Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Matsushima, Hisayoshi*; Harada, Kenji*; Tanii, Risako*; Terasawa, Tomoo; Yano, Masahiro; Asaoka, Hidehito; Gueriba, J. S.*; Di o, W. A.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
o, W. A.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14362 - 14369, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:85.62(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The fabrication of hydrogen isotope enrichment system is essential for the development of industrial, medical, life science, and nuclear fusion fields, therefore alternative enrichment techniques with high separation factor and economic feasibility have been still explored. Herein, we report the fabrication of heterogeneous electrode with layered structures consisting of palladium and graphene layers for polymer electrolyte membrane electrochemical hydrogen pumping for the hydrogen isotope enrichment. We demonstrated significant bias voltage dependence of hydrogen/deuterium (H/D) separation ability and its high H/D at lower bias voltage. Theoretical analysis also demonstrated that the observed high H/D at low bias voltage stems from hydrogen isotopes tunneling through atomically-thick graphene during the electrochemical reaction, and the bias dependent H/D results in a transition from the quantum tunneling regime to classical over- barrier regime for hydrogen isotopes transfer via the graphene. These findings provide new insight for a novel economical methodology of efficient hydrogen isotope enrichment.
Sue, Yuki*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 23(2), p.022804_1 - 022804_7, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.94(Physics, Nuclear)A destructive monitor to measure the longitudinal bunch width of a low-energy and low-intensity muon beam was developed. This bunch-width monitor (BWM) employed microchannel plates to detect a single muon with high time resolution. In addition, constant-fraction discriminators were adopted to suppress the time-walk effect. The time resolution was measured to be 65 ps in rms using a picosecond-pulsed laser. This resolution satisfied the requirements of the muon linac of the J-PARC E34 experiment. We measured the bunch width of negative-muonium ions accelerated with a radio-frequency quadrupole using the BWM. The bunch width was successfully measured to be  54
54  11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
11 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Matoba, Shiro*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012067_1 - 012067_6, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:73.22(Physics, Particles & Fields)Negative muonium atom ( e
e e
e , Mu
, Mu ) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu
) has unique features stimulating potential interesting for several scientific fields. Since its discovery in late 1980's in vacuum, it has been discussed that the production efficiency would be improved using a low-work function material. C12A7 was a well-known insulator as a constituent of alumina cement, but was recently confirmed to exhibit electric conductivity by electron doping. The C12A7 electride has relatively low-work function (2.9 eV). In this paper, the negative muonium production measurement with several materials including a C12A7 electride film will be presented. Measured production rate of the Mu were 10
were 10 /s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu
/s for all the Al, electride, and SUS target. Significant enhancement on electride target was not observed, thus it is presumed that the surface condition should be more carefully treated. There was no material dependence of the Mu averaged energy: it was 0.2
averaged energy: it was 0.2 0.1keV.
0.1keV.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 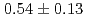 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Sue, Yuki*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Saito, Naohito; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.2571 - 2574, 2019/06
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. Further improvement of the measurement system is needed to guarantee the required accuracy. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Otani, Masashi*; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '19) (Internet), p.37 - 40, 2019/06
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 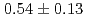 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:99.06(Quantum Science & Technology) -site randomness on the antiferroelectric/relaxor nature of the ground state; Diffuse and inelastic X-ray scattering study of Pb(In
-site randomness on the antiferroelectric/relaxor nature of the ground state; Diffuse and inelastic X-ray scattering study of Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji*; Tsukada, Shinya*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*; Terauchi, Hikaru*
Physical Review B, 98(5), p.054106_1 - 054106_10, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsuki, Takuya; Masui, Kenji; Sekine, Megumi; Tanigawa, Masafumi; Yasuda, Takeshi; Tsutagi, Koichi; Ishiyama, Koichi; Nishida, Naoki; Horigome, Kazushi; Mukai, Yasunobu; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has proposed in its long-term research and development (R&D) plan, development of a real-time measurement technology to monitor and verify nuclear material movement continuously as part of an advanced approach to effectively and efficiently conduct safeguards for reprocessing facilities. Since the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) has solutions containing both Pu and fission products (FP), a new detector development project to monitor Pu with FP is being carried out from 2015 to 2017. This project is mainly conducted in the High Active Liquid Waste Storage (HALWS) in the TRP. For the first step of this project, as the confirmation of composition of high active liquid waste (HALW) to evaluate neutron/ -ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted
-ray emitted from solution in the selected HALW tank which has the most amount of Pu in HALW tanks at the TRP, we took HALW sample and conducted  -ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/
-ray spectrum measurement for HALW. As a study of detector setting location, to survey the available neutron/ -ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/
-ray (i.e. intensity) at the outside surface of the cell where HALW tank is located, we implemented continuous measurement by neutron/ -ray detector. In this paper, we report three
-ray detector. In this paper, we report three  -ray peaks related with
-ray peaks related with  Pu and
Pu and  Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Pu measured in the composition research of HALW, which is needed to identify Pu amount by the new detector that we are developing and the result of radiation measurement on the surface of the cell.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(3), p.301 - 307, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:81.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)After the severe accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant, large amounts of contaminated stagnant water have accumulated in turbine buildings and their surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of the radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. This evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011. The release ratios of tritium, iodine, and cesium were several tens of percent, whereas those of strontium and barium were smaller by one or two orders of magnitude. The release ratios in the Fukushima accident were equivalent to those in the TMI-2 accident.
