Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(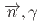 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear) rays from a neutron-induced
rays from a neutron-induced  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Xe
XeOkudaira, Takuya*; Tani, Yuika*; Endo, Shunsuke; Doskow, J.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kameda, Kento*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Luxnat, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 107(5), p.054602_1 - 054602_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:73.96(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Kono, Soma; Saegusa, Yu; Kuno, Takehiko; Sekine, Megumi; Inoue, Naoko; Noro, Naoko; Rodriguez, D.; Yamaguchi, Tomoki; Stinett, J.*
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
The gamma-ray measurement part of the Non-Destructive Assay (NDA) course of safeguards and nuclear material accountancy was developed to focus on gamma-ray measurement allotting two days out of five days. The lectures on the basic characteristics and detection methods and mechanism of gamma-ray detectors were provided as e-learnings which were developed. The part for hands-on exercises were implemented in JAEA facility. Participants have set up each gamma-ray detector, and performed measurements of uranium and the other gamma-ray emitting nuclides. Also, uranium-235 enrichment measurements have been performed. In addition, the participants trained with a handheld gamma-ray spectrometer, HM-5, that is popular for IAEA safeguards as the preparation in the measurement exercise of fresh fuel assemblies in JRR-3, a research reactor facility of JAEA. This paper reports on the development, implementation, and feedback from participants on gamma-ray measurement part of the NDA course.
 rays in the
rays in the  Sn(
Sn( )
) Sn reaction
Sn reactionEndo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 rays from the
rays from the  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Sn
SnKoga, Jun*; Takada, Shusuke*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Niinomi, Yudai*; Okudaira, Takuya*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(5), p.054615_1 - 054615_5, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Matoba, Tomoki*; Koyama, Daisuke*; Yamamoto, Yuki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Langmuir, 38(8), p.2642 - 2650, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.88(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)0xidation processes at the interface and the surface of Si(111) substrate with thin Hf films were studied using photoelectron spectroscopy in conjunction with supersonic oxygen molecular beams (SOMB). The oxidation starts at the outermost Hf layers and produces stoichiometric HfO . Hf silicates (Hf-O-Si configuration) were generated in the vicinity of the HfO
. Hf silicates (Hf-O-Si configuration) were generated in the vicinity of the HfO /Si interface in the case of the irradiation of 2.2 eV SOMB. The oxidation of the Si substrate takes place to generate SiO
/Si interface in the case of the irradiation of 2.2 eV SOMB. The oxidation of the Si substrate takes place to generate SiO compounds. Si atoms were emitted from the SiO
compounds. Si atoms were emitted from the SiO /Si interface region underneath the HfO
/Si interface region underneath the HfO overlayers to release the stress generated within the strained Si layers. The emitted Si atoms can pass through the HfO
overlayers to release the stress generated within the strained Si layers. The emitted Si atoms can pass through the HfO overlayers and react with the impinging O
overlayers and react with the impinging O gas.
gas.
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La( )
) La
La reaction
reactionOkudaira, Takuya*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Niinomi, Yudai*; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(1), p.014601_1 - 014601_6, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:63.10(Physics, Nuclear)Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 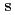 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 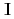 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 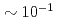 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (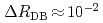 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPS
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; From NAP-HARPES to 4D-XPSToyoda, Satoshi*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*; Ohashi, Yuji*; et al.
Vacuum and Surface Science, 64(2), p.86 - 91, 2021/02
We have developed  measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
measurement and analysis techniques in X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. To begin with, time-division depth profiles of gate stacked film interfaces have been achieved by NAP-HARPES (Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved Photo Emission Spectroscopy) data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division ARPES data, which enables us to realize 4D-XPS analysis. It is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling in NAP-HARPES data is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 7 surface using high-resolution core-level photoelectron spectroscopy
7 surface using high-resolution core-level photoelectron spectroscopyKakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Matoba, Tomoki*; Koyama, Daisuke*; Yamamoto, Yuki*; Kato, Daiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Surface Science, 701, p.121691_1 - 121691_8, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.38(Chemistry, Physical)Ultrathin hafnium films on Si(111)-7 7 were studied using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopies to reveal the chemical states at interface and surface. Ultrathin Hf layers grow on clean Si(111)-7
7 were studied using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopies to reveal the chemical states at interface and surface. Ultrathin Hf layers grow on clean Si(111)-7 7 surface by lever rule. Surface and interface of Hf/Si(111) contain three components (metallic Hf layers, Hf monosilicide (HfSi) and Si-rich Hf silicide). Ultrathin Hf layers changes HfSi
7 surface by lever rule. Surface and interface of Hf/Si(111) contain three components (metallic Hf layers, Hf monosilicide (HfSi) and Si-rich Hf silicide). Ultrathin Hf layers changes HfSi islands on bared Si(111)-7
islands on bared Si(111)-7 7 surface after annealing at 1073 K. It was found that the long axes of the rectangle islands expand the direction connecting the corner holes in DAS model of clean Si(111)-7
7 surface after annealing at 1073 K. It was found that the long axes of the rectangle islands expand the direction connecting the corner holes in DAS model of clean Si(111)-7 7 surface.
