Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Kazami; Ogiwara, Norio*; Kuramochi, Masaya*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(4), p.359 - 364, 2023/07
In recent years, durable target is required according to increase of the beam power. To solve this problem, a liquid film was formed in vacuum and tested it as a target. An ethanol and a mercury were selected as liquid target materials, and we investigated whether the liquid sheet could be formed stably in a vacuum and how about the vacuum pressure. As a result, it was confirmed that the liquid films were stably formed in both case and the pressures with the films were about the vapor pressure of the materials.
Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Naruto, Kenichi*; Gondai, Yoji; Yamamoto, Masaya
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
The effectiveness evaluation of safety measures against severe accident is necessary for restart of experimental sodium-cooled fast reactor "Joyo" in Japan. These safety measures correspond to those in defense-in-depth (DiD) level 4. In the previous study, a level-1 probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) at power was performed to calculate frequencies of the accident sequences of failure of safety measures in DiD level 1 to 3, to identify dominant accident sequence groups, and to identify dominant accident sequence for selecting important accident sequences in each accident sequence group which are needed for implementing the effectiveness evaluation of safety measures in DiD level 4. Based on this, the present study implemented level-1 PRA at power to show quantitatively reduction of those occurrence frequency by the safety measure in the DiD level 4. As the result, the frequency of each accident sequence group decreased significantly, and total frequency of the accident sequence groups decreased to about 1 10
10 /reactor-year which is about 1/1000 times the one estimated in the previous study. The protected loss of heat sink was the largest contributor in all the accident groups and a dominant accident sequence in each accident group was also identified in this study.
/reactor-year which is about 1/1000 times the one estimated in the previous study. The protected loss of heat sink was the largest contributor in all the accident groups and a dominant accident sequence in each accident group was also identified in this study.
Fujita, Natsuko; Miyake, Masayasu; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Ishii, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishio, Tomohiro*; Ogawa, Yumi; Yamamoto, Yusuke; Kimura, Kenji; et al.
Dai-23-Kai AMS Shimpojiumu Hokokushu, p.1 - 4, 2022/12
The JAEA-AMS-TONO facility at the Tono Geoscience Center, JAEA has three accelerator mass spectrometers. We report the present status of the JAEA-AMS-TONO.
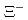 atomic X-ray spectroscopy using a counter-emulsion hybrid method
atomic X-ray spectroscopy using a counter-emulsion hybrid methodFujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Kim, S.; Nanamura, Takuya; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; Yamamoto, Takeshi; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(12), p.123D01_1 - 123D01_17, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)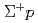 elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/c
elastic scattering in the momentum range 0.44-0.80 GeV/cNanamura, Takuya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Naruki, Megumi; Sato, Susumu; Sako, Hiroyuki; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2022(9), p.093D01_1 - 093D01_35, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:67.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -state of a
-state of a  hypernucleus,
hypernucleus, 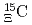
Yoshimoto, Masahiro*; Fujita, Manami; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ichikawa, Masaya; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2021(7), p.073D02_1 - 073D02_19, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:81.3(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yoshida, Junya; Akaishi, Takaya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Kim, S.; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011112_1 - 011112_8, 2021/03
 identification method by the
identification method by the 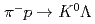 reaction for a
reaction for a 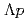 scattering experiment at J-PARC
scattering experiment at J-PARCSakao, Tamao*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011133_1 - 011133_6, 2021/03
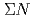 interaction from the
interaction from the 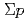 scattering experiment at J-PARC
