Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Yokota, Hiromi*; Fujimoto, Katsushige*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Bunseki Kagaku, 73(9), p.515 - 522, 2024/09
On-line isotope dilution-laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (on-line ID-LA-ICP-MS) is capable of quantification for each point ablated by laser, then the quantitative mapping of elements can be also conducted by reconstruction of the obtained each point data. The volume of data obtained as flow peaks in this system as a flow injection analysis, will be multiplied by each data such as number of m/z, scan time, time resolution and measurement position, and the total amount of data is enormous, resulting in a large human power and time consumption for data processing. In this paper, an original application software using Python to improve the efficiency of data processing in on-line ID-LA-ICP-MS was developed. To discriminate between the time-to-peak intensity and the background noise, an automatic peak detection using penalized asymmetric least squares was developed.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Ishiniwa, Hiroko*; Wada, Toshihiro*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analyst, 148(18), p.4291 - 4299, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.29(Chemistry, Analytical)Quantitative imaging of trace elements was successfully performed by online isotope dilution laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (online LA-ICP-IDMS). The sample aerosols produced by LA are mixed online with the mist created from an isotopically enriched spike solution via an in-house cyclonic spray chamber, which has a gas port on the top. Quantification was continuously achieved in each spot; subsequently, quantitative imaging was realized. Fe and Sr were selected as the model elements, and their spot quantifications based on online-isotope dilution. The method was applied to actual biological hard tissues, and the results were compared with electron probe microanalyzer data.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 38(8), p.1105 - 1114, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.86(Chemistry, Analytical)We demonstrate the sensitivity enhancement in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) by combining ultrasonic nebulization via the nitrogen mixed gas effect. We showed the effect of nitrogen gas concentration (0-5%) in the nebulizer gas on the signal sensitivity for 63 elements using commercially available (concentric and ultrasonic) nebulizers. In addition, the limit of detection was calculated in each case. Finally, we compared the sensitivity (i.e., the slope of the calibration curve), background noise intensity, and three-dimensional intensity distribution in the plasma to elucidate the effects of the concurrent use of mixed gas plasmas and nebulization methods.
 Sr using
Sr using  Sr/
Sr/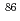 Sr isotope dilution method
Sr isotope dilution methodYanagisawa, Kayo*; Odashima, Mizuki*; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Talanta, 244, p.123442_1 - 123442_7, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.11(Chemistry, Analytical)The determination of a low concentration of  Sr was achieved by the combination of online SPE-ICP-QMS and ID method using
Sr was achieved by the combination of online SPE-ICP-QMS and ID method using  Sr/
Sr/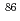 Sr ratio. No requirement of radioactive standard material and the preparation process of the calibration curve was in the quantification process and data acquisition can be in one-shot sample injection. The proposed method allowed the rapid (within 15 min/sample) quantification of
Sr ratio. No requirement of radioactive standard material and the preparation process of the calibration curve was in the quantification process and data acquisition can be in one-shot sample injection. The proposed method allowed the rapid (within 15 min/sample) quantification of  Sr in the presence of significant interferences such as isobaric
Sr in the presence of significant interferences such as isobaric  Zr and other elements. The LOD for
Zr and other elements. The LOD for  Sr was 5.6 Bq/L for a 10 mL injection and this could be improved by simply increasing the sample volume injected.
Sr was 5.6 Bq/L for a 10 mL injection and this could be improved by simply increasing the sample volume injected.
 Sr in hard tissue samples
Sr in hard tissue samplesKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Terashima, Motoki
KEK Proceedings 2021-2, p.140 - 145, 2021/12
Strontium-90 and  Y, its daughter nuclide, adverse effects on the bone marrow. Monitoring of
Y, its daughter nuclide, adverse effects on the bone marrow. Monitoring of  Sr in the bones have been required after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. However, conventional radioactivity measurement method for
Sr in the bones have been required after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. However, conventional radioactivity measurement method for  Sr requires a complicated separation of
Sr requires a complicated separation of  Y and a time-consuming measurement. ICP-MS system has been applied to
Y and a time-consuming measurement. ICP-MS system has been applied to  Sr concentration survey of water, soil, and edible part of fish. We developed measurement method of
Sr concentration survey of water, soil, and edible part of fish. We developed measurement method of  Sr with ICP-MS and applied the method for cattle bones. We determined
Sr with ICP-MS and applied the method for cattle bones. We determined  Sr in the hard tissues of animals that collected in the Fukushima prefecture. Limit of detection in the measurement was 19 Bq/kg.
