Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O
Yoshioka, Satoru*; Tsuruta, Konosuke*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Sugiyama, Takeharu*; Oba, Yojiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobayashi, Eiichi*; Okudaira, Koji*
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 103(8), p.4654 - 4663, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:29.90(Materials Science, Ceramics)X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) reveal the damaged structures in MgAl O
O spinel induced by swift heavy ions. SAXS indicates the formation of ion tracks with cylindrical shape with a diameter of 5 nm. XANES indicates the cationic disordering between tetrahedral and octahedral sites by the irradiation. Quantitative analysis of XANES also reveals that cations preferably occupy the octahedral sites at high fluence.
spinel induced by swift heavy ions. SAXS indicates the formation of ion tracks with cylindrical shape with a diameter of 5 nm. XANES indicates the cationic disordering between tetrahedral and octahedral sites by the irradiation. Quantitative analysis of XANES also reveals that cations preferably occupy the octahedral sites at high fluence.
 O
O induced by swift heavy ions
induced by swift heavy ionsYoshioka, Satoru*; Tsuruta, Konosuke*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito; Kobayashi, Eiichi*
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 20(7), p.4962 - 4969, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:28.76(Chemistry, Physical)Cationic disorder in the MgAl O
O spinel induced by swift heavy ions was investigated using the X-ray absorption near edge structure. With changes in the irradiation fluences of 200 MeV Xe ions, the Mg K-edge and Al K-edge spectra were synchronously changed. The calculated spectra based on density function theory indicate that the change in the experimental spectra was due to cationic disorder between Mg in tetrahedral sites and Al in octahedral sites. These results suggest a high inversion degree to an extent that the completely random configuration is achieved in MgAl
spinel induced by swift heavy ions was investigated using the X-ray absorption near edge structure. With changes in the irradiation fluences of 200 MeV Xe ions, the Mg K-edge and Al K-edge spectra were synchronously changed. The calculated spectra based on density function theory indicate that the change in the experimental spectra was due to cationic disorder between Mg in tetrahedral sites and Al in octahedral sites. These results suggest a high inversion degree to an extent that the completely random configuration is achieved in MgAl O
O induced by the high density electronic excitation under swift heavy ion irradiation.
induced by the high density electronic excitation under swift heavy ion irradiation.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Takaki, Seiya*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 326, p.140 - 144, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:93.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated atomic structure of ion tracks in CeO irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). TEM observations under inclined conditions showed continuous ion tracks with diffraction and structure factor contrast, and the decrease in the atomic density of the ion tracks was evaluated. High resolution STEM with high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) technique showed that the crystal structure of the Ce cation column is retained at the core region of ion tracks, although the signal intensity of the Ce cation lattice is reduced over a region nm in size. Annular bright field (ABF) STEM observation has detected that the O anion column is preferentially distorted at the core region of ion tracks within a diameter of 4 nm.
irradiated with 200 MeV Xe ions by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). TEM observations under inclined conditions showed continuous ion tracks with diffraction and structure factor contrast, and the decrease in the atomic density of the ion tracks was evaluated. High resolution STEM with high-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) technique showed that the crystal structure of the Ce cation column is retained at the core region of ion tracks, although the signal intensity of the Ce cation lattice is reduced over a region nm in size. Annular bright field (ABF) STEM observation has detected that the O anion column is preferentially distorted at the core region of ion tracks within a diameter of 4 nm.
 irradiated with swift heavy ions
irradiated with swift heavy ionsYasuda, Kazuhiro*; Eto, Motoki*; Sawada, Kenichi*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Yasunaga, Kazufumi*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 314, p.185 - 190, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:92.70(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated microstructure evolution in CeO irradiated with 210 MeV Xe ions by using transmission electron microscopy to gain the fundamental knowledge on radiation damage induced by fission fragments in nuclear fuel and transmutation target.
irradiated with 210 MeV Xe ions by using transmission electron microscopy to gain the fundamental knowledge on radiation damage induced by fission fragments in nuclear fuel and transmutation target.
