Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Watanabe, Masaya; Tsukada, Manabu*; Hoshino, Kazutoyo*; Hirai, Koki; Ikegami, Yuta*; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Hatakeyama, Yuichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-029, 36 Pages, 2024/03
At the Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF), the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220" was relocated from the 4th research building of the Nuclear Science Research Institute in FY2019, and the use of gamma ray irradiation has begun. Initially, Fuel Cycle Safety Research Group, Fuel Cycle Safety Research Division, Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, the owner of this device, conducted the tests as the main user, but since 2022, other users, including those outside the organization, have started using it. The gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220" is manufactured by Nordion International Inc. in Canada. Since it was purchased in 1989, the built-in 60Co radiation source has been updated once, and safety research related to nuclear fuel cycles, etc. It is still used for this purpose to this day. This report summarizes the equipment overview of the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220", its permits and licenses at WASTEF, usage status, maintenance and inspection, and future prospects.
Yamashita, Naoki; Aoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Tagami, Susumu
JAEA-Technology 2023-028, 22 Pages, 2024/03
At the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), which is currently undergoing decommissioning, there is growing interest in the effects of radiation-emitting radionuclides such as  Sr and
Sr and  Cs on the structural integrity. In particular, the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, which is used in many parts of 1F, is known to change depending on metal cations in solution, but the effects of
Cs on the structural integrity. In particular, the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, which is used in many parts of 1F, is known to change depending on metal cations in solution, but the effects of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs on corrosion are not yet understood. In addition, it is important to investigate the distribution of
Cs on corrosion are not yet understood. In addition, it is important to investigate the distribution of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the rust layer in order to understand the corrosion behavior, but the method has not yet been established. In this study, a glove box was prepared to conduct corrosion tests of carbon steel in NaCl containing
Cs in the rust layer in order to understand the corrosion behavior, but the method has not yet been established. In this study, a glove box was prepared to conduct corrosion tests of carbon steel in NaCl containing  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in the glove box. In addition, in order to clarify the influence of
Cs in the glove box. In addition, in order to clarify the influence of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs, which exist as metal cations in the solution, on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, we attempted to establish a detection method for radioactive materials in the rust layer using an imaging plate.
Cs, which exist as metal cations in the solution, on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel, we attempted to establish a detection method for radioactive materials in the rust layer using an imaging plate.
Yamashita, Naoki; Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki; Sano, Naruto; Tagami, Susumu
JAEA-Technology 2022-035, 29 Pages, 2023/03
In the treatment process of the current commercial reprocessing plant (Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant), the high-level liquid waste concentrator is the equipment that treats the most corrosive solution. In the high-level liquid waste concentrator, the extracted liquid waste after separation of uranium and plutonium is heated, concentrated, and reduced in volume. Therefore, the amount of gamma- rays emitted from fission products and the concentration of corrosive metal ion species such as neptunium-237 ( Np) are the highest in the reprocessing process, and the amount of corrosion in the high-level liquid waste concentrate canner is expected to be large. In this study, in order to clarify the effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction of stainless steel in nitric acid solutions containing
Np) are the highest in the reprocessing process, and the amount of corrosion in the high-level liquid waste concentrate canner is expected to be large. In this study, in order to clarify the effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction of stainless steel in nitric acid solutions containing  Np from the electrochemical viewpoint, the corrosion test apparatus for heat transfer surfaces in an airtight concrete cell at the Waste Safety TEsting Facility (WASTEF) of Nuclear Science Research Institute was modified to enable electrochemical measurements under gamma-ray irradiation. The effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction taking place on the stainless steel surface was discussed from the electrochemical test results obtained. As a result, changes in the immersion potentials of stainless steel and the polarization curves due to chemical species caused by radiolysis of gamma-ray irradiation were confirmed.
Np from the electrochemical viewpoint, the corrosion test apparatus for heat transfer surfaces in an airtight concrete cell at the Waste Safety TEsting Facility (WASTEF) of Nuclear Science Research Institute was modified to enable electrochemical measurements under gamma-ray irradiation. The effect of gamma-rays on the corrosion reaction taking place on the stainless steel surface was discussed from the electrochemical test results obtained. As a result, changes in the immersion potentials of stainless steel and the polarization curves due to chemical species caused by radiolysis of gamma-ray irradiation were confirmed.
Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Hoshino, Kazutoyo*; Tsukada, Manabu*; Sawauchi, Fumiya*; Otake, Yoshinori; Ichise, Kenichi; Tagami, Susumu
JAEA-Technology 2022-034, 47 Pages, 2023/03
The Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF) was established in 1982 as an experimental facility for long-term storage of solidified high-level radioactive waste generated in the reprocessing of spent light water reactor fuel and the subsequent safety assessment of geological disposal. It is a historic facility that started operation in 1982. This facility consists of 5 concrete cells, 1 lead cell, 6 glove boxes, and 7 hoods, and is a large-scale facility that can use nuclear fuel materials including uranium and plutonium and radioactive isotopes including TRU. In this facility, research and development requested by the research department is carried out in the Hot Material Examination Section. In addition, patrol inspections, self-inspections, etc. are also carried out as maintenance management based on safety regulations. This report summarizes the overview of WASTEF facilities, the results of operation, maintenance and management work in FY2021, and the future outlook.
Tobita, Daiki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Yamashita, Susumu; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Sugawara, Takanori
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
 Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steel
Sr dissolved solution on corrosion potential of type 316L stainless steelAoyama, Takahito; Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.110 - 115, 2022/04
no abstracts in English
 Np
NpIrisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki; Yamashita, Naoki; Sano, Naruto
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(3), p.70 - 74, 2022/03
In order to evaluate the corrosion of stainless steels used in spent nuclear fuel reprocessing facilities, the immersion corrosion tests and polarization measurements were performed using R-SUS304ULC stainless steel in nitric acid solution containing a kind of radionuclides,  Np. At temperatures above 328 K, the corrosion potential was higher than that in nitric acid solution and was near the transpassive region. From the comparison between the corrosion amount calculated by the immersion corrosion tests and the polarization resistance, the values of
Np. At temperatures above 328 K, the corrosion potential was higher than that in nitric acid solution and was near the transpassive region. From the comparison between the corrosion amount calculated by the immersion corrosion tests and the polarization resistance, the values of  =0.018-0.025 V were obtained as a conversion factor, and the possibility of calculating the corrosion amount from the electrochemical measurement was examined.
=0.018-0.025 V were obtained as a conversion factor, and the possibility of calculating the corrosion amount from the electrochemical measurement was examined.
Koyama, Shinichi; Nakagiri, Toshio; Osaka, Masahiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Takano, Masahide; et al.
Hairo, Osensui Taisaku jigyo jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 144 Pages, 2021/08
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy and Thermal Behavior Estimation of Fuel Debris))" in 2020JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management.
Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Amamoto, Ippei; Yokozawa, Takuma; Yamashita, Teruo; Nagai, Takayuki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Takebe, Hiromichi*; Mitamura, Naoki*; Tsuzuki, Tatsuya*
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2013) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2013/09
no abstracts in English
 as the dominant sludge constituent generated from the treatment of water used for cooling the stricken power reactors
as the dominant sludge constituent generated from the treatment of water used for cooling the stricken power reactorsAmamoto, Ippei; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Yokozawa, Takuma; Yamashita, Teruo; Nagai, Takayuki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Takebe, Hiromichi*; Mitamura, Naoki*; Tsuzuki, Tatsuya*
Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2013) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/09
The great amount of water used for cooling the stricken power reactors at Fukushima Dai-ichi has resulted in accumulation of "remaining water". As the remaining water is subsequently contaminated by FPs, etc., it is necessary to decontaminate it in order to reduce the volume of liquid radioactive waste and to reuse it again for cooling the reactors. Various techniques are being applied to remove FP, etc. and to make stable waste forms. One of the methods using the iron phosphate glass as a medium is being developed to stabilize the strontium-bearing sludge whose main component is BaSO . From the results hitherto, the iron phosphate glass is regarded as a potential medium for the target sludge.
. From the results hitherto, the iron phosphate glass is regarded as a potential medium for the target sludge.
 Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O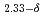 through
through  neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 K
neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 KIto, Takanori*; Hirai, Takene*; Yamashita, Junichi*; Watanabe, Shoji*; Kawata, Etsuya*; Kitamura, Naoto*; Idemoto, Yasushi*; Igawa, Naoki
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 405(8), p.2091 - 2096, 2010/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:55.02(Physics, Condensed Matter)We analyze the mechanism of oxygen ion diffusion in (Ba Sr
Sr )(Co
)(Co Fe
Fe )O
)O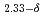 by using the Rietveld refinement, the maximum entropy method (MEM) analysis, and MEM-based pattern fitting (MPF) with
by using the Rietveld refinement, the maximum entropy method (MEM) analysis, and MEM-based pattern fitting (MPF) with  neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 K. We speculate that when
neutron diffractions at 300 and 720 K. We speculate that when 
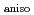 and neutron scattering density of O1(4
and neutron scattering density of O1(4 ) site with a large number of vacancies metamorphose into that with anisotropy directed toward the O1(4
) site with a large number of vacancies metamorphose into that with anisotropy directed toward the O1(4 ) and O2(8
) and O2(8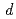 ) sites at 720 K, the oxygen ions diffuse along the paths between O1(4
) sites at 720 K, the oxygen ions diffuse along the paths between O1(4 ) and O1(4
) and O1(4 ), and O1(4
), and O1(4 ) and O2(8
) and O2(8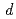 ).
