Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 10
10 W/cm
W/cm
Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Ryazantsev, S. N.*; Kulikov, R. K.*; Sedov, M. V.*; Filippov, E. D.*; Pikuz, S. A.*; Asai, Takafumi*; Kanasaki, Masato*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Jinno, Satoshi; et al.
Photonics (Internet), 10(11), p.1250_1 - 1250_11, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.78(Optics)It is challenging to clearly distinguish the impacts of the optical field and collisional ionization in the evolution of the charge state of a plasma produced when matter interacts with high-intensity laser pulses. In this work, time-dependent calculations of plasma kinetics are used to show that it is possible only when low-density gaseous targets with sufficiently small clusters are used. In the case of Ar plasma, the upper limit of the cluster radius was estimated to be 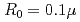 m.
m.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko*; Sakaki, Hironao*; Esirkepov, T. Zh.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Pirozhkov, A. S.*; Sagisaka, Akito*; et al.
Plasma Physics Reports, 42(4), p.327 - 337, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:54.81(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A combination of a petawatt laser and nuclear physics techniques can crucially facilitate the measurement of exotic nuclei properties. With numerical simulations and laser-driven experiments we show prospects for the Laser-driven Exotic Nuclei extraction-acceleration method proposed in [M. Nishiuchi et al., Phys. Plasmas 22, 033107 (2015)]: a femtosecond petawatt laser, irradiating a target bombarded by an external ion beam, extracts from the target and accelerates to few GeV highly charged short-lived heavy exotic nuclei created in the target via nuclear reactions.
Kanasaki, Masato; Jinno, Satoshi*; Sakaki, Hironao; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Fukuda, Yuji
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 58(3), p.034013_1 - 034013_6, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:78.41(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to understand the synergetic interplay between the Coulomb explosion of clusters and the background gas dynamics, we have conducted ion acceleration experiments using CO clusters (250 nm in dia.) embedded in background H
clusters (250 nm in dia.) embedded in background H gas with the J-KAREN laser (1 J, 40 fs, 10
gas with the J-KAREN laser (1 J, 40 fs, 10 contrast) at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of etch pit positions on CR-39 and their structures including the etch pit growth behavior analysis with the multi-step etching technique, energy spectra for protons from the background gas and carbon/oxygen ions from the clusters are obtained separately. The maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are determined as 1.6 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles.
contrast) at JAEA-KPSI. By a careful analysis of etch pit positions on CR-39 and their structures including the etch pit growth behavior analysis with the multi-step etching technique, energy spectra for protons from the background gas and carbon/oxygen ions from the clusters are obtained separately. The maximum energies of protons and carbon/oxygen ions are determined as 1.6 MeV and 1.1 MeV/u, respectively. Based on the experimental results, the acceleration mechanism of the background gas ions induced by Coulomb explosion of clusters is discussed with the help from numerical simulations which employ a particle-in-cell (PIC) method including relaxation and ionization processes of plasma particles.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T. A.*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Kanasaki, Masato; et al.
Research Using Extreme Light; Entering New Frontiers with Petawatt-Class Lasers II (Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.9515), p.95151D_1 - 95151D_4, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Experimental demonstration of multi-charged heavy ion acceleration from the interaction between the ultra-intense short pulse laser system and the metal target is presented. The laser pulse of  10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of
10 J laser energy, 36 fs pulse width, and the contrast level of  10
10 from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of
from 200 TW class Ti:sapphire J-KAREN laser system at JAEA is used in the experiment. Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated. This is achieved by the high intensity laser field of  10
10 Wcm
Wcm interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
interacting with the solid density target. The demonstrated iron ions with high charge to mass ratio (Q/M) is difficult to be achieved by the conventional heavy ion source technique in the accelerators.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Pikuz, T.*; Faenov, A.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; Orlandi, R.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 22(3), p.033107_1 - 033107_8, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:96.14(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Almost fully stripped Fe ions accelerated up to 0.9 GeV are demonstrated with a 200 TW femtosecond high-intensity laser irradiating a micron-thick Al foil with Fe impurity on the surface. An energetic low-emittance high-density beam of heavy ions with a large charge-to-mass ratio can be obtained, which is useful for many applications, such as a compact radio isotope source in combination with conventional technology.
Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Maeda, Shota; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukami, Tomoyo; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02A705_1 - 02A705_4, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)High intensity laser-plasma interaction has attracted considerable interest for a number of years. The laser-plasma interaction is accompanied by generation of various charged particle beams. Results of simultaneous novel measurements of electron-induced photonuclear neutrons (photoneutron), which are a diagnostic of the laser-plasma interaction, are proposed to use for optimization of the laser-plasma ion generation. The proposed method is demonstrated by the laser irradiation with the intensity os 1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
on the metal foil target. The photoneutrons are measured by using NE213 liquid scintillation detectors. Heavy-ion signal is registered with the CR39 track detector simultaneously. The measured signals of the electron-induced photoneutrons are well reproduced by using the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). The results obtained provide useful approach for analyzing the various laser based ion beams.
Kanasaki, Masato; Fukuda, Yuji; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*
Reza Kenkyu, 42(2), p.168 - 173, 2014/02
In laser-driven ion acceleration experiments using the cluster-gas targets, a significant amount of fast electrons, which drives the ion acceleration, are produced along with high energy ions with several-tens of MeV. In our recent experiment using CO clusters embedded in H
clusters embedded in H gas conducted with the J-KAREN laser facility (1 J, 40 fs) at JAEA-KPSI, the maximum energy of electrons reaches up to 200 MeV. Such fast electrons can produce photo-neutrons via bremsstrahlung processes followed by photo-nuclear reactions. When the CR-39 is exposed to photo-neutrons, it records etchable tracks of generated ions depending on their species and energy as background noises. In order to diagnose the laser-accelerated protons precisely using CR-39, we have developed the discrimination method for laser-accelerated protons and photo-neutrons on CR-39 based on the incident angle and incident energy.
gas conducted with the J-KAREN laser facility (1 J, 40 fs) at JAEA-KPSI, the maximum energy of electrons reaches up to 200 MeV. Such fast electrons can produce photo-neutrons via bremsstrahlung processes followed by photo-nuclear reactions. When the CR-39 is exposed to photo-neutrons, it records etchable tracks of generated ions depending on their species and energy as background noises. In order to diagnose the laser-accelerated protons precisely using CR-39, we have developed the discrimination method for laser-accelerated protons and photo-neutrons on CR-39 based on the incident angle and incident energy.
Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Kanasaki, Masato; Yogo, Akifumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Tampo, Motonobu*; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Hayashi, Yukio; Kando, Masaki; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8779 (Internet), p.87790F_1 - 87790F_7, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Biomedical)We demonstrate a new ion diagnosis method for high energy ions by utilizing a combination of a single CR-39 detector and plastic plates, which enables to detect high energy ions beyond the detection threshold limit of the CR-39. This detection method coupled with a magnetic spectrometer is applied to identify high energy ions of 50 MeV per nucleon in laser-driven ion acceleration experiments using cluster-gas targets.
Kanasaki, Masato; Hattori, Atsuto; Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Yogo, Akifumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 50, p.46 - 49, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:71.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)A precise measurement has been made utilizing a stacked CR-39 detectors unit for laser accelerated high intensity protons. The proton beams are derived from a thin polyimide target exposed to an high intense Ti:sapphire laser 8 J energy and 40 fs duration. The sample sets, stacked radiochromic film and CR-39 detectors covered with 13  m aluminum filter, are irradiated under vacuum condition. By analyzing the etch pits on the last layer of CR-39 which recorded etchable tracks, the proton energy in high energy region is evaluate more precisely than in the past. The residual ranges for each particle in the last layer has been obtained from etch pit growth curves with multi-stepetching technique. The maximum energy of proton is 14.39
m aluminum filter, are irradiated under vacuum condition. By analyzing the etch pits on the last layer of CR-39 which recorded etchable tracks, the proton energy in high energy region is evaluate more precisely than in the past. The residual ranges for each particle in the last layer has been obtained from etch pit growth curves with multi-stepetching technique. The maximum energy of proton is 14.39 0.05 MeV. This method allows us to measure the maximum energy of proton precisely, which is obtained up to the hundredth place in unit of MeV in the laser-driven particle acceleration experiment.
0.05 MeV. This method allows us to measure the maximum energy of proton precisely, which is obtained up to the hundredth place in unit of MeV in the laser-driven particle acceleration experiment.
Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Kanasaki, Masato; Yogo, Akifumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Tampo, Motonobu; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Pikuz, T.; Hayashi, Yukio; Kando, Masaki; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 50, p.92 - 96, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:67.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new diagnosis method for high energy ions utilizing a single CR-39 detector mounted on plastic plates is demonstrated to identify the presence of the high energy component beyond the CR-39's detection threshold limit. On irradiation with a 25 MeV per nucleon He ion beam from conventional rf-accelerators, a large number of etch pits having elliptical opening shapes are observed on the rear surface. Detailed investigations reveal that these etch pits are created by heavy ions inelastically backscattered from the plastic plates. This ion detection method is applied to laser-driven ion acceleration experiments using cluster-gas targets, and acceleration of ions with energies up to 50 MeV per nucleon are identified.
Kanasaki, Masato; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko*; Tampo, Motonobu; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oda, Keiji*; Kondo, Kiminori
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.142 - 147, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.30(Physics, Applied)A new diagnosis method has been developed utilizing back scattered particles for high energy intense ion beams. The CR-39 detector mounted on the uniform back-scatterer was irradiated with  He
He ions with an energy 25 MeV/n, which is never recorded as etchable track in CR-39. We found that it is possible to diagnose the high energy intense ion beams by analyzing the etch pits created on the rear surface of CR-39 that directly contacted on the back-scatterers. It turns out that most of etch pits in the rear surface are made by the backscattered particles through the investigation of the growth pattern of each etch pit with multi-step etching technique. This method allows simple diagnosis of the ion beam profile and the presence of high energy component of ions beyond the detection threshold limit of the CR-39 in mixed radiation fields such as laser-driven ion acceleration experiments.
ions with an energy 25 MeV/n, which is never recorded as etchable track in CR-39. We found that it is possible to diagnose the high energy intense ion beams by analyzing the etch pits created on the rear surface of CR-39 that directly contacted on the back-scatterers. It turns out that most of etch pits in the rear surface are made by the backscattered particles through the investigation of the growth pattern of each etch pit with multi-step etching technique. This method allows simple diagnosis of the ion beam profile and the presence of high energy component of ions beyond the detection threshold limit of the CR-39 in mixed radiation fields such as laser-driven ion acceleration experiments.
Kanasaki, Masato; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko; Tampo, Motonobu; Kondo, Kiminori; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(5), p.056401_1 - 056401_4, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:25.60(Physics, Applied)A single CR-39 detector mounted on plastic plates is irradiated with a 100 MeV He ion beam. Although the beam energy is much greater than the detection threshold limit of the CR-39 detector, a large number of etch pits having elliptical openings are observed on the rear surface. Detailed investigations reveal that these etch pits are created by heavy ions inelastically backscattered from the plastic plates. This method allows a simple diagnosis of the ion beam profile and the presence of the high-energy component beyond the detection threshold limit of the CR-39 detector, especially in mixed-radiation fields such as laser-driven ion acceleration experiments.
Kanasaki, Masato; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kondo, Kiminori; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hattori, Atsuto*; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(5), p.261 - 275, 2012/05
CR-39 solid state nuclear track detector, which was developed for optical lens, has been applied for various field such as radon surveys, measurement of galactic cosmic ray, cell irradiation experiment and so on. The CR-39 detectors have the great advantages of being insensitive to high energy photons and electrons and capable of detecting only ions in the mixed fields such as laser driven relativistic plasmas. Though there are some analytical methods of CR-39 to diagnose ion beam, unfortunately, only few researchers in the field of plasma know the methods. This article looks at how to use CR-39 detectors and introduce the accomplishment of the joint study JAEA and Kobe Univ. for application of CR-39 detectors to ion beam diagnosis.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sakaki, Hironao; Ogura, Koichi; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Kanasaki, Masato; Yogo, Akifumi; Hori, Toshihiko; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 19(3), p.030706_1 - 030706_4, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:24.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A 7 MeV proton beam collimated to 16 mrad containing more than 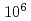 particles is experimentally demonstrated by focusing a 2J, 60 fs pulse of a Ti:sapphire laser onto targets of different materials and thicknesses placed in a millimeter scale conical holder. The electric potential induced on the target holder by laser-driven electrons accelerates and dynamically controls a portion of a divergent quasi-thermal proton beam originated from the target, producing a quasi-monoenergetic "pencil" beam.
particles is experimentally demonstrated by focusing a 2J, 60 fs pulse of a Ti:sapphire laser onto targets of different materials and thicknesses placed in a millimeter scale conical holder. The electric potential induced on the target holder by laser-driven electrons accelerates and dynamically controls a portion of a divergent quasi-thermal proton beam originated from the target, producing a quasi-monoenergetic "pencil" beam.
