Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Miyata, Noboru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Bigault, T.*; Saerbeck, T.*; Courtois, P.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 130(8), p.083904_1 - 083904_10, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.56(Physics, Applied)Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Miyata, Noboru*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011092_1 - 011092_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
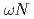 scattering length from
scattering length from  photoproduction on the proton near the reaction threshold
photoproduction on the proton near the reaction thresholdIshikawa, Takatsugu*; Fujimura, Hisako*; Fukasawa, Hiroshi*; Hashimoto, Ryo*; He, Q.*; Honda, Yuki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Iwata, Takahiro*; Kaida, Shun*; Kasagi, Jirota*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(5), p.052201_1 - 052201_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:44.35(Physics, Nuclear)Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 22, p.011011_1 - 011011_5, 2018/11
Neutron multilayer mirrors are one of the most important optical elements for neutron scattering experiments. Good interface quality in terms of sharpness and smoothness plays a critical role in determining the performance of optical elements. We have shown that a multilayer with a large vertical correlation length and small lateral correlation length effectively suppresses the diffuse scattering intensity. In this study, the effect of the interface roughness correlation on the neutron reflectivity of the multilayer mirror is investigated using the reflectivity calculation based on the distorted wave Born approximation.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Miyata, Noboru*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Takeda, Masayasu; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 888, p.70 - 78, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.78(Instruments & Instrumentation)The multilayer structure of Fe/Si and Fe/Ge systems fabricated by ion beam sputtering (IBS) was investigated using X-ray and polarized neutron reflectivity measurements and scanning transmission electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis. The obtained result revealed that the incorporation of sputtering gas particles (Ar) in the Ge layer gives rise to a marked reduction in the neutron scattering length density (SLD) and contributes to the SLD contrast between the Fe and Ge layers almost vanishing for spin-down neutrons. This leads to a possibility of fine-tuning of the SLD for the IBS, which is required to realize a high polarization efficiency of a neutron polarizing supermirror. Fe/Ge polarizing supermirror with 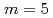 fabricated showed a spin-up reflectivity of 0.70 at the critical momentum transfer. The polarization was higher than 0.985 for the
fabricated showed a spin-up reflectivity of 0.70 at the critical momentum transfer. The polarization was higher than 0.985 for the 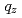 range where the correction for the polarization inefficiencies of the beamline works properly.
range where the correction for the polarization inefficiencies of the beamline works properly.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Bigault, T.*; Wildes, A. R.*; Dewhurst, C. D.*; Saerbeck, T.*; Honecker, D.*; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Courtois, P.*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 862(1), p.012017_1 - 012017_6, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:90.11(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The in-plane magnetic structure of Fe/Si multilayers with a polycrystalline grain size less than the ferromagnetic exchange length was investigated using polarized neutron off-specular scattering and grazing-incidence small-angle scattering measurements. These complementary measurements, each of them covering different length scales, together with the data analysis based on the distorted wave Born approximation, revealed lateral correlation in the fluctuating orientation of the magnetization in the layer on a sub- m length scale. The obtained in-plane magnetic structure is consistent with the random anisotropy model, i.e. competition between the exchange interactions between neighboring spins and the local magnetocrystalline anisotropy.
m length scale. The obtained in-plane magnetic structure is consistent with the random anisotropy model, i.e. competition between the exchange interactions between neighboring spins and the local magnetocrystalline anisotropy.
Tamura, Itaru; Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Nakamura, Kiyoshi; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Aizawa, Kazuya; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 528, p.012012_1 - 012012_7, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.13(Optics)To achieve efficient implementation of usage of neutron beam instruments, the instruments were rearranged at C2 cold neutron beam line at JRR-3 by using a newly developed compact vertical splitting system. The splitting system has two compact multi channel benders. The bender has been developed using Ni/Ti supermirrors coated on both sides of 0.2 mm thickness silicon substrates. The curvature radius of the bender is 938 mm and the length of the bender is 320 mm yielding deflection angles of 20 . Supermirrors with m=3 were deposited on both sides of silicon substrate by an ion beam sputtering apparatus in JAEA. Neutron flux at the end of the neutron guide that installed at the bender exit of which the deflection angle is 20
. Supermirrors with m=3 were deposited on both sides of silicon substrate by an ion beam sputtering apparatus in JAEA. Neutron flux at the end of the neutron guide that installed at the bender exit of which the deflection angle is 20 was measured by the gold foil activation method. It was measured 1.58
was measured by the gold foil activation method. It was measured 1.58  10
10 n/cm
n/cm /s. The present study showed that the supermirrors coated on both sides with high reflectivity are suitable for the compact bender.
/s. The present study showed that the supermirrors coated on both sides with high reflectivity are suitable for the compact bender.
Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Kubota, Masato; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Chinese Journal of Physics, 50(2), p.161 - 170, 2012/04
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Okayasu, Satoru; Takeda, Masayasu; Zettsu, Nobuyuki*; Nagano, Mikinori*; Yamamura, Kazuya*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Journal of Applied Physics, 111(6), p.063904_1 - 063904_10, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:18.13(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Asaoka, Hidehito; Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Takeda, Masayasu; Shamoto, Shinichi
Thin Solid Films, 520(8), p.3300 - 3303, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We succeeded in realizing the epitaxial growth of a Sr layer on Si(111) with an atomically abrupt heterointerface - in spite of its large lattice mismatch (12%) with Si - by introducing a monoatomic layer of H on Si. In order to identify the buried H, we carried out a combination analysis involving neutron reflectometry and resonant nuclear reaction of  H(
H( N,
N,
 )
) C analysis. We found different neutron reflectivity profiles resulting from a contrast variation between the H and D atoms at the buried heterointerface. Furthermore, the depth
C analysis. We found different neutron reflectivity profiles resulting from a contrast variation between the H and D atoms at the buried heterointerface. Furthermore, the depth  -ray intensity profiles revealed that the H at the heterointerface acts as an effective buffer layer that enables it to manage the highly mismatched epitaxy on Si.
-ray intensity profiles revealed that the H at the heterointerface acts as an effective buffer layer that enables it to manage the highly mismatched epitaxy on Si.
Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Maruyama, Ryuji; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Tasaki, Seiji*; Hino, Masahiro*; Matsubayashi, Masahito
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 634(1, Suppl.), p.S90 - S93, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)In a neutron spin interferometer (NSI), incident neutrons are in states of up- and down-spin eigenstates and a phase difference between the eigenstates is observed after transmission through a magnetic sample. Since the phase difference is proportional to an integral of magnetic field along a trajectory of neutrons, NSI imaging provides projection images of a distribution of magnetic field in the sample. We tried to visualize magnetic field in permalloy film with and without stress as a demonstration of the NSI imaging. An experiment was carried out at C3-1-2-2, MINE2 port at the neutron guide hall of JRR-3M with wavelength of 0.88nm and wavelength resolution of 0.3% in FWHM. Permalloy film with thickness of 0.1 mm was used as a sample and was stressed by bending with angles of 45 and 180  . As a result, images of decrease of a saturated magnetization and an increase of leak magnetic field with increasing the bending angle were obtained.
. As a result, images of decrease of a saturated magnetization and an increase of leak magnetic field with increasing the bending angle were obtained.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Hino, Masahiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Achiwa, Norio*; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2594 - 2599, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.75(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron resonance spin echo (NRSE) is one of the most useful techniques for quasi-elastic scattering with high energy resolution. The path length variation due to the beam divergence has to be corrected in high resolution NRSE measurement because it gives the limit in the energy resolution. A neutron focusing technique using neutron supermirrors is effective to overcome this problem. When a cylindrical shaped neutron supermirror placed in the center of the flight path with a pair of RSFs has the object and the image plane corresponding to the each coil plane of the first and the second RSF, the path length difference can be corrected for the neutron beam with large divergent angle, which leads to the realization of high intensity as well as high resolution in NRSE measurement. In this study, the correction method of the beam divergence with a cylindrical shaped supermirror and its experimental results are discussed.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Journal of Applied Physics, 105(8), p.083527_1 - 083527_8, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:62.18(Physics, Applied)Neutron supermirrors are one of the most useful multilayer devices in neutron experiments since a polychromatic neutron beam can be reflected. The diffuse intensity from a supermirror has to be suppressed since it causes a serious problem of low signal to background noise in focusing systems. The diffuse intensity can be decreased by more than an order of magnitude by adopting NiC/Ti multilayers instead of conventional Ni/Ti multilayers, which leads to a high performance focusing system with a diffuse intensity down to the order of 10 of the specular intensity. In this study, in order to obtain the mechanism that controls the diffuse intensity from a supermirror, we investigated the crystal structure of Ni and NiC monolayers and the interface structure of Ni/Ti and NiC/Ti multilayers and demonstrated that a multilayer with a large vertical correlation length and a small lateral correlation length effectively suppresses the diffuse intensity from a supermirror.
of the specular intensity. In this study, in order to obtain the mechanism that controls the diffuse intensity from a supermirror, we investigated the crystal structure of Ni and NiC monolayers and the interface structure of Ni/Ti and NiC/Ti multilayers and demonstrated that a multilayer with a large vertical correlation length and a small lateral correlation length effectively suppresses the diffuse intensity from a supermirror.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.68 - 70, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron supermirrors have been utilized as reflective optical devices at many neutron sources for transporting, focusing, polarizing neutron beam. In order to produce such devices for the new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), an ion beam sputtering system with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m has been installed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The fabrication methods and the performance of the supermirrors are discussed.