Sr in the hard tissues of animals that collected in the Fukushima prefecture. Limit of detection in the measurement was 19 Bq/kg.
 Sr in cattle bone and tooth samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr in cattle bone and tooth samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 36(8), p.1678 - 1682, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.68(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid analysis of  Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of
Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. Therefore, the ICP-MS method can be rapid and useful procedure of  Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Sr in small bone and tooth samples derived from terrestrial animals.
Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Abe, Hironobu; Kitamura, Akihiro; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(29), p.19281 - 19290, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Online solid-phase extraction-inductively coupled plasma-quadrupole mass spectrometry with oxygen dynamic reaction cell (online SPE-ICP-MS-DRC) was shown to be a thorough automatic analytical system, circumventing the need for human handling. At three stepwise separations (SPE-DRC-Q mass filters), we showed that interference materials allowed the coexistence of abundance ratios of 1.5 10
10 for
for  Tc/Mo. Using this optimized system, a detection limit of
Tc/Mo. Using this optimized system, a detection limit of  Tc was 9.3 pg/L (5.9 mBq/L) for a 50 mL injection and sequential measurements were undertaken at a cycle of 24 min/sample.
Tc was 9.3 pg/L (5.9 mBq/L) for a 50 mL injection and sequential measurements were undertaken at a cycle of 24 min/sample.
 Sr in hard tissue samples
Sr in hard tissue samplesKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Terashima, Motoki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Abe, Hironobu
KEK Proceedings 2020-4, p.180 - 185, 2020/11
Strontium-90 and  Y, its daughter nuclide, adverse effects on the bone marrow. Monitoring of
Y, its daughter nuclide, adverse effects on the bone marrow. Monitoring of  Sr in the bones have been required after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. However, conventional radioactivity measurement method for
Sr in the bones have been required after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. However, conventional radioactivity measurement method for  Sr requires a complicated separation of
Sr requires a complicated separation of  Y and a time-consuming measurement. ICP-MS system has been applied to
Y and a time-consuming measurement. ICP-MS system has been applied to  Sr concentration survey of water, soil, and edible part of fish. We applied the ICP-MS system for the bones for the first time. In this study, reference bone (JSAC 0785 fish bone) was used as measurement samples. Sample preparation of the bone was performed using a microwave digestion instrument. After sample preparation,
Sr concentration survey of water, soil, and edible part of fish. We applied the ICP-MS system for the bones for the first time. In this study, reference bone (JSAC 0785 fish bone) was used as measurement samples. Sample preparation of the bone was performed using a microwave digestion instrument. After sample preparation,  Sr was determined using ICP-MS system with cascade separation steps based on on-line column separation and oxygen reaction. Strontium-90 in the bones was successfully separated from Ca, Ba, Y, Zr, Fe, Se, and Ge, which interfered in ICP-MS measurement, in the separation steps.
Sr was determined using ICP-MS system with cascade separation steps based on on-line column separation and oxygen reaction. Strontium-90 in the bones was successfully separated from Ca, Ba, Y, Zr, Fe, Se, and Ge, which interfered in ICP-MS measurement, in the separation steps.
 Sr using automatic solid-phase extraction inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr using automatic solid-phase extraction inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryYanagisawa, Kayo*; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 36(9), p.1131 - 1135, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.20(Chemistry, Analytical)In this paper, we propose an online water infusion system for rapid quantification of radioactive strontium-90 ( Sr) with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled solid-phase extraction and O
Sr) with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled solid-phase extraction and O dynamic reaction (cascade ICP-MS). The proposed system automatically provides a higher dilution ratio, which is at most 3.3 times the ratio obtained by the previous method, without increasing the analysis time (within 15 min). A detection limit of 2.7 Bq/kg wet (0.54 pg/kg wet) was achieved. The recovery test results were consistent with two different spiked values.
dynamic reaction (cascade ICP-MS). The proposed system automatically provides a higher dilution ratio, which is at most 3.3 times the ratio obtained by the previous method, without increasing the analysis time (within 15 min). A detection limit of 2.7 Bq/kg wet (0.54 pg/kg wet) was achieved. The recovery test results were consistent with two different spiked values.
