Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, M.*; McDermott, R. M.*; Angioni, C.*; Camenen, Y.*; Citrin, J.*; Jakubowski, M.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Mantica, P.*; Mariani, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 65(3), p.033001_1 - 033001_132, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress in physics understanding and theoretical model development of plasma transport and confinement in the ITPA Transport and Confinement Topical Group since the publication of the ITER Physics Basis was summarized focusing on the contributions to ITER and burning plasma prediction and control. This paper provides a general and streamlined overview on the advances that were mainly led by the ITPA TC joint experiments and joint activities for the last 15 years. This paper starts with the scientific strategy and scope of the ITPA TC Topical group and overall picture of the major progress, followed by the progress of each research field: particle transport, impurity transport, ion and electron thermal turbulent transport, momentum transport, impact of 3D magnetic fields on transport, confinement mode transitions, global confinement, and reduced transport modeling.
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yasumiishi, Misa*; Masoudi, P.*; Nishimura, Taku*; Ochi, Kotaro; Ye, X.*; Aldstadt, J.*; Komissarov, M.*
Radiation Measurements, 168, p.106978_1 - 106978_16, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, we surveyed air dose rates using hand-held and backpack-type scintillators in a forest of deciduous and evergreen trees in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. The effects of topographic features on air dose rates were examined using multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) against five selected topographic parameters. The air dose rates were distributed unevenly in the forest, and air dose rates varied by more than 1 Sv/h as a function of time, likely owing to ground wetness etc. The effect of different topographic parameters varied between survey dates. The MARS model predictions with all topographic parameters yielded an R
Sv/h as a function of time, likely owing to ground wetness etc. The effect of different topographic parameters varied between survey dates. The MARS model predictions with all topographic parameters yielded an R of 0.54 or higher. To discuss whether the effect of topography on air dose rates and soil contamination levels is consistent, air dose rates measured in the field were compared with those estimated from the depth profile of radiocesium in soil. Most air dose rates estimated from the soil samples were in the range of field measurements.
of 0.54 or higher. To discuss whether the effect of topography on air dose rates and soil contamination levels is consistent, air dose rates measured in the field were compared with those estimated from the depth profile of radiocesium in soil. Most air dose rates estimated from the soil samples were in the range of field measurements.
Okeme, I. C.*; Scott, T. B.*; Martin, P. G.*; Satou, Yukihiko; Ojonimi, T. I.*; Olaluwoye, M. O.*
Minerals (Internet), 10(3), p.241_1 - 241_15, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:46.30(Geochemistry & Geophysics) followed by the formation of molecular poly-oxo cluster {
followed by the formation of molecular poly-oxo cluster {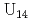 } containing hemimellitate uranium(IV)
} containing hemimellitate uranium(IV)Dufaye, M.*; Martin, N. P.*; Duval, S.*; Volkringer, C.*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Loiseau, T.*
RSC Advances (Internet), 9(40), p.22795 - 22804, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:42.89(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Two coordination compounds bearing tetravalent uranium (UIV)) were synthesized in the presence of tritopic hemimellitic acid in acetonitrile with a controlled amount of water (H O/U
O/U 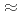 8) and structurally characterized. The slow hydrolysis reaction together with the partial decomposition of the starting organic reactants into oxalate and acetate molecules induces the generation of such a large poly-oxo cluster with fourteen uranium centers. Structural comparisons with other closely related uranium-containing clusters, such as the {
8) and structurally characterized. The slow hydrolysis reaction together with the partial decomposition of the starting organic reactants into oxalate and acetate molecules induces the generation of such a large poly-oxo cluster with fourteen uranium centers. Structural comparisons with other closely related uranium-containing clusters, such as the {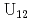 }
}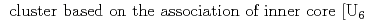 O
O ] with three dinuclear sub-units {
] with three dinuclear sub-units {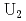 }, were performed.
}, were performed.
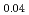 (Sb
(Sb Bi
Bi )
)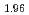 Te
Te
Ye, M.*; Xu, T.*; Li, G.*; Qiao, S.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Nurmamat, M.*; Sumida, Kazuki*; Ishida, Yukiaki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(14), p.144413_1 - 144413_7, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:56.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Te
Te
Ye, M.*; Li, W.*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Wang, J.*; Pan, H.*; Nurmamat, M.*; Sumida, Kazuki*; Ji, F.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 6, p.8913_1 - 8913_7, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:90.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Magnetically doped topological insulators are predicted to exhibit exotic phenomena including the quantized anomalous Hall effect and a dissipationless transport, which facilitate the development of low-power-consumption devices using electron spins. The realization of the quantized anomalous Hall effect is so far restricted to the Cr-doped (Sb,Bi) Te
Te system at extremely low temperature; however, the microscopic origin of its ferromagnetism is poorly understood. Here we present an element-resolved study for Cr-doped (Sb,Bi)
system at extremely low temperature; however, the microscopic origin of its ferromagnetism is poorly understood. Here we present an element-resolved study for Cr-doped (Sb,Bi) Te
Te using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism to unambiguously show that the long-range magnetic order is mediated by the p-hole carriers of the host lattice, and the interaction between the Sb(Te) p and Cr d states is crucial.
using X-ray magnetic circular dichroism to unambiguously show that the long-range magnetic order is mediated by the p-hole carriers of the host lattice, and the interaction between the Sb(Te) p and Cr d states is crucial.
