Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 symmetry for anisotropic
symmetry for anisotropic 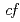 hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi
hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Higashiya, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165121_1 - 165121_10, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Davies, S. J. C.*; Bolea-Alamanac, B.*; Endo, Kaori*; Yamamoto, Yu*; Yamasaki, Shudo*; Malins, A.; Evans, J.*; Sullivan, S.*; Ando, Shuntaro*; Nishida, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of Transport & Health, 28, p.101564_1 - 101564_11, 2023/01
 Sb
Sb uncovered by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
uncovered by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroismSaito, Yuji; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Yasui, Akira*; Kadono, Toshiharu*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Kikuchi, Daisuke*; Sato, Hideyuki*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Sekiyama, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(16), p.165152_1 - 165152_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -ray measurements of the
-ray measurements of the  Th isomer
Th isomerMuramatsu, Haruka*; Hayashi, Tasuku*; Yuasa, Naoki*; Konno, Ryohei*; Yamaguchi, Atsushi*; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa*; Yamasaki, Noriko*; Maehata, Keisuke*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Takimoto, Misaki; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 200(5-6), p.452 - 460, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.58(Physics, Applied) Th nuclear clock isomer determined by absolute
Th nuclear clock isomer determined by absolute  -ray energy difference
-ray energy differenceYamaguchi, Atsushi*; Muramatsu, Haruka*; Hayashi, Tasuku*; Yuasa, Naoki*; Nakamura, Keisuke; Takimoto, Misaki; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Konashi, Kenji*; Watanabe, Makoto*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 123(22), p.222501_1 - 222501_6, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:89.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary) symmetry in CeCu
symmetry in CeCu Ge
Ge ; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
; Soft X-ray absorption and hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopyAratani, Hidekazu*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Kawada, Moeki*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Fujioka, Shuhei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kuga, Kentaro*; Kiss, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(12), p.121113_1 - 121113_6, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ge
Ge in the normal state
in the normal stateNakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Mori, Takeo*; Tsuruta, Atsushi*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Yasui, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review B, 97(11), p.115160_1 - 115160_7, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ge
Ge
Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Mori, Takeo*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Yasui, Akira*; Yamagami, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 220, p.50 - 53, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.41(Spectroscopy)We report the soft X-ray angle-resolved photoemission study for LaNi Ge
Ge to reveal the electronic structures derived from non-4
to reveal the electronic structures derived from non-4 bands of the heavy fermion compound CeNi
bands of the heavy fermion compound CeNi Ge
Ge . The photoemission spectra recorded at the La M
. The photoemission spectra recorded at the La M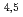 absorption edges clearly show the enhancement of the La 5
absorption edges clearly show the enhancement of the La 5 components in the valence band spectra. The circular dichroism of photoemission spectra reveals the band-dependent dichroic response due to the orbital symmetry.
components in the valence band spectra. The circular dichroism of photoemission spectra reveals the band-dependent dichroic response due to the orbital symmetry.
Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Tachibana, Shoichi*; Iwasaki, Daisuke*; Higashino, Yuji*; Yoshimi, Chiaki*; Nakagawa, Koya*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(11), p.115103_1 - 115103_10, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:57.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, we systematically investigate three-dimensional(3D) momentum-resolved electronic structures of Ruddlesden-Popper-type iridium oxides Sr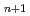 Ir
Ir O
O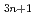 using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO
using soft-X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (SX-ARPES). Our results provide direct evidence of an insulator-to-metal transition that occurs upon increasing the dimensionality of the IrO -plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled
-plane structure. This transition occurs when the spin-orbit-coupled 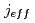 = 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO
= 1/2 band changes its behavior in the dispersion relation and moves across the Fermi energy. By scanning the photon energy over 350 eV, we reveal the 3D Fermi surface in SrIrO and
and 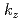 -dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr
-dependent oscillations of photoelectron intensity in Sr Ir
Ir O
O . To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
. To corroborate the physics deduced using low-energy ARPES studies, we propose to utilize SX-ARPES as a powerful complementary technique, as this method surveys more than one whole Brillouin zone and provides a panoramic view of electronic structures.