Nishihara, Kenji; Yamagishi, Isao; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Tanaka, Kiwamu; Kuno, Takehiko; Inada, Satoshi; Goto, Yuichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(1), p.13 - 19, 2012/03
After the severe accident in the Fukushima-1 Nuclear Power Plant, large amount of contaminated stagnant water has been produced in turbine buildings and those surroundings. This rapid communication reports calculation of radionuclide inventory in the core, collection of measured inventory in the stagnant water, and estimation of radionuclide release ratios from the core to the stagnant water. The present evaluation is based on data obtained before June 3, 2011.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(3), p.2509 - 2514, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards
and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards  . On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at
. On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at  . These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.
. These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In
and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 34(1), p.19 - 22, 2009/03
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (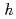 /2
/2  /2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada
/2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada  ., Phys, Rev. B
., Phys, Rev. B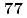 094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
 -phase zirconium hydrides and deuterides
-phase zirconium hydrides and deuteridesTsuchiya, Bun*; Yasuda, Ryo; Teshigawara, Makoto; Konashi, Kenji*; Nagata, Shinji*; Shikama, Tatsuo*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 376(1), p.60 - 65, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.99(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Distributions of hydrogen isotope concentrations in e-phase zirconium hydrides and deuterides ( -ZrHx and
-ZrHx and  -ZrDx: 1.8
-ZrDx: 1.8  x
x  2.0) were investigated by neutron radiography (NRG). The NRG images of the thermal neutron transmission and backscattering revealed hydrogen concentration dependence and isotope differences. The thermal neutron mass attenuation coefficients in relation to the hydrogen isotope concentrations were determined from the transmission NRG images. The results showed the isotope effects of the thermal neutron mass attenuation coefficients for
2.0) were investigated by neutron radiography (NRG). The NRG images of the thermal neutron transmission and backscattering revealed hydrogen concentration dependence and isotope differences. The thermal neutron mass attenuation coefficients in relation to the hydrogen isotope concentrations were determined from the transmission NRG images. The results showed the isotope effects of the thermal neutron mass attenuation coefficients for  -ZrHx to be about 6-9 times higher than those for
-ZrHx to be about 6-9 times higher than those for  -ZrDx. The neutron scattering processes for transmission and backscattering NRG images of
-ZrDx. The neutron scattering processes for transmission and backscattering NRG images of  -ZrHx and
-ZrHx and  -ZrDx were also analyzed using a general Monte Carlo neutron-particle transport (MCNP) code.
-ZrDx were also analyzed using a general Monte Carlo neutron-particle transport (MCNP) code.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering study
revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering studyOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Physical Review B, 77(9), p.094136_1 - 094136_8, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:59.93(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or relaxor states can appear in Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
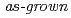 Pb(In
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O single crystal studied by a complementary use of X-ray and neutron scatterings
single crystal studied by a complementary use of X-ray and neutron scatteringsOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(2), p.024606_1 - 024606_6, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.83(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Structural properties of 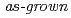 Pb(In
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) single crystals at room temperature (RT) were investigated by X-ray and neutron scattering techniques, taking much account of the difference in the penetration depth and spatial resolution of X-rays and those of neutrons. A strong diffuse scattering was observed by X-ray while h/4, k/4, 0 superlattice reflections were found by neutron, indicating a relaxor state in the outer-layer of the crystal and an antiferroelectric (AFE) state in the bulk. The phonon dispersion was measured for the first time for the PIN series. Two transverse optic (TO1 and TO2) modes were clarified near the zone center though neither water-fall behavior nor folding of phonon branches was confirmed. We have thus concluded that a major part of the
(PIN) single crystals at room temperature (RT) were investigated by X-ray and neutron scattering techniques, taking much account of the difference in the penetration depth and spatial resolution of X-rays and those of neutrons. A strong diffuse scattering was observed by X-ray while h/4, k/4, 0 superlattice reflections were found by neutron, indicating a relaxor state in the outer-layer of the crystal and an antiferroelectric (AFE) state in the bulk. The phonon dispersion was measured for the first time for the PIN series. Two transverse optic (TO1 and TO2) modes were clarified near the zone center though neither water-fall behavior nor folding of phonon branches was confirmed. We have thus concluded that a major part of the 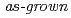 PIN crystal at RT is ferroelectric (FE). These results imply that the
PIN crystal at RT is ferroelectric (FE). These results imply that the  -site chemical ordering, i.e. inhomogeneity, which controls the structural properties of PIN, is unevenly distributed throughout the crystal. We speculate that small AFE grains coexist with the FE matrix while the outer-layer is in a relaxor state in the
-site chemical ordering, i.e. inhomogeneity, which controls the structural properties of PIN, is unevenly distributed throughout the crystal. We speculate that small AFE grains coexist with the FE matrix while the outer-layer is in a relaxor state in the 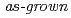 PIN.
PIN.
Tsuchiya, Bun*; Teshigawara, Makoto; Nagata, Shinji*; Konashi, Kenji*; Yasuda, Ryo; Nishino, Yasuharu; Nakagawa, Tetsuya*; Yamawaki, Michio*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 190(1-4), p.699 - 703, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)Practicability of Elastic Recoil Detection (ERD) and Neutron Radiography (NRG) methods for hydrogen concentration in titanium hydrides (d-TiHx : 1.6<x<2.0) is investigated. In ERD methods, the hydrogen concentration in the surface of TiHx is recognized. In NRG method, the hydrogen concentration over the balk was confirmed. These results show that both methods are effective means for estimating the hydrogen concentration in hydride materials.