scattering experiment at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1643, p.012174_1 - 012174_6, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.57(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nishino, Hiroyuki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Naruto, Kenichi*; Gondai, Yoji; Yamamoto, Masaya; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2020 (ASRAM 2020) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2020/11
The objective of this study is to evaluate the occurrence frequency of accident sequences which may lead to core damage if provisions in defense in depth (DiD) level 1 to 3 are the only safety measures. For this objective, the existing safety measures in this SFR are categorized into those for the DiD level 1-3 and those for the DiD level 4. The safety measures for the DiD level 1-3 are as follows; (1) main reactor shutdown system, (2) double boundary structure in the primary main and auxiliary cooling system and the reactor vessel, which maintain the reactor coolant level sufficient for coolant circulation in the primary main cooling system, (3) decay heat removal in a forced circulation mode. Accident sequences are categorized into typical SFR-specific groups and station blackout (SBO) in this study. The SFR-specific groups are unprotected loss of flow, unprotected transient over power, unprotected loss of heat sink, loss of reactor level, and protected loss of heat sink (PLOHS). The occurrence frequency of these accident sequence groups was quantified to identify major contributors. As the result, PLOHS excluding SBO was indicated as the dominant contribution of 80% or more in the all accident sequence groups and the annual occurrence frequency of the PLOHS was 1.0E-4 order of magnitude. For the PLOHS, loss of offsite power (LOOP) was indicated as major contribution of 30% in initiating events. In the accident sequences of the PLOHS initiated from LOOP, a dominant sequence was combination of common cause failure of primary pumps in the main cooling system and failure-to-start of the auxiliary cooling system after LOOP. The second dominant contribution (15% or more) in the all accident sequence groups is PLOHS in SBO (i.e., decay heat removal failure due to SBO). Each of the other accident sequence groups was 1%.
Yoshida, Masafumi; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Grisham, L. R.*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.616 - 619, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.3(Nuclear Science & Technology)In JT-60 Super Advanced for the fusion experiment, 22A, 100s negative ions are designed to be extracted from the world largest ion extraction area of 450 mm  1100 mm. One of the key issues for producing such as high current beams is to improve non-uniform production of the negative ions. In order to improve the uniformity of the negative ions, a tent-shaped magnetic filter has newly been developed and tested for JT-60SA negative ion source. The original tent-shaped filter significantly improved the logitudunal uniformity of the extracted H
1100 mm. One of the key issues for producing such as high current beams is to improve non-uniform production of the negative ions. In order to improve the uniformity of the negative ions, a tent-shaped magnetic filter has newly been developed and tested for JT-60SA negative ion source. The original tent-shaped filter significantly improved the logitudunal uniformity of the extracted H ion beams. The logitudinal uniform areas within a
ion beams. The logitudinal uniform areas within a  10 deviation of the beam intensity were improved from 45% to 70% of the ion extraction area. However, this improvement degrades a horizontal uniformity. For this, the uniform areas was no more than 55% of the total ion extraction area. In order to improve the horizontal uniformity, the filter strength has been reduced from 660 Gasus
10 deviation of the beam intensity were improved from 45% to 70% of the ion extraction area. However, this improvement degrades a horizontal uniformity. For this, the uniform areas was no more than 55% of the total ion extraction area. In order to improve the horizontal uniformity, the filter strength has been reduced from 660 Gasus cm to 400 Gasus
cm to 400 Gasus cm. This reduction improved the horizontal uniform area from 75% to 90% without degrading the logitudinal uniformity. This resulted in the improvement of the uniform area from 45% of the total ion extraction areas. This improvement of the uniform area leads to the production of a 22A H
cm. This reduction improved the horizontal uniform area from 75% to 90% without degrading the logitudinal uniformity. This resulted in the improvement of the uniform area from 45% of the total ion extraction areas. This improvement of the uniform area leads to the production of a 22A H ion beam from 450 mm
ion beam from 450 mm  1100 mm with a small amount increase of electron current of 10%. The obtained beam current fulfills the requirement for JT-60SA.
1100 mm with a small amount increase of electron current of 10%. The obtained beam current fulfills the requirement for JT-60SA.