 -space mapping of the electronic structure in an oxide-oxide interface
-space mapping of the electronic structure in an oxide-oxide interfaceBerner, G.*; Sing, M.*; Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Yasui, Akira*; Saito, Yuji; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Nishitani, Yoshihito*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Pavlenko, N.*; Kopp, T.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 110(24), p.247601_1 - 247601_5, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:136 Percentile:96.23(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The interface between LaAlO and SrTiO
and SrTiO hosts a two-dimensional electron system of itinerant carriers, although both oxides are band insulators. Interface ferromagnetism coexisting with superconductivity has been found and attributed to local moments. Experimentally, it has been established that Ti 3
hosts a two-dimensional electron system of itinerant carriers, although both oxides are band insulators. Interface ferromagnetism coexisting with superconductivity has been found and attributed to local moments. Experimentally, it has been established that Ti 3 electrons are confined to the interface. Using soft X-ray angle-resolved resonant photoelectron spectroscopy we have directly mapped the interface states in
electrons are confined to the interface. Using soft X-ray angle-resolved resonant photoelectron spectroscopy we have directly mapped the interface states in  space. Our data demonstrate a charge dichotomy. A mobile fraction contributes to Fermi surface sheets, whereas a localized portion at higher binding energies is tentatively attributed to electrons trapped by O vacancies in the SrTiO
space. Our data demonstrate a charge dichotomy. A mobile fraction contributes to Fermi surface sheets, whereas a localized portion at higher binding energies is tentatively attributed to electrons trapped by O vacancies in the SrTiO .
.
Nagata, Hidezumi*; Hirao, Norie*; Onoki, Takamasa*; Baba, Yuji; Yamasaki, Yuki*; Nakahira, Atsushi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 116(1350), p.216 - 219, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:51.50(Materials Science, Ceramics)Bulky palladium catalyst supported on mesoporous silica (Pd-MCM-41) was successfully synthesized by hydrothermal hot-pressing method. The structure of the palladium species in Pd-MCM-41 bulk before and after heat-treatment process was investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). On the basis of these results, the microstructures and mesoporous properties of Pd-MCM-41 were discussed. As a result, it was revealed that the obtained Pd-MCM-41 bulks possessed a high area of over 1000 m /g and the electronic state of palladium in Pd-MCM-41 bulk is almost equal to palladium (0) metal.
/g and the electronic state of palladium in Pd-MCM-41 bulk is almost equal to palladium (0) metal.
Wada, Atsushi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; Yamanoi, Yoshinori*; Nankawa, Takuya; Namiki, Kosuke*; Yamasaki, Mikio*; Murata, Masaki*; Nishihara, Hiroshi*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 80(2), p.335 - 345, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:56.69(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Lanthanide complexes with linear and cyclic octadentate oligopyridine-amine ligands were synthesized, and their molecular structures were determined by single-crystal X-ray crystallography. All of the complexes had a distorted capped square antiprism (CSAP) geometry, and the coordination environments of lanthanide complexes were more distortedfor the complexes with the linear ligand than those with the cyclic ligand. The Eu complexes with the linear ligand showed more intense emissions, which were attributed to the
complexes with the linear ligand showed more intense emissions, which were attributed to the  D
D

 F
F transition, than the complex withthe cyclic ligand in acetonitrile, which can be attributed to the distortion in the coordination environments. These results indicate that the coordination environments of lanthanide complexes, and thus the luminescence properties, can be controlled by tuning the geometrical structures of polydentate ligands.
transition, than the complex withthe cyclic ligand in acetonitrile, which can be attributed to the distortion in the coordination environments. These results indicate that the coordination environments of lanthanide complexes, and thus the luminescence properties, can be controlled by tuning the geometrical structures of polydentate ligands.


 )
) O
O (
( =Cr,Ti)
=Cr,Ti)Mo, S.-K.*; Kim, H.-D.*; Denlinger, J. D.*; Allen, J. W.*; Park, J.-H.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Saito, Yuji; Muro, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 74(16), p.165101_1 - 165101_12, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:84.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present high-resolution bulk-sensitive photoemission spectra of (V

 )
) O
O (
( =Cr,Ti). The measurements were made for the paramagnetic metal (PM), paramagnetic insulator (PI), and antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) phases of (V
=Cr,Ti). The measurements were made for the paramagnetic metal (PM), paramagnetic insulator (PI), and antiferromagnetic insulator (AFI) phases of (V

 )
) O
O . In the PM phase, we observe a prominent quasiparticle peak in general agreement with theory, which combines dynamical mean-field theory with the local density approximation. For both the PI and AFI phases, the vanadium 3
. In the PM phase, we observe a prominent quasiparticle peak in general agreement with theory, which combines dynamical mean-field theory with the local density approximation. For both the PI and AFI phases, the vanadium 3 parts of the valence spectra are not simple one peak structures. For the PI phase, there is not yet a good theoretical understanding of these structures. Spectra taken in the same phases with different compositions show interesting monotonic changes as the dopant concentration increases, regardless of the dopant species. With increased Cr-doping, the AFI phase gap decreases and the PI phase gap increases.