Sumida, Kazuki*; Shirai, Kaito*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Taniguchi, Masaki*; Ye, M.*; Ueda, Shigenori*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Aseguinolaza, I. R.*; Barandiar n, J. M.*; et al.
n, J. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 91(13), p.134417_1 - 134417_6, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.09(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Se
Se
Ye, M.*; Kuroda, Kenta*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Saito, Yuji; Okamoto, Kazuaki*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Shirai, Kaito*; Miyamoto, Koji*; Arita, Masashi*; Nakatake, Masashi*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 25(23), p.232201_1 - 232201_5, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:46.74(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Maiko; Kaye, S.*; Rice, J.*; Solomon, W.*; Tala, T.*; Bell, R. E.*; Burrell, K. H.*; Ferreira, J.*; Kamada, Yutaka; McDonald, D. C.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 52(12), p.123005_1 - 123005_11, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:61.94(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The purpose of this study is to find a common feature on momentum transport coefficients including diffusive and non-diffusive terms in all machines. The momentum database enables us to assess a parametric dependency of momentum transport in a wider range of dimensionless parameters related to transport. Such observation will contribute to make a scaling/modeling on momentum transport for future devices like ITER and DEMO. On the other hand, the investigation of a difference in observation by comparing the experimental conditions will give a useful information to realize what plasma parameter is the key for the momentum transport coefficients.
Schaffer, M. J.*; Snipes, J. A.*; Gohil, P.*; de Vries, P.*; Evans, T. E.*; Fenstermacher, M. E.*; Gao, X.*; Garofalo, A. M.*; Gates, D. A.*; Greenfield, C. M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103028_1 - 103028_11, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:82.79(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Experiments at DIII-D investigated the effects of ferromagnetic error fields similar to those expected from proposed ITER Test Blanket Modules (TBMs). Studied were effects on: plasma rotation and locking; confinement; L-H transition; edge localized mode (ELM) suppression by resonant magnetic perturbations; ELMs and the H-mode pedestal; energetic particle losses; and more. The experiments used a 3-coil mock-up of 2 magnetized ITER TBMs in one ITER equatorial port. The experiments did not reveal any effect likely to preclude ITER operations with a TBM-like error field. The largest effect was slowed plasma toroidal rotation v across the entire radial profile by as much as 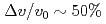 via non-resonant braking. Changes to global
via non-resonant braking. Changes to global 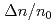 ,
, 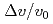 and
and 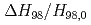 were
were  3 times smaller. These effects are stronger at higher
3 times smaller. These effects are stronger at higher  and lower
and lower 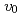 . Other effects were smaller.
. Other effects were smaller.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 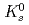 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Chapman, I. T.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Coda, S.*; Gerhardt, S.*; Graves, J. P.*; Howell, D. F.*; Isayama, Akihiko; La Haye, R. J.*; Liu, Y.*; Maget, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 50(10), p.102001_1 - 102001_7, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:87.49(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Moreau, D.*; Mazon, D.*; Walker, M. L.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Flanagan, S. M.*; Gohil, P.*; Groebner, R. J.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Schuster, E.*; Ou, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
La Haye, R. J.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Maraschek, M.*
Nuclear Fusion, 49(4), p.045005_1 - 045005_8, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:82.84(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Callen, J. D.*; Anderson, J. K.*; Arlen, T. C.*; Bateman, G.*; Budny, R. V.*; Fujita, Takaaki; Greenfield, C. M.*; Greenwald, M.*; Groebner, R. J.*; Hill, D. N.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1449 - 1457, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.97(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hender, T. C.*; Wesley, J. C.*; Bialek, J.*; Bondeson, A.*; Boozer, A. H.*; Buttery, R. J.*; Garofalo, A.*; Goodman, T. P.*; Granetz, R. S.*; Gribov, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S128 - S202, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:1017 Percentile:98.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Prater, R.*; La Haye, R. J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Petty, C. C.*; Strait, E. J.*; Ferron, J. R.*; Humphreys, D. A.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Lohr, J.*; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(5), p.371 - 377, 2007/05
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:88.22(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The 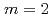 /
/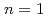 neoclassical tearing mode (NTM) has been observed to strongly degrade confinement and frequently lead to a disruption in high
neoclassical tearing mode (NTM) has been observed to strongly degrade confinement and frequently lead to a disruption in high  discharges in DIII-D if allowed to grow to large size. Stabilization of grown NTMs by application of highly localized electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) at the island location has led to operation at increased plasma pressure, up to the no-wall kink limit. After the NTM is stabilized by the ECCD, the correct location for the current drive is maintained using information from real-time equilibrium reconstructions which include measurements from the motional Stark effect diagnostic. This same process is used alternatively to prevent the mode from ever growing, leading to performance at the pressure limit in high performance hybrid discharges with
discharges in DIII-D if allowed to grow to large size. Stabilization of grown NTMs by application of highly localized electron cyclotron current drive (ECCD) at the island location has led to operation at increased plasma pressure, up to the no-wall kink limit. After the NTM is stabilized by the ECCD, the correct location for the current drive is maintained using information from real-time equilibrium reconstructions which include measurements from the motional Stark effect diagnostic. This same process is used alternatively to prevent the mode from ever growing, leading to performance at the pressure limit in high performance hybrid discharges with  above 4%. Modeling using the modified Rutherford equation shows that the required power is in close agreement with the experimental threshold for prevention of the 2/1 NTM.
above 4%. Modeling using the modified Rutherford equation shows that the required power is in close agreement with the experimental threshold for prevention of the 2/1 NTM.