Kawahara, Hirotaka; Yamamoto, Masaya; Tomita, Etsuo; Takamatsu, Misao
JAEA-Technology 2012-030, 50 Pages, 2012/09
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, in-vessel observation results showed that 6 pins which were connected between the handling head and the wrapper tube joint of the instrumented test subassembly (MARICO-2) were disconnected. Therefore, in order to confirm whether the disconnected 6 pins will influence reactor's safety or not, loose parts behavior in the reactor vessel was evaluated.
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kato, Shoichi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Yamamoto, Masaya; Sekine, Takashi; Ito, Chikara
JAEA-Research 2011-039, 20 Pages, 2012/02
Application of zirconium alloy as a neutron reflector around the driver fuel region of the Japanese experimental fast reactor JOYO has been planned for a further increase of core average burn-up. In order to investigate the compatibility of the zirconium alloys with high-temperature sodium which is coolant of the JOYO, corrosion test in sodium and tensile test of the exposed alloys were performed. The corrosion test was done at 500 C and 650
C and 650 C in stagnant/flowing sodium for two kinds of zirconium alloys, and then weight change measurement and metallurgical observation were carried out. The tensile test was performed in air at the same temperature with the sodium exposure.
C in stagnant/flowing sodium for two kinds of zirconium alloys, and then weight change measurement and metallurgical observation were carried out. The tensile test was performed in air at the same temperature with the sodium exposure.
Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Asaoka, Hidehito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Takeda, Masayasu; Shamoto, Shinichi
Thin Solid Films, 520(8), p.3300 - 3303, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in realizing the epitaxial growth of a Sr layer on Si(111) with an atomically abrupt heterointerface - in spite of its large lattice mismatch (12%) with Si - by introducing a monoatomic layer of H on Si. In order to identify the buried H, we carried out a combination analysis involving neutron reflectometry and resonant nuclear reaction of  H(
H( N,
N,
 )
) C analysis. We found different neutron reflectivity profiles resulting from a contrast variation between the H and D atoms at the buried heterointerface. Furthermore, the depth
C analysis. We found different neutron reflectivity profiles resulting from a contrast variation between the H and D atoms at the buried heterointerface. Furthermore, the depth  -ray intensity profiles revealed that the H at the heterointerface acts as an effective buffer layer that enables it to manage the highly mismatched epitaxy on Si.
-ray intensity profiles revealed that the H at the heterointerface acts as an effective buffer layer that enables it to manage the highly mismatched epitaxy on Si.
Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 241(12), p.4672 - 4681, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of key phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The key phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several key phenomena are summarized. The present results demonstrate COMPASS will be useful to understand and clarify the key phenomena of CDAs in SFRs in details.
Maeda, Shigetaka; Yamamoto, Masaya; Soga, Tomonori; Sekine, Takashi; Aoyama, Takafumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(4), p.693 - 700, 2011/04
Core modification was investigated to further increase the core burn-up of the experimental fast reactor Joyo. This modification also enables the core to accommodate more irradiation test subassemblies that have lower fissile material content compared to the driver fuel. The design calculations showed that the replacement of the radial reflector elements made of stainless steel with those made of zirconium of nickel-base ally is effective in improving neutron efficiency. The irradiation tests capacity can be increased by reducing the number of control rods based on the re-evaluation of the design margin in the control rod worth calculation. These modifications will be useful to save driver fuels and to enhance the Joyo's irradiation capability.
Donomae, Takako; Katsuyama, Kozo; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Maeda, Koji; Yamamoto, Masaya; Soga, Tomonori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(4), p.580 - 584, 2011/04
One of the challenges in developing a long-life control rod is to restrain absorber-cladding mechanical interaction (ACMI). Its lifetime was limited by ACMI, which is induced by the swelling and relocation of B C pellets. To restrain ACMI, a shroud tube was inserted into the gap between the B
C pellets. To restrain ACMI, a shroud tube was inserted into the gap between the B C pellets and the cladding tube. And sodium was selected as bonding material instead of helium to restrain increases in the pellet temperature. As a result of these improvements, the estimated lifetime of the control rod at Joyo was doubled. In this paper, the results of post irradiation examination are reported.