parts of the valence spectra are not simple one peak structures. For the PI phase, there is not yet a good theoretical understanding of these structures. Spectra taken in the same phases with different compositions show interesting monotonic changes as the dopant concentration increases, regardless of the dopant species. With increased Cr-doping, the AFI phase gap decreases and the PI phase gap increases.
 O
O
Mo, S.-K.*; Denlinger, J. D.*; Kim, H.-D.*; Park, J.-H.*; Allen, J. W.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Kadono, Koji*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 90(18), p.186403_1 - 186403_4, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:144 Percentile:95.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
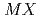 (
( =Pt, Pd;
=Pt, Pd; 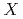 =P, As, Sb)
=P, As, Sb)Iwasaki, T.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Okazaki, Makoto*; Kadono, Koji*; Utsunomiya, Hiroshi*; Imada, Shin*; Saito, Yuji; Muro, Takayuki*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; et al.
Physical Review B, 65(19), p.195109_1 - 195109_9, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:71.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
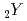 Sn (
Sn (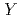 =Ti, Zr, and Nb)
=Ti, Zr, and Nb)Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; Arai, Ryuji*; Utsunomiya, Hiroshi*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Muro, Takayuki*; Saito, Yuji; Kanomata, Takeshi*; Ishida, Shoji*
Physical Review B, 65(10), p.104410_1 - 104410_6, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:89.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) of core-level absorption [x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS)] spectra in the soft x-ray region has been measured for the ferromagnetic Heusler alloys Co TiSn, Co
TiSn, Co ZrSn, and Co
ZrSn, and Co NbSn. The many-peak structures which are clearly observed in the Co 2p-3d XAS-MCD spectra cannot be well explained by atomic multiplet calculations but are better explained by the Co 3d unoccupied states predicted by linear muffin-tin orbital atomic sphere approximation band structure calculations. The MCD spectra show an obvious contribution of the orbital angular momentum component to the magnetic moment in these alloys. The ratio between the orbital angular momentum and spin derived from the MCD spectra varies by more than a factor of 2 within these alloys. The mechanism of this variation is discussed in comparison with the band structure calculations.
NbSn. The many-peak structures which are clearly observed in the Co 2p-3d XAS-MCD spectra cannot be well explained by atomic multiplet calculations but are better explained by the Co 3d unoccupied states predicted by linear muffin-tin orbital atomic sphere approximation band structure calculations. The MCD spectra show an obvious contribution of the orbital angular momentum component to the magnetic moment in these alloys. The ratio between the orbital angular momentum and spin derived from the MCD spectra varies by more than a factor of 2 within these alloys. The mechanism of this variation is discussed in comparison with the band structure calculations.
 TiS
TiS
Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; Utsunomiya, Hiroshi*; Muro, Takayuki*; Saito, Yuji; Negishi, H.*; Sasaki, M.*; Inoue, M.*; Suga, Shigemasa*
Physica E, 10(1-3), p.387 - 390, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:31.87(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)no abstracts in English
 Th isomer energy measurement with TES calorimeters
Th isomer energy measurement with TES calorimetersTanaka, Keita*; Hirano, Kosuke*; Yamaguchi, Atsushi*; Muramatsu, Haruka*; Hayashi, Tasuku*; Yuasa, Naoki*; Nakamura, Keisuke; Takimoto, Misaki; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Shirasaki, Kenji*; et al.
no journal, ,
Kato, Junya; Miyauchi, Atsushi; Yamasaki, Akito*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Haruka*; Yuasa, Naoki*; Hayashi, Tasuku*; Konno, Ryohei*; Yamaguchi, Atsushi*; Mitsuda, Kazuhisa*; Yamasaki, Noriko*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Nakamura, Keisuke; Takimoto, Misaki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kato, Junya; Miyauchi, Atsushi; Aoshima, Atsushi; Shiotsuki, Masao; Yamashita, Teruo; Nakajima, Masayoshi; Morikawa, Yo; Miura, Akihiko; Fukui, Toshiki*; Yamasaki, Akito*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English