).
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Yamashita, Kiyonobu*; Nojiri, Naoki; Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Fujisaki, Shingo; Nakano, Masaaki*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 150(3), p.310 - 321, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:40.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)Annular cores were formed in startup-core-physics tests of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) to obtain experimental data for verification of calculation codes. The first criticality, control rod positions at critical conditions, neutron flux distribution, excess reactivity etc. were measured as representative data. These data were evaluated with Monte Carlo code MVP that can consider the heterogeneity of coated fuel particles (CFP) distributed randomly in fuel compacts directly. It was made clear that the heterogeneity effect of CFP on reactivity for annular cores is smaller than that for fully-loaded cores. Measured and calculated effective multiplication factors (k) were agreed with differences less than 1% k. Measured neutron flux distributions agreed with calculated results. The revising method was applied for evaluation of excess reactivity to exclude negative shadowing effect of control rods. The revised and calculated excess reactivity agreed with differences less than 1%
k. Measured neutron flux distributions agreed with calculated results. The revising method was applied for evaluation of excess reactivity to exclude negative shadowing effect of control rods. The revised and calculated excess reactivity agreed with differences less than 1% k/k.
k/k.
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Nojiri, Naoki; Ando, Hiroei*; Yamashita, Kiyonobu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 233(1-3), p.23 - 36, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:63.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the nuclear design of the HTTR, the reactivity balance is planned so that the design requirements are fully satisfied. Moreover, the reactivity coefficients are evaluated to confirm the safety characteristics of the reactor. The power distribution in the core was optimized by changing the uranium enrichment to maintain the fuel temperature at less than the limit (1600 C). Deviation from the optimized distribution due to the burnup of fissile materials was avoided by flattening time-dependent changes in local reactivities. Flattening was achieved by optimizing the specifications of the burnable poisons. The original nuclear design model had to be modified based on the first critical experiments. The Monte Carlo code MVP was also used to predict criticality of the initial core. The predicted excess reactivities are now in good agreement with the experimental results.
C). Deviation from the optimized distribution due to the burnup of fissile materials was avoided by flattening time-dependent changes in local reactivities. Flattening was achieved by optimizing the specifications of the burnable poisons. The original nuclear design model had to be modified based on the first critical experiments. The Monte Carlo code MVP was also used to predict criticality of the initial core. The predicted excess reactivities are now in good agreement with the experimental results.
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Nojiri, Naoki; Yamashita, Kiyonobu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 233(1-3), p.155 - 162, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)The HTTR uses low-enriched uranium fuel with burnable poison rod. For validation of the nuclear design code system for the HTTR, a critical assembly of VHTRC had been constructed. The calculation uncertainties of effective multiplication factor, neutron flux distribution, burnable poison reactivity worth, and control rod worth, temperature coefficients were evaluated. Calculation accuracy of a Monte Carlo code is also evaluated.
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Nojiri, Naoki; Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Shimakawa, Satoshi; Ando, Hiroei; Mori, Takamasa
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Monte Karuro Ho Ni Yoru Ryushi Shimyureshon No Genjo To Kadai, p.201 - 210, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
 ray from fuel of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor; Method of measurement and results
ray from fuel of High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor; Method of measurement and resultsFujimoto, Nozomu; Nojiri, Naoki; Takada, Eiji*; Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Kikuchi, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Kojima, Takao; Umeta, Masayuki; Hoshino, Osamu; Kaneda, Makoto*; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2001-002, 64 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Nakano, Masaaki*; Nojiri, Naoki; Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Fujisaki, Shingo; Yamashita, Kiyonobu
JAERI-Conf 99-006, p.328 - 333, 1999/08
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Kiyonobu; Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Fujimoto, Nozomu; Fujisaki, Shingo; Nakano, Masaaki*; Nojiri, Naoki; Tamura, Seiji*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 41(1), p.35 - 38, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Nojiri, Naoki; Nakano, Masaaki; Ando, Hiroei; Fujimoto, Nozomu; Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Fujisaki, Shingo; Yamashita, Kiyonobu
JAERI-Tech 98-032, 59 Pages, 1998/08
no abstracts in English
Fujimoto, Nozomu; Nojiri, Naoki; Nakano, Masaaki*; Takeuchi, Mitsuo; Fujisaki, Shingo; Yamashita, Kiyonobu
JAERI-Tech 98-021, 66 Pages, 1998/06
no abstracts in English