C pellets and the cladding tube. And sodium was selected as bonding material instead of helium to restrain increases in the pellet temperature. As a result of these improvements, the estimated lifetime of the control rod at Joyo was doubled. In this paper, the results of post irradiation examination are reported.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Taniguchi, Masaki; Kojima, Atsushi; Dairaku, Masayuki; Hanada, Masaya; Hemsworth, R. S.*; Mizuno, Takatoshi*; Takemoto, Jumpei; Tanaka, Masanobu*; Tanaka, Yutaka*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
At JAEA, a multi-aperture multi-grid accelerator has been developed for the ITER neutral beam system. A target is H ion beam acceleration of 0.5 A (200 A/m
ion beam acceleration of 0.5 A (200 A/m ) at 1 MeV. In real accelerators, it was found that the voltage holding was about a half of that obtained in an ideal small electrode. After applying necessary gap length and radii of edges of grid supports to lower local electric field concentrations, the accelerator succeeded in sustaining 1 MV for 4000 s. As a result, beam parameters were increased to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m
) at 1 MeV. In real accelerators, it was found that the voltage holding was about a half of that obtained in an ideal small electrode. After applying necessary gap length and radii of edges of grid supports to lower local electric field concentrations, the accelerator succeeded in sustaining 1 MV for 4000 s. As a result, beam parameters were increased to 879 keV, 0.36 A (157 A/m ) at perveance matched condition from 796 kV, 0.32 A (140 A/m
) at perveance matched condition from 796 kV, 0.32 A (140 A/m ) reported in FEC2008. In the beam acceleration, the beamlet deflections due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion caused direct interceptions, that resulted in limitations in the beam energy and current. Compensation of these beamlet deflections has been tested applying aperture offset and field shaping plate, which were examined in a three-dimensional beam analysis.
) reported in FEC2008. In the beam acceleration, the beamlet deflections due to magnetic field and space charge repulsion caused direct interceptions, that resulted in limitations in the beam energy and current. Compensation of these beamlet deflections has been tested applying aperture offset and field shaping plate, which were examined in a three-dimensional beam analysis.
Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Morita, Koji*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Naito, Masanori*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Uehara, Yasushi*; et al.
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-8) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2010/10
In this paper, FY2009 results of the COMPASS code development are reported. Validation calculations for melt freezing and blockage formation, eutectic reaction of metal fuel, duct wall failure (thermal-hydraulic analysis), fuel pin failure and disruption and duct wall failure (structural analysis) are shown. Phase diagram calculations, classical and first-principles molecular dynamics were used to investigate physical properties of eutectic reactions: metallic fuel/steel and control rod material/steel. Basic studies for the particle method and SIMMER code calculations supported the COMPASS code development. COMPASS is expected to clarify the basis of experimentally-obtained correlations used in SIMMER. Combination of SIMMER and COMPASS will be useful for safety assessment of CDAs as well as optimization of the core design.
Morita, Koji*; Zhang, S.*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ito, Takahiro*; Shirakawa, Noriyuki*; Inoue, Fusao*; Yugo, Hiroaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-18) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2010/05
A five-year research project has been initiated in 2005 to develop a code based on the MPS (Moving Particle Semi-implicit) method for detailed analysis of specific phenomena in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The code is named COMPASS (Computer Code with Moving Particle Semi-implicit for Reactor Safety Analysis). The specific phenomena include (1) fuel pin failure and disruption, (2) molten pool boiling, (3) melt freezing and blockage formation, (4) duct wall failure, (5) low-energy disruptive core motion, (6) debris-bed coolability, and (7) metal-fuel pin failure. Validation study of COMPASS is progressing for these key phenomena. In this paper, recent COMPASS results of detailed analyses for the several specific phenomena are summarized.