Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagiya, Shun*; Onodera, Shintaro*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Tanida, Hiroshi*; Ishitobi, Takayuki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034706_1 - 034706_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Motome, Yuiko; Agake, Toshiki; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2024-015, 30 Pages, 2025/01
The tables for calibration of control rods were verified, which is used positive period method and improved rod drop method of periodic inspection at Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). Those tables are "DOUBLING TIME-REACTIVITY" and "DECAY OF NEUTRON FLUX AFTER INSTANTANEOUS REDUCTION OF REACTIVITY". They are prepared around 1975. Since those tables do not clearly express source of values and records of data used in calculations, the authors verified those tables again. For the verification, the tables were reproduced as follows. For the positive period method, the relationship between the period and reactivity was analytically evaluated by using the inhour equation with NSRR's parameters. For the improved rod drop method, the ratios of neutron flux after the rod drop with parameters of negative reactivities was calculated using the EUREKA- 2 code. As a result, the values described in the tables well agree with those by the present evaluation because it is confirmed that standard deviations of the differences in the value by between the present evaluation and the tables are less than 0.035%. For this reason, it is verified that these tables are valid in the practical use for NSRR operations.
 Si
Si
Kon, Fusako*; Tabata, Chihiro; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044701_1 - 044701_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
The benchmark analyses on the TRIGA reactor of the IEU-COMP-THERM-013 (ICT-013) in the ICSBEP handbook using the MVP version 3 code were carried out with the Japanese, US and European nuclear data libraries, including JENDL-5. The analyses on effective neutron multiplication factors (k 's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k
's) were also performed for another TRIGA reactor defined in the ICT-003 as well as the ICT-013. As a result, it is confirmed that the calculated k 's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k
's vary in the range of 0.8% with the libraries. The results also suggest that there might be unknown bias in the ICT-013 for the calculated k 's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k
's. For the analyses on the control rod worths of the ICT-013, it is confirmed that differences in the worths among the libraries become smaller than those in k 's. Most of the errors involved in k
's. Most of the errors involved in k 's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k
's are considered to be cancelled in the calculation of the worths since the worths are obtained by subtraction of the reciprocals of two sorts of k 's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
's. The differences in the worths by between the benchmark and alternative methods defined in the ICT-013 were tried to be examined from the aspect of the differences in horizontal flux distributions by between those methods. It is confirmed that the differences in the worths for two shim control rods, which are fully withdrawn at a delayed critical state, are well understood by that attempt, but on the other hand the differences are not sufficiently explained for a regulating control rod, which is partially inserted to attain delayed criticality.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-023, 190 Pages, 2021/11
Computational analyses on nuclear criticality characteristics were carried out for heterogeneous lattice systems composed of water moderator and fuel rods utilized in low-power research and test reactors, in which the depletion of fuel due to burnup is relatively small, by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP Version 2 with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. In the analyses, the minimum critical number of fuel rods was evaluated using calculated neutron multiplication factors for the heterogeneous systems of the uranium dioxide fuel rod in the Static Experiments Critical Facility (STACY) and the Tank-type Critical Assembly (TCA), and the uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rod in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). In addition, six sorts of the ratio of reaction rates, which are components of neutron multiplication factors, were calculated in the analyses to explain the variation of neutron multiplication factors with the ratio of water moderator to fuel volume in a unit fuel rod cell. Those results of analyses are considered to be useful for the confirmation of reasonableness and validity of criticality safety measures as data showing criticality characteristics for water-moderated heterogeneous lattice systems composed of the existing fuel rods in research and test reactors, of which criticality data are not sufficiently provided by the Criticality Safety Handbook.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Dai-41-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2020/11
In light of recent delay of plutonium use in Japan and the increasing criticism of nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security in the nuclear fuel cycle, the validity of these criticisms will be examined for the sustainable development of the nuclear fuel cycle policy. Issues on the view point of nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security are examined.
Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Enerugi Rebyu, 40(8), p.56 - 57, 2020/07
Strict application of IAEA safeguards and nuclear security should be implemented for Japan's full-scale nuclear fuel cycle. Based on the knowledge and experience of research and development in the nuclear fuel cycle, nuclear material management, the effective and efficient promotion of new technologies should be promoted with scientific and demonstrative measures to strengthen the world's nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. Development or sophistication of new technologies, human resource development, and reinforcement of the international framework are future challenge in the international community.
Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Enerugi Rebyu, 40(7), p.58 - 59, 2020/06
Japan have promoted the peaceful use of plutonium with the nuclear non-proliferation commitment based on IAEA safeguards agreement and Japan-US nuclear cooperation agreement, as well as ensuring transparency of the policy that Japan has no plutonium without purpose of use. In promoting the nuclear fuel cycle, adherence to those measures and maintaining plutonium utilization by means of plutonium-thermal, and a fast reactor cycle to achieve large-scale and long-term energy supply and environmental improvement, therefore, further research and development is essential.
Mochiji, Toshiro; Senzaki, Masao*; Tamai, Hiroshi; Iwamoto, Tomonori*; Ishiguro, Yuzuru*; Kitade, Yuta; Sato, Heigo*; Suehiro, Rie*; Taniguchi, Tomihiro*; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; et al.
Enerugi Rebyu, 40(6), p.58 - 59, 2020/05
In order to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, it is important not only to ensure safety but also to ensure nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. Japan has contributed to the international community through strengthening nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security capabilities with technical and human resource development. However, in the wake of the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011, Japan's nuclear power plants have not restarted or plutonium use has not progressed smoothly. Concerns have been shown. Towards appropriate steps of Japan's nuclear fuel cycle policy, such concerns are examined and future efforts are summarized.
 F from
F from  O
O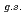 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 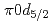 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O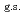 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
 probed by static dc magnetization measurements
probed by static dc magnetization measurementsShimizu, Yusei*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Physical Review B, 93(2), p.024502_1 - 024502_8, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Shimizu, Yusei*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Aoki, Dai*; Brison, J.-P.*; Braithwaite, D.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.015009_1 - 015009_6, 2014/06
 Si
Si
Tabata, Chihiro*; Inami, Toshiya; Michimura, Shinji*; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Philosophical Magazine, 94(32-33), p.3691 - 3701, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:56.69(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) by precise dc magnetization measurements
by precise dc magnetization measurementsShimizu, Yusei*; Haga, Yoshinori; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Physical Review Letters, 109(21), p.217001_1 - 217001_5, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:67.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Izawa, Kazuhiko; Aoyama, Yasuo; Sono, Hiroki; Ogawa, Kazuhiko; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
Proceedings of 9th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality (ICNC 2011) (CD-ROM), 11 Pages, 2012/02
For reactor physics and criticality safety researches, the Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) will be modified. In the modification, the present STACY, solution-fuel-type homogeneous cores, will be converted to fuel-pin-type heterogeneous cores moderated by light water. For nuclear safety design of the modified STACY, computational analyses have been carried out by using a Monte Carlo code MVP and a transport code system DANTSYS with cross-section data based on the JENDL-3.3. In the analyses, basic nuclear characteristics have been evaluated, such as criticality, water-level worth and reactor shutdown margin. By the results of these analyses, the feasibility of reactivity control mechanism and the sufficiency of reactor shutdown margin of the modified STACY were confirmed. In addition, temperature and void coefficients of reactivity and kinetic parameters were obtained to comprehend nuclear characteristics of the modified STACY.

Shimizu, Yusei*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Wakabayashi, Takumi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Tenya, Kenichi*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(9), p.093701_1 - 093701_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Shimizu, Yusei*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Wakabayashi, Takumi*; Tenya, Kenichi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA100_1 - SA100_3, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.92(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Pd
Pd Si
Si
Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Tateiwa, Naoyuki; Mayama, Taichi*; Saito, Hitoshi*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Haga, Yoshinori; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Goto, Terutaka*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(Suppl.A), p.SA105_1 - SA105_3, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.60(Physics, Multidisciplinary)