Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Takafumi*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Arakawa, Masakazu*; Maruyama, Akio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Sangyo Oyo Kogakukai Rombunshi, 11(2), p.109 - 114, 2023/09
Surface chemistry experimental end-station at BL23SU in SPring-8 is widely used to study various surfaces and interfaces of functional materials by means of soft X-rays synchrotron radiation. To analyze surface chemical reactions between gas and solid surfaces, an accurate control of flow-rates of gases is essential. This paper describes a computerized automatic gas flow control system to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of gas-surface reaction experiments in the pressure range of ultra-high vacuum (molecular flow) conditions. The system uses feedback control to operate the slow-leak valve to control the gas-pressure. As a result, the system achieved results equivalent to those of a skilled experimenter.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Corrosion Science and Technology, 20(3), p.105 - 111, 2021/06
We constructed three dimensional computational model using cellular automata method to simulate the intergranular corrosion propagation of stainless steel. In the model, the computational system was constructed by three types of cells: grain (bulk), grain boundary (GB), and solution cell. Our simulations revealed that the surface roughness calculated by the model adopted distributed dissolution rates of GBs was greater than that adopted constant dissolution rates of GBs. The cross-sectional images obtained by our simulation were comparable with that obtained by corrosion tests. These results indicate that the surface roughness during corrosion relates the distribution of corrosion rate.
Irisawa, Eriko; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kato, Chiaki; Motooka, Takafumi; Ban, Yasutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(4), p.337 - 344, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 2016 EFCOG Nuclear & Facility Safety Workshop (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/09
At the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident, seawater was injected into spent fuel pools of Unit 2-4 for the emergency cooling. Seawater might cause localized corrosion of spent fuel cladding. This would lead to leakage of not only fissile materials but also fission products from fuel cladding. The behavior, however, is not understood well. In this paper, the effects of seawater on corrosion behavior and mechanical property of were studied by using a spent fuel cladding from a BWR. We immersed the spent cladding tubes in diluted artificial seawater for 300h at 353 K, and conducted their visual, cross-sectional and strength examinations. As a localized corrosion index, the pitting potentials of specimens fabricated from the cladding were measured as functions of chloride ion concentration ranging from 20 to 2500 ppm. The visual examination showed that localized corrosion has not occurred, and cross-sectional examination showed no cracks. The strength of immersed tubes was comparable to that of non-immersed tubes. Additionally, pitting potential could not be measured over 1.0 V; pitting corrosion was hardly occurred. These results suggested that the specimens from the spent fuel cladding tube was very resistant to localized corrosion.
 radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater
radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawaterMotooka, Takafumi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 18, 2015/03
The effect of changes in water by  -ray irradiation on the pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater was investigated. Surface analysis and electrochemical test were conducted. They showed that the hydrogen peroxide produced by
-ray irradiation on the pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater was investigated. Surface analysis and electrochemical test were conducted. They showed that the hydrogen peroxide produced by  irradiation forms a passive film and the passive film is resistant to the pit initiation.
irradiation forms a passive film and the passive film is resistant to the pit initiation.
Motooka, Takafumi; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Suikagaku Bukai Bukaiho, 7 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2015/03
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, the seawater was injected into Spent Fuel Pool (SFP) after the accident in March 2013. It is considered that corrosion in SFP will be accelerated by the seawater injection. To prevent the corrosion, Tokyo Electronic Power Company injected hydrazine into SFP. We confirmed the hydrazine injection effect in a short time by irradiation test.
Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 19th International Corrosion Congress (19th ICC) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/11
We constructed three dimensional computational model using cellular automata method to simulate the intergranular corrosion propagation of stainless steel. By the simulation using the model, we verified the relationship between surface roughness during corrosion and dispersion of dissolution rate of grain boundaries (GB). The relationship was investigated by the simulation applying constant dissolution rate for GB cells and distributed dissolution rate of GB cells. Our simulations revealed that the surface roughness calculated by the model adopted distributed dissolution rates of GBs was greater than that adopted constant dissolution rates of GBs. The cross-sectional images obtained by our simulation were comparable with that obtained by corrosion tests. These results indicate that the surface roughness during corrosion relates the distribution of corrosion rate.