Fujiwara, Kenso; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Iijima, Kazuki
Environmental Radiochemical Analysis VI, p.89 - 96, 2019/09
Since Strontium-90 (Sr-90) is one of the high yield and hazardous fission products, accurate and low-level detection of Sr-90 is essential for environmental samples. Especially, in case of nuclear power plant accidents, rapid and precise assessment of Sr-90 for environmental monitoring and health physics is required. In order to evaluate the migration of radionuclides in the environment, not only Sr-90 in water but also those in soil and biological samples should be measured. A new method for rapid quantification of Sr-90 by online solid phase extraction coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SPE-ICP-MS) has been developed. In this method, it is unavoidable to eliminate the interference by polyatomic ion (e.g., ArCa, Ca ) induced by isotopes and matrices in fishes and soil. In this study, SPE-ICP-MS method was applied to the measurement of Sr-90 in fishes, and the influence of the Sr isotopes and coexisting ions such as Ca was evaluated.
) induced by isotopes and matrices in fishes and soil. In this study, SPE-ICP-MS method was applied to the measurement of Sr-90 in fishes, and the influence of the Sr isotopes and coexisting ions such as Ca was evaluated.
Saegusa, Jun; Yanagisawa, Kayo; Hasumi, Atsushi; Shimizu, Takenori; Uchida, Yoshiaki*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 137, p.210 - 215, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.35(Chemistry, Physical)Following the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) accident, large-scale radiation monitoring and environmental clean-up activities have been conducted throughout the Fukushima region. Outside air temperatures there reach 40 C in summer and -20
C in summer and -20 C in winter, which are beyond the quoted range of many radiation survey instruments. For the purpose, temperature performances of four types of portable Japanese survey instruments which are widely used in Fukushima were experimentally investigated with a temperature-controlled chamber.
C in winter, which are beyond the quoted range of many radiation survey instruments. For the purpose, temperature performances of four types of portable Japanese survey instruments which are widely used in Fukushima were experimentally investigated with a temperature-controlled chamber.
Kuwata, Haruka*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Yanagisawa, Kayo; Manabe, Sachi*; Takeishi, Minoru; Watanabe, Hitoshi; Uezu, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Sr in animal bone by ICP-MS
Sr in animal bone by ICP-MSKoarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro
no journal, ,
Strontium-90 and  Y, its daughter nuclide, adverse effects on the bone marrow. Monitring of
Y, its daughter nuclide, adverse effects on the bone marrow. Monitring of  Sr have been required after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. However, radioactivity measurement method requires a complicated separation and a time-consuming
Sr have been required after the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. However, radioactivity measurement method requires a complicated separation and a time-consuming  -ray measurement. ICP-MS system has been applied to
-ray measurement. ICP-MS system has been applied to  Sr contamination survey of soil and water samples. We applied the ICP-MS system for the bones for the first time. In this study, reference bone was used as measurement samples. After sample preparation,
Sr contamination survey of soil and water samples. We applied the ICP-MS system for the bones for the first time. In this study, reference bone was used as measurement samples. After sample preparation,  Sr was determined using ICP-MS system with cascade separation steps based on on-line column separation and oxygen reaction. Strontium-90 in the bones was successfully separated from Ca, Ba, Y, Zr, Fe, and Ge, which interfered in ICP-MS measurement, in the separation steps. We found that the ICP-MS system could be applied to the rapid measurement of
Sr was determined using ICP-MS system with cascade separation steps based on on-line column separation and oxygen reaction. Strontium-90 in the bones was successfully separated from Ca, Ba, Y, Zr, Fe, and Ge, which interfered in ICP-MS measurement, in the separation steps. We found that the ICP-MS system could be applied to the rapid measurement of  Sr in the bones.
Sr in the bones.
Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kitamura, Akihiro
no journal, ,
Strontium-90 ( Sr) is one of the fission products and required a long time in the conventional radioactivity analysis (about a month). Therefore, we introduced the mass spectrometry analysis system combined inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and pretreatment units to determine
Sr) is one of the fission products and required a long time in the conventional radioactivity analysis (about a month). Therefore, we introduced the mass spectrometry analysis system combined inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and pretreatment units to determine  Sr more quickly. This system was mainly used for low matrix samples such as rainwater, but this time we report the measurement results of
Sr more quickly. This system was mainly used for low matrix samples such as rainwater, but this time we report the measurement results of  Sr in fishes containing a lot of matrix (such as calcium).
Sr in fishes containing a lot of matrix (such as calcium).
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
Determinations of radioisotopes in fuel debris and radioactive wastes are important for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. Difficult-to-measure radioisotopes such as Sr-90 have been measured by radiometric analysis and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), the methods have not achieved the distribution of the radioisotopes on the sample's surface due to its digestion process of the samples before measurements. Laser ablation (LA)-ICP-MS can obtain the distribution information of radionuclides directly on the surface of solid samples. In contrast, the quantification with the method is difficult caused by the spectral interferences and matrix effects from samples. In this study, a quantification method was developed combined with LA-ICP-MS and isotope dilution method. The proposed method was applied for Sr-90 quantification.
Matsueda, Makoto; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Abe, Hironobu; Kitamura, Akihiro; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujiwara, Kenso; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Iijima, Kazuki
no journal, ,
Since Sr-90 is one of the high yield and hazardous fission products, accurate and low-level detection of Sr-90 is essential for environmental samples. Especially, in case of nuclear power plant accidents, rapid and precise assessment of Sr-90 for environmental monitoring and health physics is required. In order to evaluate the migration of radionuclides in the environment, not only Sr-90 in water but also those in soil and biological samples should be measured. A new method for rapid quantification of Sr-90 by online solid phase extraction coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SPE-ICP-MS) has been developed. In this method, it is unavoidable to eliminate the interference by polyatomic ion (e.g., ArCa, Ca ) induced by isotopes and matrices in fishes and soil. In this study, SPE-ICP-MS method was applied to the measurement of Sr-90 in fishes, and the influence of the Sr isotopes and coexisting ions such as Ca was evaluated.
) induced by isotopes and matrices in fishes and soil. In this study, SPE-ICP-MS method was applied to the measurement of Sr-90 in fishes, and the influence of the Sr isotopes and coexisting ions such as Ca was evaluated.
Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Kuwata, Haruka*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Uezu, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Terashima, Motoki; Fujiwara, Kenso; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Takahashi, Atsushi*; Suzuki, Toshihiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Rapid analysis of  Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. The ICP-MS method was improved by ICP-MS/MS and oxygen-ammonia mixed gas reaction.
Sr in bone and tooth samples of cattle were achieved by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) coupled with mass shift and solid phase extraction techniques. Limit of detection (LOD) in the ICP-MS measurement of 0.1 g samples was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. Analytical time of the ICP-MS method was reduced from 20 days to 11 hours, compared with the radiometric method. The ICP-MS method was improved by ICP-MS/MS and oxygen-ammonia mixed gas reaction.
Koarai, Kazuma; Matsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Yanagisawa, Kayo*; Fujiwara, Kenso; Terashima, Motoki; Kino, Yasushi*; Oka, Toshitaka; Okutsu, Kenichi*; Yamashita, Takuma*; et al.
no journal, ,
We demonstrated a method of  Sr measurement in small pieces of hard tissues with radioactivity measurement or ICP-MS measurement. Interference elements of the measurements were removed by chemical separation. We could determine
Sr measurement in small pieces of hard tissues with radioactivity measurement or ICP-MS measurement. Interference elements of the measurements were removed by chemical separation. We could determine  Sr in 0.1 g of hard tissues by radioactivity measurement method and ICP-MS method. Limit of detection of the ICP-MS method was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. The ICP-MS method is adequate method for distribution analysis of
Sr in 0.1 g of hard tissues by radioactivity measurement method and ICP-MS method. Limit of detection of the ICP-MS method was lower than that of the radioactivity measurement. The ICP-MS method is adequate method for distribution analysis of  Sr in the hard tissues.
Sr in the hard tissues.