Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashi, Koichi*; Lederer, M.*; Fukumoto, Yohei*; Goto, Masashi*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Happo, Naohisa*; Harada, Masahide; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oikawa, Kenichi; Oyama, Kenji*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 120(13), p.132101_1 - 132101_6, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 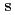 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 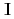 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 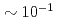 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (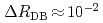 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Li, Y.; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Itabashi, Yu*; Yamamoto, Masato*; Kanto, Yasuhiro*; Suzuki, Masahide*; Miyamoto, Yuhei*
JAEA-Review 2020-011, 130 Pages, 2020/09
For the improvement of the structural integrity assessment methodology on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs), the probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL has been developed and improved in Japan Atomic Energy Agency based on the latest knowledge. The PASCAL code evaluates the failure probabilities and frequencies of Japanese RPVs under transient events such as pressure thermal shock considering neutron irradiation embrittlement. In order to confirm the reliability of the PASCAL as a domestic standard code and to promote the application of PFM on the domestic structural integrity assessments of RPVs, it is important to perform verification activities, and summarize the verification processes and results as a document. On the basis of these backgrounds, we established a working group, composed of experts on this field besides the developers, on the verification of the PASCAL module and the source program of PASCAL was released to the members of working group. This report summarizes the activities of the working group on the verification of PASCAL in FY2016 and FY2017.
Iguchi, Masahide; Morimoto, Masaaki; Chida, Yutaka*; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Nakajima, Hideo; Nakahira, Masataka; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Yamamoto, Akio*; Miyake, Takashi*; Sawa, Naoki*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 24(3), p.3801004_1 - 3801004_4, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:35.68(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Kubo, Junichi*; Rahman, N.*; Takahashi, Nobuaki; Kawai, Takahiko*; Matsuba, Go*; Nishida, Koji*; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Yamamoto, Masahide*
Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 112(3), p.1647 - 1652, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:62.54(Polymer Science)Aiming at improvement of mechanical and dielectric properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) we prepared composites of PVA and magnesium nitrate. It was found that the composites were very soft and rubber-like, and the glass transition temperature decreased with increasing the salt concentration. Wide-angle X-ray diffraction and small-angle X-ray scattering revealed that the crystallites of PVA were destroyed by the additive and it was a cause of the softening.
Shima, Shigeki*; Gasa, Shinichi*; Amano, Hikaru; Nagao, Seiya*; Yamamoto, Masayoshi*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*; Furukawa, Masahide*; Kimura, Hideki*; Kawamura, Hisao*
JAEA-Conf 2008-003, p.28 - 31, 2008/04
Concentrations of  I in surface seawater around Japan were approximately 2
I in surface seawater around Japan were approximately 2 10
10 atoms/L in literatures. However, the atomic ratio of iodine to cesium was ten times as high as that of the global fallout. The origin of
atoms/L in literatures. However, the atomic ratio of iodine to cesium was ten times as high as that of the global fallout. The origin of  I in the water columns seems to be difficult to be explained by only the global fallout. Discharge from European plants was one of the possible origins of iodine from the standpoint of air mass trajectory analysis. Concentration of
I in the water columns seems to be difficult to be explained by only the global fallout. Discharge from European plants was one of the possible origins of iodine from the standpoint of air mass trajectory analysis. Concentration of  I in rain water was 10 times higher than that in surface seawater. Anthropogenic inorganic iodine in surface seawater predominantly dissolves as an iodide ion (I
I in rain water was 10 times higher than that in surface seawater. Anthropogenic inorganic iodine in surface seawater predominantly dissolves as an iodide ion (I ).
).
Matsuda, Masahide*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Nakai, Kei*; Endo, Kiyoshi*; Kumada, Hiroaki; Kageji, Teruyoshi*; Matsumura, Akira*
Proceedings of 12th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy (ICNCT-12), p.40 - 42, 2006/10
To describe the failure patterns and survival seen with high-grade glioma treated with BNCT, the dose distribution and the clinical responses were retrospectively analyzed. BSH-based BNCT was performed in 12 patients with high-grade glioma (grade IV 7, grade III 5). The post-diagnosis median survival time of 12 patients was 19.8 months (range 3.3-47.2). Four cases of local control, 3 of local recurrence, 3 of distant intraparenchymal recurrence and 2 of subarachnoid dissemination were recorded. According to the analysis of the failure patterns, minimum GTV dose of 26 GyEq or more is necessary for local control.
Yamai, Hideki*; Konishi, Satoshi; Hara, Masahide*; Okuno, Kenji; Yamamoto, Ichiro*
Fusion Technology, 28(3), p.1591 - 1596, 1995/10
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Harada, Masahide; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Okudaira, Takuya*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Ino, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
In neutron fundamental physics, a study of correlation term  of a neutron spin s and a target nuclear spin
of a neutron spin s and a target nuclear spin 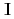 is important because the
is important because the  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving (TRNC) terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving (TRNC) terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 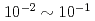 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We attempted to develop a polarized Xe target in a compact
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We attempted to develop a polarized Xe target in a compact  SEOP system and measure neutron polarizing ability caused by the
SEOP system and measure neutron polarizing ability caused by the  term at a 9.6 eV
term at a 9.6 eV  -wave resonance peak of
-wave resonance peak of  Xe, by detecting change
Xe, by detecting change 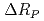 of a ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. As preliminary results, we observed a signified value of
of a ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. As preliminary results, we observed a signified value of 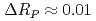 after demonstrating that our apparatus could distinguish Doppler broadening effect as systematic error.
after demonstrating that our apparatus could distinguish Doppler broadening effect as systematic error.