 radiolysis on pit initiation of zircaloy-2 in water containing sea salt
radiolysis on pit initiation of zircaloy-2 in water containing sea saltMotooka, Takafumi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(7-8), p.987 - 995, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)Igarashi, Takahiro; Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 63(7), p.431 - 437, 2014/07
In order to obtain the relation between an intergranular corrosion behavior and an impurities for stainless steel, cellular automata modeling and simulation of intergranular corrosion was carried out. From intergranular corrosion simulation considering non-uniform phosphorus component distribution on grain boundary, it suggested that complicated intergranular corrosion shape as in experimental data was caused by the large precipitation of phosphorus compounds in part of grain boundary.
Komatsu, Atsushi; Motooka, Takafumi; Makino, Masashi; Nogiwa, Kimihiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 63(3), p.98 - 103, 2014/03
The effect of phosphorous on intergranular corrosion of type 310 stainless steel at transpassive potential was investigated using phosphorous added ultra high purity type 310 stainless steel. Intergranular corrosion depth was measured by scanning electron microscopic observation. Grain boundaries were observed using three dimensional atom probe. Intergranular corrosion was observed on phosphorous added stainless steel. The sample heat treated at 600 C showed severe integranular corrosion morphology. Observation by three dimensional atom probe revealed that grain boundary with high dissolution rate had segregated zone of chromium and phosphorous about 5nm in width, on the other hand, grain boundary with low dissolution rate had no segregated zone. From these results, it is suggested that intergranular corrosion of phosphorous added type 310 stainless steel at transpassive potential is affected by segregation of phosphorous and chromium along grain boundaries.
C showed severe integranular corrosion morphology. Observation by three dimensional atom probe revealed that grain boundary with high dissolution rate had segregated zone of chromium and phosphorous about 5nm in width, on the other hand, grain boundary with low dissolution rate had no segregated zone. From these results, it is suggested that intergranular corrosion of phosphorous added type 310 stainless steel at transpassive potential is affected by segregation of phosphorous and chromium along grain boundaries.
Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Kato, Chiaki; Motooka, Takafumi; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Kano, Yoichi*; Ebina, Tetsunari*
Materials Transactions, 54(6), p.1001 - 1005, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zirconium has been utilized in nuclear fuel reprocessing plants because of its superior corrosion resistance in nitric acid solutions. However, stress corrosion cracking (SCC) susceptibility of zirconium has been reported in boiling nitric acid solutions at the passivity breakdown potential. However, it has not been clear the SCC initiation and propagation behavior of zirconium. In this study, to clarify the SCC initiation and propagation behavior of zirconium, constant load tensile tests were carried out in boiling nitric acid solutions. From the results, many cracks were initiated under the oxide film and maximum crack led to rupture in the potentials that nobler than passivity breakdown potential. These results showed that the SCC of zirconium in boiling nitric acid solutions is due to the oxide formation. And this SCC behavior suggests that the SCC behavior of zirconium can be attributed to tarnish rupture model.
