cm depth of site A and Site B, respectively). The BC horizon of site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. And the soil thin section observation showed that the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the lower layer is not fully developed and forms a block structure. The content of the five forms of Fe and Mn are residual form
dominant vegetation. Soil samples were taken from each horizon of the soil profiles for chemical analysis at the sites, and thin sections were obtained from the soil core samples (0-5 cm, 10-15 cm, 30-35 cm depth of site A and Site B, respectively). The BC horizon of site B has a lower Eh, which may be due to the less voids in the underlying soil, which results in seasonal accumulation of water. And the soil thin section observation showed that the 0-5cm of soil is in good structure, but the lower layer is not fully developed and forms a block structure. The content of the five forms of Fe and Mn are residual form  oxide-bound form
oxide-bound form  organic-bound form
organic-bound form  carbonate-bound form
carbonate-bound form  exchangeable form in this study site.
exchangeable form in this study site.
 influenced by root endophytic bacteria
influenced by root endophytic bacteriaNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Yamaji, Keiko*; Haruma, Toshikatsu; Doyama, Kohei*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamaji, Keiko*; Nakamoto, Yukihiro*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Doyama, Kohei*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Tanaka, Kazuya; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Doyama, Kohei*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 growing at the ore-sedimentary site; Iron plaque formation possibly related to endophytic bacteria
growing at the ore-sedimentary site; Iron plaque formation possibly related to endophytic bacteriaNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Kozai, Naofumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English