Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mohamad, A. B.; Chen, J.*; Ioka, Ikuo*; Suzuki, Eriko; Kondo, Keietsu; Abe, Yosuke; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Okada, Yuji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 625, p.156513_1 - 156513_9, 2026/04
Times Cited Count:0 -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.37(Physics, Applied)Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kurata, Masaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Sato, Daiki*; Murakami, Nozomu*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.206 - 216, 2019/09
After the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant, research and development (R&D) program for establishing technical basis of accident-tolerant fuel (ATF) started from 2015 in Japan. Since then, both experimental and analytical studies necessary for designing a new light water reactor (LWR) core with ATF candidate materials are being conducted within the Japanese ATF R&D Consortium for implementing ATF to the existing LWRs, accompanying with various technological developments required. Until now, we have accumulated experimental data of the candidate materials by out-of-pile tests, developed fuel evaluation codes to apply to the ATF candidate materials, and evaluated fuel behavior simulating operational and accidental conditions by the developed codes. In this paper, the R&D progresses of the ATF candidate materials considered in Japan are reviewed based on the information available such as proceedings of international conference and academic papers, providing an overview of ATF program in Japan.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Nagase, Fumihisa; Kurata, Masaki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of Annual Topical Meeting on LWR Fuels with Enhanced Safety and Performance (TopFuel 2016) (USB Flash Drive), p.21 - 30, 2016/09
Fuel rod, channel box, and control rod designed with new materials and concepts have been developed in Japan for increasing accident tolerance of LWRs. In order to efficiently and properly implement the accident tolerant fuels (ATFs) and the other components, it is necessary not only to accumulate fundamental and practical data but also to consider technology readiness, recognize knowledge gaps, and establish strategy for design and fabrication. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has established the above "technical basis" and drafted a research plan towards implementation of the ATFs and components as a program sponsored and organized by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI). It is useful to take advantage of the experiences in commercial uses of zirconium-base alloys in LWRs and, therefore, JAEA has conducted this METI project in cooperation with power plant providers, fuel venders, research institutes and universities who have been involved in the development of the ATF materials. The present paper describes the main results of the project conducted to establish the technical basis of the ATFs and components.
 C and
C and  O nuclei by low-energy proton beams
O nuclei by low-energy proton beamsAkagi, Takashi*; Yagi, Masashi*; Yamashita, Tomohiro*; Murakami, Masao*; Yamakawa, Yoshiyuki*; Kitamura, Keiji*; Ogura, Koichi; Kondo, Kiminori; Kawanishi, Shunichi*
Radiation Measurements, 59, p.262 - 269, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:79.23(Nuclear Science & Technology)In proton therapy, positron emitters are induced from  C and
C and  O nuclei by protons on the beam path in the patient. Many studies for monitoring positron emitters with beam-induced PET technique have been performed by various groups to verify the proton beam range and the dose in the patient for quality assurance. The aim of this study was to develop a method for measuring the production cross sections of positron emitters using standard equipment for proton therapy. The time-activity curve was then obtained with a high-sensitivity PET scanner to extract the number of positron emitters produced in the target. The production cross sections for four reaction channels:
O nuclei by protons on the beam path in the patient. Many studies for monitoring positron emitters with beam-induced PET technique have been performed by various groups to verify the proton beam range and the dose in the patient for quality assurance. The aim of this study was to develop a method for measuring the production cross sections of positron emitters using standard equipment for proton therapy. The time-activity curve was then obtained with a high-sensitivity PET scanner to extract the number of positron emitters produced in the target. The production cross sections for four reaction channels:  O(p,pn)
O(p,pn) O,
O,  O(p,3p3n)
O(p,3p3n) C,
C,  O(p,2p2n)
O(p,2p2n) N, and
N, and  C(p,pn)
C(p,pn) C were then measured. The cross sections for the
C were then measured. The cross sections for the  O(p,pn)
O(p,pn) O reaction channel were consistent with data of previous experiments within the uncertainties, while those of
O reaction channel were consistent with data of previous experiments within the uncertainties, while those of  C(p,pn)
C(p,pn) C were generally lower than data of previous experiments.
C were generally lower than data of previous experiments.