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationMotooka, Takafumi; Komatsu, Atsushi; Tsukada, Takashi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
ECS Transactions, 53(21), p.25 - 32, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.78(Electrochemistry)Komatsu, Atsushi; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Motooka, Takafumi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 62(5), p.198 - 203, 2013/05
Reduction mechanism of nitrate ion on titanium electrode was investigated using electrochemical method. Cathodic polarization curve of titanium was measured in nitric acid with different concentrations of ions (H ,NO
,NO
 ,HNO
,HNO ). Reduction mechanism of nitrate ion on titanium was investigated from Tafel slope and reaction order of each ions. It was considered that reduction of titanium oxide was involved in reduction mechanism of nitrate ion on titanium, and reduction mechanism was suggested as follows. NO
). Reduction mechanism of nitrate ion on titanium was investigated from Tafel slope and reaction order of each ions. It was considered that reduction of titanium oxide was involved in reduction mechanism of nitrate ion on titanium, and reduction mechanism was suggested as follows. NO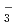
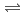 NO
NO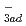 (QE), TiO
(QE), TiO + H
+ H + e
+ e
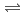 TiOOH (QE), NO
TiOOH (QE), NO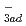 + TiOOH
+ TiOOH  (NO
(NO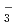 - TiOOH)
- TiOOH)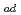 (RDS), (NO
(RDS), (NO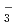 - TiOOH)
- TiOOH)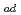 + H
+ H + e
+ e
 NO
NO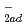 + TiO
+ TiO + H
+ H O
O
 -ray irradiation on the deoxygenation of salt-containing water using hydrazine
-ray irradiation on the deoxygenation of salt-containing water using hydrazineMotooka, Takafumi; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 50(4), p.363 - 368, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.40(Nuclear Science & Technology) ray irradiation on deoxygenation by hydrazine in artificial seawater
ray irradiation on deoxygenation by hydrazine in artificial seawaterMotooka, Takafumi; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(4), p.249 - 254, 2012/12
At the spent nuclear fuel pools in the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, hydrazine has been added to reduce dissolved oxygen in the pool water containing salts. The reduction behavior of dissolved oxygen in seawater with hydrazine in the presence of radiation is unknown. The effect of  ray irradiation on deoxygenation by hydrazine in artificial seawater was investigated at room temperature. We placed the artificial seawater with small amount of hydrazine under
ray irradiation on deoxygenation by hydrazine in artificial seawater was investigated at room temperature. We placed the artificial seawater with small amount of hydrazine under  ray irradiation at dose rates of 0.3
ray irradiation at dose rates of 0.3  7.5 kGy/h. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the solutions was measured before and after the irradiation. The concentration of dissolved oxygen hardly decreased in the absence of
7.5 kGy/h. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the solutions was measured before and after the irradiation. The concentration of dissolved oxygen hardly decreased in the absence of  radiation in a few hours, whereas the concentration of dissolved oxygen markedly decreased in the presence of
radiation in a few hours, whereas the concentration of dissolved oxygen markedly decreased in the presence of  radiation. The concentration of dissolved oxygen decreased with irradiation time. At this moment, hydrazine concentration was decreased more than twice the dissolved oxygen concentration. This shows that a part of
radiation. The concentration of dissolved oxygen decreased with irradiation time. At this moment, hydrazine concentration was decreased more than twice the dissolved oxygen concentration. This shows that a part of  radiolysis products of hydrazine act as deoxidizers. Dissolved oxygen in artificial seawater could be decreased by small addition of hydrazine in the presence of
radiolysis products of hydrazine act as deoxidizers. Dissolved oxygen in artificial seawater could be decreased by small addition of hydrazine in the presence of  radiation at room temperature.
radiation at room temperature.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Shiraishi, Hironori; Inoue, Shun; Motooka, Takafumi; Kato, Chiaki; Yamamoto, Masahiro; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Nojima, Yasuo*; Fujine, Sachio*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2012/07
In PUREX process for spent fuel reprocessing plants, heating portions in the components are severely corroded in the boiling solution under heat transfer (HT) conditions. In this paper, authors have focused on the effects of surface temperature and heat flux on corrosion rates (CRs) of stainless steels in boiling nitric acid under HT conditions. Two types of cells for HT and immersion conditions were applied for corrosion tests. Test solution used was 33 mol/m vanadium added to 3 kmol/m
vanadium added to 3 kmol/m nitric acid solution, and was heated at boiling temperature under atmospheric pressure. Additionally, a boiling curve which was indicated the relation between heat flux and degree of superheating was investigated experimentally. Surface temperatures during corrosion tests were estimated from a boiling curve. The results showed that CR did not depend on heat flux, but depended on surface temperature. Arrhenius plots on CRs indicated that CR was accelerated by solution boiling against non-boiling.
nitric acid solution, and was heated at boiling temperature under atmospheric pressure. Additionally, a boiling curve which was indicated the relation between heat flux and degree of superheating was investigated experimentally. Surface temperatures during corrosion tests were estimated from a boiling curve. The results showed that CR did not depend on heat flux, but depended on surface temperature. Arrhenius plots on CRs indicated that CR was accelerated by solution boiling against non-boiling.