has been installed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The fabrication methods and the performance of the supermirrors are discussed.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Thin Solid Films, 515(14), p.5704 - 5706, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:81.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The development of neutron supermirrors is important for neutron scattering experiments since it offers a considerable increase in the available neutron intensity. Up to now, many studies have been carried out to realize high reflectivity and large  , where
, where  is the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel. We have developed neutron supermirrors by employing the ion beam sputtering (IBS) technique because it enables the production of layers with high density and small grain size. Although the IBS technique produces high quality layers, its disadvantage is that the deposition area is relatively small. In order to produce the optical devices using supermirrors, which is planned in the project of a new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), a new IBS instrument with a large deposition area whose diameter is 500 mm has been designed and installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The deposition rate has been confirmed to be almost uniform over the entire deposition area. We have carried out the development of Ni/Ti supermirror with large
is the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel. We have developed neutron supermirrors by employing the ion beam sputtering (IBS) technique because it enables the production of layers with high density and small grain size. Although the IBS technique produces high quality layers, its disadvantage is that the deposition area is relatively small. In order to produce the optical devices using supermirrors, which is planned in the project of a new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), a new IBS instrument with a large deposition area whose diameter is 500 mm has been designed and installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The deposition rate has been confirmed to be almost uniform over the entire deposition area. We have carried out the development of Ni/Ti supermirror with large  . In this presentation, the performance of those supermirrors fabricated with the IBS instrument is discussed.
. In this presentation, the performance of those supermirrors fabricated with the IBS instrument is discussed.
Yamazaki, Dai; Moriai, Atsushi; Tamura, Itaru; Maruyama, Ryuji; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2007-030, 21 Pages, 2007/03
A new neutron reflectometer "SUIREN" has been developed and started its operation at the research reactor JRR-3 of JAEA in 2006. SUIREN (Apparatus for Surface and Interface investigations with Reflection of Neutrons) provides monochromatic neutron beam with wavelength of 3.8  and vertical sample geometry, which is suitable for studies on interfaces involving solid layers of soft materials, magnetic materials, neutron mirrors and many other things. Collimated neutron intensity is about 2.1
and vertical sample geometry, which is suitable for studies on interfaces involving solid layers of soft materials, magnetic materials, neutron mirrors and many other things. Collimated neutron intensity is about 2.1 10
10
 2.6
2.6 10
10 n/s/cm
n/s/cm with =0.08 deg at the sample position. Background is as low as 4.5
with =0.08 deg at the sample position. Background is as low as 4.5 10
10 n/s when a local beam shutter is closed. A demonstration experiment showed that specular reflectivity of a silicon substrate of 3 inches in diameter can be measured down to 10
n/s when a local beam shutter is closed. A demonstration experiment showed that specular reflectivity of a silicon substrate of 3 inches in diameter can be measured down to 10 over 0
over 0  Qz
Qz  0.22
0.22 
 in 27 hours. This paper describes the beam-line and components of the SUIREN reflectometer, some results of test measurements and future plans.
in 27 hours. This paper describes the beam-line and components of the SUIREN reflectometer, some results of test measurements and future plans.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 18th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources (ICANS-18) (CD-ROM), p.197 - 200, 2007/00
The development of high performance neutron supermirrors with high reflectivity and large  , the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel, is important for the J-PARC project since it greatly increases the available neutron intensity. Neutron supermirrors consist of alternating layers of two materials with different refractive indices for neutrons. An ion beam sputtering instrument with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m
, the ratio of the effective critical angle of the supermirror to that of natural nickel, is important for the J-PARC project since it greatly increases the available neutron intensity. Neutron supermirrors consist of alternating layers of two materials with different refractive indices for neutrons. An ion beam sputtering instrument with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m has been installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in order to produce neutron guides, benders, and other neutron optical devices, which are planned for application in the J-PARC project. We have succeeded in fabricating the supermirror with large critical angle of
has been installed at the Japan Atomic Energy Agency in order to produce neutron guides, benders, and other neutron optical devices, which are planned for application in the J-PARC project. We have succeeded in fabricating the supermirror with large critical angle of 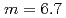 and that with high reflectivity (
and that with high reflectivity ( 85%) for
85%) for 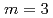 .
.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Hino, Masahiro*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 385-386(2), p.1256 - 1258, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:70.33(Physics, Condensed Matter)Neutron supermirror has become an important device to transport, bending and focusing a neutron beam. We have developed it using ion beam sputtering (IBS) instrument since it enables us to produce good quality layers with high density and small grain size. We have also investigated ion-polishing technique, which suppresses the interface roughness of multilayers. We have now installed new IBS instrument with effective deposit area of 500 mm in diameter for the realization of supermirror guide and bender with large effective critical angle. In this presentation, the performance of the supermirrors fabricated with it and the future development of neutron optical devices using supermirrors will be discussed.
Yamazaki, Toshihiko; Uryu, Mitsuru; Nakanishi, Ryuji; Kawai, Nobuyasu*; Hashimura, Hirohiko*
Nihon Kenchiku Gakkai 2005-Nendo Taikai Gakujutsu Koen Kogaishu, p.847 - 848, 2005/09
None