Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in air
O in the film on Fe oxidized at high temperature in airHaruna, Takumi*; Yamamoto, Tatsuya*; Miyairi, Yoji*; Shibata, Toshio*; Taniguchi, Naoki; Sakamaki, Keiko; Tachikawa, Hirokazu*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 64(5), p.201 - 206, 2015/05
Diffusion coefficients of D O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D
O in the films was determined in order to estimate corrosion rate of carbon steel for the overpack in ground water. Fe plates were heated to form oxide films. The films were characterized with XRD and SEM. After that, the specimen was contacted with D O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D
O for 5184 ks, followed by subjected to TDS to obtain an amount of D O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe
O absorbing into the film. As a result, single-layered film of Fe O
O was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe
was formed at 573 and 723 K, and double-layered film of Fe O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D
was formed at 873 K. It was found that an amount of D O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D
O in the film correlated linearly with a square root of the absorption period, and that the amount was steady for a long period. From the results and Fick's second law, diffusion coefficients of D O was determined as 9.7
O was determined as 9.7 10
10 cm
cm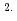 s
s for the Fe
for the Fe O
O film, and 5.5
film, and 5.5 10
10 cm
cm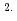 s
s to 2.2
to 2.2 10
10 cm
cm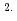 s
s for Fe
for Fe O
O film.
film.
Ishino, Masahiko; Kado, Masataka; Shinohara, Kunio*; Yamamoto, Yoshimasa*; Hirai, Itaru*; Kishimoto, Maki; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE Europe Optics + Optoelectronics 2011, Vol.8139, p.81390R_1 - 81390R_8, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Optics)Ultra thin gold films are favorable laser plasma targets for a soft X-ray microscopy, because the thin films emit intense soft X-rays at the wavelength of water window region. Using rear side emissions, the distance between the X-ray source and the specimens can be reduced so that the X-ray flux on specimens increases. The microscope system can be designed to be compact when the specimen holder and X-ray source are combined in one piece. The biological specimen holder combined with an ultra thin film target has been developed. This X-ray microscope system needs not any X-ray optics which causes a decrease in X-ray photons for imaging. X-ray images of hydrated living cells have been obtained successfully by use of the newly developed specimen holder. Specimen holder combined with plasma X-ray source will be a key component of a compact soft X-ray microscope using in a laboratory.
Ishino, Masahiko; Kado, Masataka; Kishimoto, Maki; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; Yamamoto, Yoshimasa*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kado, Masataka; Ishino, Masahiko; Kishimoto, Maki; Shinohara, Kunio*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; Yamamoto, Yoshimasa*; Kinjo, Yasuhito*
no journal, ,
Contact soft X-ray microscopes with laser plasma X-ray sources are anticipated technology to be able to observe live hydrated biological cells with high spatial resolution. However there were no works reported which identified specific organelles clearly, because the obtained X-ray images are too complicated due to overlapping of cell structures. We have observed the same biological cells with both of a contact soft X-ray microscope and a confocal laser microscope and compared images obtained with both microscopes in order to identify organelles obtained with the soft X-ray microscope. As the results we succeeded to identify actin filaments and mitochondria clearly and found that the organelles obtained with the soft X-ray microscope were more detailed than those with the confocal laser microscope.