 O
O under swift heavy ion irradiation
under swift heavy ion irradiationYasuda, Kazuhiro*; Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Eto, Motoki*; Kawasoe, Shinji*; Matsumura, Sho*; Ishikawa, Norito
International Journal of Materials Research, 102(9), p.1082 - 1088, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.36(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Accumulation and recovery of radiation-induced damage with swift heavy ions instoichiometric magnesium aluminate spinel, MgAl O
O , has been investigated. Microstructural change and atomic disordering was examined through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques, with bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) TEM images, and high angular resolution electron channelling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS), for single crystal MgAl
, has been investigated. Microstructural change and atomic disordering was examined through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) techniques, with bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) TEM images, and high angular resolution electron channelling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS), for single crystal MgAl O
O irradiated with 200 MeV Xe, and 340 or 350 MeV Au ions. The density of core damage region, detected by BFTEM with Fresnelcontrast, increased proportionally with ion fluence at the early stage of accumulation. This result is discussed with a balance between the formation and recovery of the core damage region under irradiation, and the influence region to induce the recovery was evaluated to be 7-9 nm in radius. The structure of the core damage region is found from HR and BFTEM images to be a columnar vacancy-rich region with a low atomic density.
irradiated with 200 MeV Xe, and 340 or 350 MeV Au ions. The density of core damage region, detected by BFTEM with Fresnelcontrast, increased proportionally with ion fluence at the early stage of accumulation. This result is discussed with a balance between the formation and recovery of the core damage region under irradiation, and the influence region to induce the recovery was evaluated to be 7-9 nm in radius. The structure of the core damage region is found from HR and BFTEM images to be a columnar vacancy-rich region with a low atomic density.
Yamamoto, Tomokazu*; Shimada, Mikio*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*; Matsumura, Sho*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.235 - 238, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:69.07(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the microstructure change and atomic disordering process in magnesium aluminate spinel, MgO  Al
Al O
O with
with  =1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe
=1.1 and 2.4, irradiated with swift heavy ions of 200-MeV Xe and 350-MeV Au
and 350-MeV Au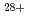 . Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12
. Transmission electron microscopy techniques of bright-field (BF) and high-resolution (HR) imaging, as well as high angular resolution electron channeling X-ray spectroscopy (HARECXS) are employed in quantitative analysis of irradiation-induced structural change. Ion tracks show columnar dark contrast of 4-7 nm in diameter at the incident surface in BF images. Strong strain contrast often arises among plural ion tracks formed closely. Clear lattice fringes are observed in HR images even inside the ion tracks. It indicates that the spinel crystals are not amorphized but partially disordered along the ion tracks. Quantitative HARECXS analysis shows that cation disordering progresses with ion fluence. It is revealed that the disordered regions are extended over 12 2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
2 nm in diameter along the ion tracks.
Yagyu, Junichi; Ogiwara, Norio; Saido, Masahiro; Okabe, Tomokazu; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Shunya; Takeshita, Hidefumi; Aoki, Yasushi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 241-243, p.579 - 584, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:75.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; Yamamoto, Tadatoshi; ; Takebe, Shinichi; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Komiya, Tomokazu; S.Li*; Z.Wang*; et al.
JAERI-Research 94-009, 44 Pages, 1994/07
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Tadatoshi; Takebe, Shinichi; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Komiya, Tomokazu; ;
JAERI-M 89-189, 18 Pages, 1989/11
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Tadatoshi; Takebe, Shinichi; Ogawa, Hiromichi; Tanaka, Tadao; Mukai, Masayuki; Komiya, Tomokazu; ;
JAERI-M 89-144, 23 Pages, 1989/10
no abstracts in English
Motooka, Takafumi; Kato, Chiaki; Komiya, Tomokazu; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
The effects on the corrosion acceleration of stainless steel by neptunium and vanadium were examined by re-oxidative behavior investigation and the corrosion test in boiling nitric acid solutions. As a result, it was suggested that the corrosion acceleration effect by Np was able to be simulated by vanadium by adjusting the amount of V and concentration of nitric acid.