Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -site randomness on the antiferroelectric/relaxor nature of the ground state; Diffuse and inelastic X-ray scattering study of Pb(In
-site randomness on the antiferroelectric/relaxor nature of the ground state; Diffuse and inelastic X-ray scattering study of Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji*; Tsukada, Shinya*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*; Terauchi, Hikaru*
Physical Review B, 98(5), p.054106_1 - 054106_10, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.88(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(3), p.2509 - 2514, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards
and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards  . On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at
. On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at  . These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.
. These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In
and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 34(1), p.19 - 22, 2009/03
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (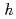 /2
/2  /2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada
/2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada 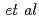 ., Phys, Rev. B
., Phys, Rev. B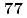 094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering study
revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering studyOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Physical Review B, 77(9), p.094136_1 - 094136_8, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:61.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or relaxor states can appear in Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 33(1), p.15 - 18, 2008/03
Pb 
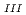 -edge absorption spectra of ordered and disordered Pb(In
-edge absorption spectra of ordered and disordered Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) were analyzed. The absorption edges of both the ordered and disordered PIN were shifted depending on the thermal condition of post-annealing. A clear edge shift was observed between the ordered and disordered PIN crystals. The local environments of the Pb atoms were different in these PIN crystals. This edge shift can be interpreted by introducing disarrangement of B-site atoms. Disordering of B-site atoms has not only an effect on the local bond distribution but also an effect on the long-range order crystal structure.
(PIN) were analyzed. The absorption edges of both the ordered and disordered PIN were shifted depending on the thermal condition of post-annealing. A clear edge shift was observed between the ordered and disordered PIN crystals. The local environments of the Pb atoms were different in these PIN crystals. This edge shift can be interpreted by introducing disarrangement of B-site atoms. Disordering of B-site atoms has not only an effect on the local bond distribution but also an effect on the long-range order crystal structure.
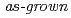 Pb(In
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O single crystal studied by a complementary use of X-ray and neutron scatterings
single crystal studied by a complementary use of X-ray and neutron scatteringsOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(2), p.024606_1 - 024606_6, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Structural properties of 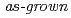 Pb(In
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) single crystals at room temperature (RT) were investigated by X-ray and neutron scattering techniques, taking much account of the difference in the penetration depth and spatial resolution of X-rays and those of neutrons. A strong diffuse scattering was observed by X-ray while h/4, k/4, 0 superlattice reflections were found by neutron, indicating a relaxor state in the outer-layer of the crystal and an antiferroelectric (AFE) state in the bulk. The phonon dispersion was measured for the first time for the PIN series. Two transverse optic (TO1 and TO2) modes were clarified near the zone center though neither water-fall behavior nor folding of phonon branches was confirmed. We have thus concluded that a major part of the
(PIN) single crystals at room temperature (RT) were investigated by X-ray and neutron scattering techniques, taking much account of the difference in the penetration depth and spatial resolution of X-rays and those of neutrons. A strong diffuse scattering was observed by X-ray while h/4, k/4, 0 superlattice reflections were found by neutron, indicating a relaxor state in the outer-layer of the crystal and an antiferroelectric (AFE) state in the bulk. The phonon dispersion was measured for the first time for the PIN series. Two transverse optic (TO1 and TO2) modes were clarified near the zone center though neither water-fall behavior nor folding of phonon branches was confirmed. We have thus concluded that a major part of the 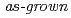 PIN crystal at RT is ferroelectric (FE). These results imply that the
PIN crystal at RT is ferroelectric (FE). These results imply that the  -site chemical ordering, i.e. inhomogeneity, which controls the structural properties of PIN, is unevenly distributed throughout the crystal. We speculate that small AFE grains coexist with the FE matrix while the outer-layer is in a relaxor state in the
-site chemical ordering, i.e. inhomogeneity, which controls the structural properties of PIN, is unevenly distributed throughout the crystal. We speculate that small AFE grains coexist with the FE matrix while the outer-layer is in a relaxor state in the 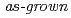 PIN.
PIN.
Shibata, Yasushi*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Hori, Naohiko; Kishi, Toshiaki; Kumada, Hiroaki; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, Kei*; et al.
JAERI-Research 2005-009, 41 Pages, 2005/03
The measurement of neutron flux and boron concentration in the blood during medical irradiation is indispensable in order to evaluate the radiation in boron neutron capture therapy. It is, however, difficult to measure the blood boron concentration during neutron irradiation because access to the patient is limited. Therefore we prospectively investigated the predictability of blood boron concentrations using the data obtained at the first craniotomy after infusion of a low dosage of BSH. When the test could not be carried out, the blood boron concentration during irradiation was also predicted by using the 2-compartment model. If the final boron concentration after the end of the infusion is within 95% confidence interval of the prediction, direct prediction from biexponential fit will reduce the error of blood boron concentrations during irradiation to around 6%. If the final boron concentration at 6 or 9 hours after the end of infusion is out of 95% confidence interval of the prediction, proportional adjustment will reduce error and expected error after adjustment to around 12%.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O crystals
crystalsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Matsumoto, Norimasa; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 15(3), p.467 - 474, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:34.85(Physics, Condensed Matter)Thermal properties of ordered and disordered Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) single clystals were investigated. The defect-induced phase separation provided a good agreement of the instability of the relaxor nd antiferroelectric states of the PIN crystals.
(PIN) single clystals were investigated. The defect-induced phase separation provided a good agreement of the instability of the relaxor nd antiferroelectric states of the PIN crystals.
Shibata, Yasushi*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, Kei*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Hori, Naohiko; et al.
Research and Development in Neutron Capture Therapy, p.1055 - 1060, 2002/09
We prospectively investigated the predictability of blood boron concentrations using the data obtained at the first craniotomy after infusion of a low dose of sodium undecahydroclosododecaborate (BSH). Nine patients with malignant glial tumors underwent Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) between 1995 and 2001. In 7 patients, 1g of BSH was infused before the first tumor removal and boron concentrations were determined using prompt gamma ray analysis (PGA). Then, 12 hours before BNCT, patients were infused at a dose of 100mg/kg BSH, and the boron concentrations were determined again. The boron biodistribution data showed a biexponential pharmacokinetic profile. If the final boron concentration at 6 or 9 hours after the end of the infusion is within the 95% confidence interval of the prediction, direct prediction from biexponential fit will reduce the error of blood boron concentrations during irradiation to around 6%.
Shibata, Yasushi*; Matsumura, Akira*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Yasuda, Susumu*; Nakai, K.*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; Hori, Naohiko; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer, p.145 - 146, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Yasuda, Susumu*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Matsumura, Akira*; Shibata, Yasushi*; Akutsu, Hiroyoshi*; Matsushita, Akira*; Nakai, K.*; Nose, Tadao*; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kumada, Hiroaki; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Symposium on Neutron Capture Therapy for Cancer, p.171 - 172, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb )O
)O studied by X-ray diffraction
studied by X-ray diffractionOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb )O
)O revealed by changing B-site randomness
revealed by changing B-site randomnessOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) varies among antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) and relaxor states depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) varies among antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) and relaxor states depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the FE ground state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness competes with the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the FE ground state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness competes with the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Yasuda, Naohiko*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb )O
)O ; Inelastic X-ray scattering in control of the B-site randomness
; Inelastic X-ray scattering in control of the B-site randomnessOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) varies among antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) and relaxor states depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) varies among antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) and relaxor states depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the FE ground state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness competes with the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the FE ground state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness competes with the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Yasuda, Naohiko*; Mizuki, Junichiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Nb
Nb )O
)O revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering study
revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering studyOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English