Fukuda, Yuji; Tampo, Motonobu; Sakaki, Hironao; Kondo, Kiminori; Kanasaki, Masato; Yamauchi, Tomoya*
Hoshasen, 37(3), p.169 - 172, 2011/10
In the laser-driven ion acceleration experiments, it is almost impossible to predict maximum ion energy in advance, because the maximum energy varies according to experimental condition. Recently, solid state nuclear track detectors such as CR-39 detectors have been extensively used in laser-driven ion acceleration experiments. This is because the CR-39 have a great advantage that they are insensitive to high energy photons and electrons and capable of detecting only ions. However, the CR-39 cannot detect fast ions with energies beyond its detection threshold limit. A stack of CR-39 or a method utilizing backscattered particles are developed to detect high energy ions. Moreover, vacuum effects on CR-39 make it difficult to identify ion energies and ion species. We introduce applications of CR-39 detectors in laser-driven particle acceleration experiments in JAEA-KPSI.
Kanasaki, Masato; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Hori, Toshihiko*; Tampo, Motonobu; Kondo, Kiminori; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kamiya, Tomihiro
Hoshasen, 37(3), p.127 - 132, 2011/10
A diagnosis method has been developed utilizing back scattered particles with the single PADC detector for high energy intense ion beams. The PADC detector mounted on the uniform back-scatterer was irradiated with He ions with an energy of 100 MeV, which is never recorded as etchable tracks in PADC. It turns out that most of etch pits in the rear surface are made by the back-scattered particles through the investigation of the growth pattern of each etch pit. This method allows simple diagnosis of the ion beam profile and intensity distribution with wide energy range in mixed radiation fields such as laser-driven ion acceleration experiments.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A.*; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
Progress in Ultrafast Intense Laser Science VII, p.225 - 240, 2011/05
 http://www.springer.com/physics/atomic,+molecular,+optical+%26+plasma+physics/book/978-3-642-18326-3
http://www.springer.com/physics/atomic,+molecular,+optical+%26+plasma+physics/book/978-3-642-18326-3We present substantial enhancement of the accelerated ion energies up to 10-20 MeV per nucleon by utilizing the unique properties of the cluster-gas target irradiated with 40-fs laser pulses of only 150 mJ energy, corresponding to approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using thin foil targets. A particle-in-cell simulation infers that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in sub-critical density plasmas. The demonstrated method can be important in the development of efficient laser ion accelerators for hadron therapy and other applications.
Fukuda, Yuji; Faenov, A. Y.; Tampo, Motonobu; Pikuz, T. A.*; Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Kando, Masaki; Hayashi, Yukio; Yogo, Akifumi; Sakaki, Hironao; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(16), p.165002_1 - 165002_4, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:171 Percentile:96.61(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A new approach for accelerating ions, based on the use of a cluster-gas target and a compact ultrashort pulse laser, is presented. It is shown that ions with energy 10-20 MeV per nucleon having a small divergence (full angle) of 3.4 are generated, corresponding to an approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell code simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in near-critical density plasmas.
are generated, corresponding to an approximately tenfold increase in the ion energies compared to previous experiments using solid targets. It is inferred from a particle-in-cell code simulation that the high energy ions are generated at the rear side of the target due to the formation of a strong dipole vortex structure in near-critical density plasmas.
Oda, Keiji*; Imasaka, Yuichi*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Nakane, Yoshihiro; Endo, Akira; Tawara, Hiroko*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
Radiation Measurements, 40(2-6), p.570 - 574, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Oda, Keiji*; Ichijo, H.*; Miyawaki, Nobumasa*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*; Nakane, Yoshihiro
Radiation Measurements, 34(1-6), p.171 - 175, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.93(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English