Kobayashi, Masaki*; Niwa, Hideharu*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Horiba, Koji*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Ofuchi, Hironori*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ikeda, Takashi; Koshigoe, Yuka*; Ozaki, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 196(20), p.8346 - 8351, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:64.69(Chemistry, Physical)The electronic structure of Co atoms in CoPc-based carbon catalysts, which were prepared by pyrolyzing a mixture of CoPc and phenol resin polymer up to 1000 C, has been investigated using XAFS analysis and HXPES. The Co K XAFS spectra show that most of the Co atoms are in the metallic state and small quantities of oxidized Co components are present in the samples even after acid washing to remove Co atoms. Based on the difference in probing depth between XAFS and HXPES, it was found that after acid washing, the surface region with the aggregated Co clusters is primarily composed of metallic Co. Since the electrochemical properties remain almost unchanged even after the acid washing process, the residual metallic and oxidized Co atoms themselves will hardly contribute to the ORR activity of the CoPc-based carbon cathode catalysts, implying that the active sites of the CoPc-based catalysts primarily consist of light elements such as C and N.
C, has been investigated using XAFS analysis and HXPES. The Co K XAFS spectra show that most of the Co atoms are in the metallic state and small quantities of oxidized Co components are present in the samples even after acid washing to remove Co atoms. Based on the difference in probing depth between XAFS and HXPES, it was found that after acid washing, the surface region with the aggregated Co clusters is primarily composed of metallic Co. Since the electrochemical properties remain almost unchanged even after the acid washing process, the residual metallic and oxidized Co atoms themselves will hardly contribute to the ORR activity of the CoPc-based carbon cathode catalysts, implying that the active sites of the CoPc-based catalysts primarily consist of light elements such as C and N.
 studied by photoemission and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopies
studied by photoemission and soft X-ray absorption spectroscopiesUtsumi, Yuki*; Sato, Hitoshi*; Kurihara, Hidenao*; Maso, Hiroyuki*; Hiraoka, Koichi*; Kojima, Kenichi*; Tobimatsu, Komei*; Okochi, Takuo*; Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; et al.
Physical Review B, 84(11), p.115143_1 - 115143_7, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:46.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have studied conduction-band (CB) electronic states of a typical valence-transition compound YbInCu by means of temperature-dependent hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES), soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (SX-PES) of the valence band. We have described the valence transition in YbInCu
by means of temperature-dependent hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (HX-PES), soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS), and soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (SX-PES) of the valence band. We have described the valence transition in YbInCu in terms of the charge transfer from the CB to Yb 4
in terms of the charge transfer from the CB to Yb 4 states.
states.
Niwa, Hideharu*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Horiba, Koji*; Harada, Yoshihisa*; Oshima, Masaharu*; Terakura, Kiyoyuki*; Ikeda, Takashi; Koshigoe, Yuka*; Ozaki, Junichi*; Miyata, Seizo*; et al.
Journal of Power Sources, 196(3), p.1006 - 1011, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:90.63(Chemistry, Physical)We report on the electronic structure of three different types of N-containing carbon-based cathode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells observed by hard X-ray photoemission spectroscopy. C 1s spectra show the importance of 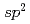 carbon network formation for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity. Samples having high oxygen reduction reaction activity in terms of oxygen reduction potential contain high concentration of graphite-like nitrogen. Based on a quantitative analysis of our results, the oxygen reduction reaction activity of the carbon-based cathode catalysts will be improved by increasing concentration of graphite-like nitrogen in a developed
carbon network formation for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity. Samples having high oxygen reduction reaction activity in terms of oxygen reduction potential contain high concentration of graphite-like nitrogen. Based on a quantitative analysis of our results, the oxygen reduction reaction activity of the carbon-based cathode catalysts will be improved by increasing concentration of graphite-like nitrogen in a developed 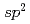 carbon network.
carbon network.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi*; Nagae, Yuji; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki*; Miwa, Yukio*; Takaya, Shigeru; Hoshiya, Taiji; Tsukada, Takashi*; Aoto, Kazumi; Ishii, Toshimitsu*; Omi, Masao*; et al.
JNC TY9400 2005-013, 150 Pages, 2005/09
None
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Nagae, Yuji*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Miwa, Yukio; Takaya, Shigeru*; Hoshiya, Taiji*; Tsukada, Takashi; Aoto, Kazumi*; Ishii, Toshimitsu; Omi, Masao; et al.
JAERI-Research 2005-023, 132 Pages, 2005/09
JAERI and JNC have started a JAERI-JNC joint research program in fiscal year 2003, which has been aimed for efficient progress and synergistic effect on the research activities in both Institutes. This study has been chosen one of the joint research themes because it has been our common objective in the field of structural materials of FBR and LWR components. The purpose of the study is to clarify damage mechanism of structural materials used under irradiation, and then to develop the methods for damage evaluation and detection in earlier stage of progressing process of damage. In fiscal year 2004 and 2005, micro-corrosion measurement, electrochemical corrosion test and leakage magnetic flux density measurement apparatuses were developed and equipped in two hot facilities and irradiated and unirradiated crept specimens, irradiated high purity model austenitic stainless alloys were also prepared and applied to this study. These apparatuses and specimens were used for damage evaluation, and these feasibilities for nuclear power plant materials were studied.