Kogawara, Takafumi; Wakai, Eiichi; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Yamamoto, Michiyoshi; Molla, J.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(12), p.2904 - 2907, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Kato, Chiaki; Motooka, Takafumi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Fushoku Boshoku Kyokai Dai-58-Kai Zairyo To Kankyo Toronkai Koenshu, p.17 - 20, 2011/09
It is reported that high concentration NO
 ion accelerated corrosion of stainless steel in nitric acid solutions including the high concentration nitrate due to reoxidation of oxidizability ions such as Cr(VI). The valence state of oxidizability ions in a boiling nitric acid aqueous solution was calculated quantitatively by developed thermodynamics model of boiling nitric acid solutions and comparison with the measured value and calculated value was conducted. As the applications of the thermodynamics model, the influence of the NO
ion accelerated corrosion of stainless steel in nitric acid solutions including the high concentration nitrate due to reoxidation of oxidizability ions such as Cr(VI). The valence state of oxidizability ions in a boiling nitric acid aqueous solution was calculated quantitatively by developed thermodynamics model of boiling nitric acid solutions and comparison with the measured value and calculated value was conducted. As the applications of the thermodynamics model, the influence of the NO
 concentration in high concentration nitrate solutions accelerated re-oxidation of oxidizability ions such as Cr(VI) was investigated. As a result, optimized thermodynamics model of boiling nitric acid solutions is able to calculate REDOX potential of nitric acid solution and evaluate quantitatively the valence state of oxidizability ions in a boiling nitric acid aqueous solution.
concentration in high concentration nitrate solutions accelerated re-oxidation of oxidizability ions such as Cr(VI) was investigated. As a result, optimized thermodynamics model of boiling nitric acid solutions is able to calculate REDOX potential of nitric acid solution and evaluate quantitatively the valence state of oxidizability ions in a boiling nitric acid aqueous solution.
Motooka, Takafumi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Zairyo To Kankyo, 60(9), p.394 - 401, 2011/09
Corrosion behaviors of metal applicable as nuclear energy and bio-material were investigated in sodium hydroxide solutions. Tested materials were zirconium, titanium, tantalum and niobium. They were immersed in 0.1 to 6.1mol/dm sodium hydroxide solutions for 48h, and then weight loss measurement, XRD and XPS analyses were conducted. Potentiodynamic polarization curves were obtained in some solutions. The corrosion rates were greater in the order of Nb
sodium hydroxide solutions for 48h, and then weight loss measurement, XRD and XPS analyses were conducted. Potentiodynamic polarization curves were obtained in some solutions. The corrosion rates were greater in the order of Nb Ta
Ta Ti
Ti Zr. Polarization curves showed that Ti, Ta and Zr passivated, however, Nb corroded. XRD patterns showed that Nb dissolved as niobate compounds. XPS spectra showed that Zr and Ti formed oxide films such as ZrO
Zr. Polarization curves showed that Ti, Ta and Zr passivated, however, Nb corroded. XRD patterns showed that Nb dissolved as niobate compounds. XPS spectra showed that Zr and Ti formed oxide films such as ZrO and TiO
and TiO on their surface. SEM photographs indicated that uniform corrosion occurred for tested materials. There existed the differences of the stable species among the thermodynamic, corrosion test and surface analysis data. It is expected for expanding the thermodynamics data of these materials in alkali region.
on their surface. SEM photographs indicated that uniform corrosion occurred for tested materials. There existed the differences of the stable species among the thermodynamic, corrosion test and surface analysis data. It is expected for expanding the thermodynamics data of these materials in alkali region.
Maeda, Shigetaka; Yamamoto, Masaya; Soga, Tomonori; Sekine, Takashi; Aoyama, Takafumi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 48(4), p.693 - 700, 2011/04
Core modification was investigated to further increase the core burn-up of the experimental fast reactor Joyo. This modification also enables the core to accommodate more irradiation test subassemblies that have lower fissile material content compared to the driver fuel. The design calculations showed that the replacement of the radial reflector elements made of stainless steel with those made of zirconium of nickel-base ally is effective in improving neutron efficiency. The irradiation tests capacity can be increased by reducing the number of control rods based on the re-evaluation of the design margin in the control rod worth calculation. These modifications will be useful to save driver fuels and to enhance the Joyo's irradiation capability.