7 surface.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:88.75(Instruments & Instrumentation) rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
LaYamamoto, Tomoki*; Okudaira, Takuya; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064624_1 - 064624_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:84.46(Physics, Nuclear) -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Okudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 356, p.029_1 - 029_5, 2019/12
The technology development section carries out the development of the neutron polarization device:  He Spin Filter. It is often used for the fundamental physics region. In order to explain the matter-dominated universe, a time reversal violation is necessary and searches for new physics are conducted in the world. The T-violation search using a polarized neutron beam is planned at J-PARC. A large
He Spin Filter. It is often used for the fundamental physics region. In order to explain the matter-dominated universe, a time reversal violation is necessary and searches for new physics are conducted in the world. The T-violation search using a polarized neutron beam is planned at J-PARC. A large  He spin filter is needed to polarize high energy neutrons for the experiment and is developed in JAEA. Recently, we developed the accurate measurement system to evaluate the polarization of
He spin filter is needed to polarize high energy neutrons for the experiment and is developed in JAEA. Recently, we developed the accurate measurement system to evaluate the polarization of  He and a vacuum system to make the
He and a vacuum system to make the  He spin filter, and large
He spin filter, and large  He spin filters for epi-thermal neutron was made using the system. The current status of the development of the
He spin filters for epi-thermal neutron was made using the system. The current status of the development of the  He spin filter will be talked.
He spin filter will be talked.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:303 Percentile:99.67(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
 rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
LaOkudaira, Takuya*; Takada, Shusuke*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nagamoto, Kosuke*; Nakao, Taro*; Okada, Anju*; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034622_1 - 034622_15, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:77.96(Physics, Nuclear) -rays at the ANNRI in the MLF of the J-PARC
-rays at the ANNRI in the MLF of the J-PARCTakada, Shusuke*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Goto, Fumiya*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nakao, Taro*; Sakai, Kenji; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 13(2), p.P02018_1 - P02018_21, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.38(Instruments & Instrumentation)Meguro, Yoshihiro; Tomioka, Osamu; Imai, Tomoki*; Fujimoto, Shigeyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio; Yoshida, Zenko; Honda, Tadashi*; Koya, Fumio*; Kitamura, Nobu*; Wada, Ryutaro*; et al.
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposium 2004 (WM '04) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/03
Supercritical CO fluid leaching (SFL) method using supercritical CO
fluid leaching (SFL) method using supercritical CO fluid containing a complex of HNO
fluid containing a complex of HNO - tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) was applied to removal of uranium from radioactive solid wastes. Sea sands, incineration ashes and porous alumina bricks were employed as matrixes of simulated solid wastes. Real radioactive incineration ash wastes and firebrick wastes were also subjected to the SFL treatment. It was found that uranium could be efficiently removed from both of the simulated wastes and real wastes by the SFL method. The removal efficiency of uranium from the real waste was lower than that from the corresponding artificial waste. About 1 g and 35 mg of uranium were recovered from 10 g of the real ash waste and 37 g of the real firebrick waste, respectively.
- tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP) was applied to removal of uranium from radioactive solid wastes. Sea sands, incineration ashes and porous alumina bricks were employed as matrixes of simulated solid wastes. Real radioactive incineration ash wastes and firebrick wastes were also subjected to the SFL treatment. It was found that uranium could be efficiently removed from both of the simulated wastes and real wastes by the SFL method. The removal efficiency of uranium from the real waste was lower than that from the corresponding artificial waste. About 1 g and 35 mg of uranium were recovered from 10 g of the real ash waste and 37 g of the real firebrick waste, respectively.
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Ino, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
In neutron fundamental physics, a study of correlation term  of a neutron spin s and a target nuclear spin
of a neutron spin s and a target nuclear spin 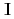 is important because the
is important because the  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving (TRNC) terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving (TRNC) terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 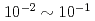 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We attempted to develop a polarized Xe target in a compact
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We attempted to develop a polarized Xe target in a compact  SEOP system and measure neutron polarizing ability caused by the
SEOP system and measure neutron polarizing ability caused by the  term at a 9.6 eV
term at a 9.6 eV  -wave resonance peak of
-wave resonance peak of  Xe, by detecting change
Xe, by detecting change 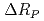 of a ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. As preliminary results, we observed a signified value of
of a ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. As preliminary results, we observed a signified value of 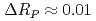 after demonstrating that our apparatus could distinguish Doppler broadening effect as systematic error.
after demonstrating that our apparatus could distinguish Doppler broadening effect as systematic error.