Kato, Takashi; Tsuji, Hiroshi; Ando, Toshinari; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nakajima, Hideo; Sugimoto, Makoto; Isono, Takaaki; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Kawano, Katsumi; Oshikiri, Masayuki*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 56-57, p.59 - 70, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:75.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Hiroshi; Okuno, Kiyoshi*; Thome, R.*; Salpietro, E.*; Egorov, S. A.*; Martovetsky, N.*; Ricci, M.*; Zanino, R.*; Zahn, G.*; Martinez, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 41(5), p.645 - 651, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:82.39(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Mohamad, A. B.; Furumoto, Kenichiro; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Ioka, Ikuo; Sato, Daiki*; Okada, Yuji*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Mohamad, A. B.; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Osaka, Masahiko; Kaji, Yoshiyuki
no journal, ,
After the nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi power plant, global interest has expanded in exploring fuels with enhanced performance during severe accident, and enhancing the accident tolerance of light water reactors (LWRs) became a topic of serious discussion all over the world. In Japan, research and development (R&D) program for establishing technical basis of ATF has been conducted by JAEA in cooperation with power plant providers, fuel venders and universities. In this presentation, the overview of ATF R&D program in Japan will be introduced with the explanation on JAEA's role in ATF R&D program including the recent result from fundamental ATF studies.
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Mohamad, A. B.; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Osaka, Masahiko; Murakami, Nozomu*; Owaki, Masao*; Sasaki, Masana*; et al.
no journal, ,
Japan's Accident Tolerant Fuel (ATF) research and development (R&D) program has been conducted since 2015 in cooperation with power plant providers, fuel venders and universities for making the most use of the experiences in R&D, practical design, and evaluations of fuels and cores of commercial Light Water Reactors (LWRs). An overview of the present R&D progress is given, in relation to the role of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the program. The ATF candidate materials currently under consideration are the following three claddings: the silicon carbide (SiC) composite which is potentially applicable for Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR) and Boiling Water Reactor (BWR), the FeCrAl steel strengthened by dispersion of fine oxide particles (FeCrAl-ODS) for BWR, and Cr-coated zircalloy claddings for PWR. In addition to the cladding materials, R&D on the SiC-made BWR channel box and accident tolerant control rods are also underway.
 O
O Schottky junction from gamma ray region
Schottky junction from gamma ray regionFukuda, Tatsuo; Fukada, Yukimasa; Kobata, Masaaki; Yoshii, Kenji; Shobu, Takahisa; Tominaga, Aki; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*; Tanida, Hajime; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Shinichiro; Ioka, Ikuo; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Kawanishi, Tomohiro; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Fukahori, Tokio; Nozawa, Takashi*; Watanabe, Seiichi*; Murakami, Nozomu*; Sato, Hisaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Pham, V. H.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Yamashita, Shinichiro
no journal, ,
Pham, V. H.; Ishibashi, Ryo*; Sasaki, Masana*; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Yamashita, Shinichiro
no journal, ,
Silicon carbide is the most prominent candidate for accident tolerant fuel cladding in terms of oxidation resistance and cladding integrity at high temperatures in steam. However, dilution of silica from SiC in aqueous environment under long-term corrosion can become a concern when considering SiC as nuclear graded materials. In order to improve its corrosion resistance in water for normal operations, coating of Ti layer on SiC was proposed. In this study, oxidation behavior and oxidation kinetics of Ti-coated SiC are studied via a thermogravimetric system at 1200-1500 C. Influence of the Ti coating layer on oxidation kinetics and behavior of SiC will then be discussed and reported.
C. Influence of the Ti coating layer on oxidation kinetics and behavior of SiC will then be discussed and reported.
 C
CPham, V. H.; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Okada, Yuji*; Sato, Daiki*
no journal, ,
Chromium coated zirconium alloy has gained significant attention as a potential candidate for accident-tolerant fuel cladding tube in recent years. Although various works reported by different authors have been conducted to investigate the oxidation behavior of the materials at high temperature steam, an oxidation model that can predict reliable oxidation kinetics of the materials is still on demand. In this work, oxidation behavior of Cr-coated Zry is studied via a thermogravimetric system at 1200 1350
1350 C. Oxidation rate and kinetics based on the mass change of the samples during the tests are then reported and discussed. Results of this investigation showed that oxidation kinetics of the materials followed linear law at 1200
C. Oxidation rate and kinetics based on the mass change of the samples during the tests are then reported and discussed. Results of this investigation showed that oxidation kinetics of the materials followed linear law at 1200 C and parabolic laws at temperatures above 1300
C and parabolic laws at temperatures above 1300 C.
C.