Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloy
FCC hierarchical martensite transformation under dynamic impact in FeMnAlNiTi alloyLi, C.*; Fang, W.*; Yu, H. Y.*; Peng, T.*; Yao, Z. T.*; Liu, W. G.*; Zhang, X.*; 徐 平光; Yin, F.*
Materials Science & Engineering A, 892, p.146096_1 - 146096_11, 2024/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.04(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The quasi-static superelastic responses and hierarchical martensite transformation from body-centered cubic (BCC) to face-centered cubic (FCC) under dynamic impact in Fe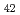 Mn
Mn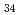 Al
Al Ni
Ni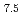 Ti
Ti alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC
alloys were investigated. Polycrystalline and oligocrystalline alloys were produced through solution heat treatment and cyclic heat treatment processes, respectively. The results show the volume fraction of residual martensite for oligocrystalline alloys is lower, which exhibits better superelastic responses compared with polycrystalline alloys. Dynamic impact tests indicate that, despite the weakening of the grain boundary strengthening effect, the ultimate strength of the oligocrystalline alloys closely matches that of the polycrystalline alloys under dynamic impact. The martensite transformation of the FeMnAlNiTi alloy is characterized as hierarchical under dynamic impact, and increasing strain rates and grain sizes can enhance the BCC  FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
FCC martensite transformation, resulting in higher martensite phase fractions for oligocrystalline alloys. The increase in ultimate strength is attributed to the dynamic Hall-Petch effect introduced by more martensite phase interfaces under dynamic impact.
He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:95.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)In CrCoNi, a so-called medium-entropy alloy, an fcc-to-hcp phase transformation has long been anticipated. Here, we report an in situ loading study with neutron diffraction, which revealed a bulk fcc-to-hcp phase transformation in CrCoNi at 15 K under tensile loading. By correlating deformation characteristics of the fcc phase with the development of the hcp phase, it is shown that the nucleation of the hcp phase was triggered by intrinsic stacking faults. The confirmation of a bulk phase transformation adds to the myriads of deformation mechanisms available in CrCoNi, which together underpin the unusually large ductility at low temperatures.
 Ge
Ge
Wo, H.*; Wang, Q.*; Shen, Y.*; Zhang, X.*; Hao, Y.*; Feng, Y.*; Shen, S.*; He, Z.*; Pan, B.*; Wang, W.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.217003_1 - 217003_5, 2019/05
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:42.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report neutron scattering measurements of single-crystalline YFe Ge
Ge in the normal state, which has the same crystal structure as the 122 family of iron pnictide superconductors. YFe
in the normal state, which has the same crystal structure as the 122 family of iron pnictide superconductors. YFe Ge
Ge does not exhibit long-range magnetic order but exhibits strong spin fluctuations. Like the iron pnictides, YFe
does not exhibit long-range magnetic order but exhibits strong spin fluctuations. Like the iron pnictides, YFe Ge
Ge displays anisotropic stripe-type antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations at (
displays anisotropic stripe-type antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations at (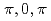 ). More interesting, however, is the observation of strong spin fluctuations at the in-plane ferromagnetic wave vector (
). More interesting, however, is the observation of strong spin fluctuations at the in-plane ferromagnetic wave vector (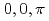 ). These ferromagnetic spin fluctuations are isotropic in the (
). These ferromagnetic spin fluctuations are isotropic in the (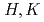 ) plane, whose intensity exceeds that of stripe spin fluctuations. Both the ferromagnetic and stripe spin fluctuations remain gapless down to the lowest measured energies. Our results naturally explain the absence of magnetic order in YFe
) plane, whose intensity exceeds that of stripe spin fluctuations. Both the ferromagnetic and stripe spin fluctuations remain gapless down to the lowest measured energies. Our results naturally explain the absence of magnetic order in YFe Ge
Ge and also imply that the ferromagnetic correlations may be a key ingredient for iron-based materials.
and also imply that the ferromagnetic correlations may be a key ingredient for iron-based materials.
 T
T As
As (
( = Co,Ni)
= Co,Ni)Tam, D. M.*; Song, Y.*; Man, H.*; Cheung, S. C.*; Yin, Z.*; Lu, X.*; Wang, W.*; Frandsen, B. A.*; Liu, L.*; Gong, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 95(6), p.060505_1 - 060505_6, 2017/02
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:71.49(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We use neutron diffraction and muon spin relaxation to study the effect of in-plane uniaxial pressure on the antiferromagnetic (AF) orthorhombic phase in BaFe T
T As
As and its Co- and Ni-substituted members near optimal superconductivity. In the low-temperature AF ordered state, uniaxial pressure necessary to detwin the orthorhombic crystals also increases the magnetic ordered moment, reaching an 11% increase under 40 MPa for BaFe
and its Co- and Ni-substituted members near optimal superconductivity. In the low-temperature AF ordered state, uniaxial pressure necessary to detwin the orthorhombic crystals also increases the magnetic ordered moment, reaching an 11% increase under 40 MPa for BaFe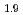 Co
Co As
As , and a 15% increase for BaFe
, and a 15% increase for BaFe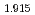 Ni
Ni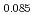 As
As . We also observe an increase of the AF ordering temperature (
. We also observe an increase of the AF ordering temperature (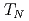 ) of about 0.25 K/MPa in all compounds, consistent with density functional theory calculations that reveal better Fermi surface nesting for itinerant electrons under uniaxial pressure. The doping dependence of the magnetic ordered moment is captured by combining dynamical mean field theory with density functional theory, suggesting that the pressure-induced moment increase near optimal superconductivity is closely related to quantum fluctuations and the nearby electronic nematic phase.
) of about 0.25 K/MPa in all compounds, consistent with density functional theory calculations that reveal better Fermi surface nesting for itinerant electrons under uniaxial pressure. The doping dependence of the magnetic ordered moment is captured by combining dynamical mean field theory with density functional theory, suggesting that the pressure-induced moment increase near optimal superconductivity is closely related to quantum fluctuations and the nearby electronic nematic phase.
 (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor
superconductorHu, D.*; Yin, Z.*; Zhang, W.*; Ewings, R. A.*; 池内 和彦*; 中村 充孝; Roessli, B.*; Wei, Y.*; Zhao, L.*; Chen, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(9), p.094504_1 - 094504_7, 2016/09
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:59.36(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)最適Pドープされた超伝導体BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) (T
(T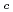 =30K)におけるスピン励起の温度及びエネルギー依存性が非弾性中性子散乱実験を使って調べられた。我々の実験結果は密度汎関数理論や動的平均場理論で予想される計算結果と矛盾しておらず、BaFe
=30K)におけるスピン励起の温度及びエネルギー依存性が非弾性中性子散乱実験を使って調べられた。我々の実験結果は密度汎関数理論や動的平均場理論で予想される計算結果と矛盾しておらず、BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) における平均プニクトゲン高さの減少が、電子相関の強さを弱め、磁気励起の有効バンド幅の増加に寄与することを示唆している。
における平均プニクトゲン高さの減少が、電子相関の強さを弱め、磁気励起の有効バンド幅の増加に寄与することを示唆している。
Zanino, R.*; Bagnasco, M.*; Baker, W.*; Bellina, F.*; Bruzzone, P.*; della Corte, A.*; Ilyin, Y.*; Martovetsky, N.*; Mitchell, N.*; Muzzi, L.*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 16(2), p.886 - 889, 2006/06
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:40.69(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)那珂核融合研究所においてITERポロイダル磁場コイル導体インサート(PFCI)の実験が予定されている。このため、PFCIの適切な実験プログラムを作成することを目的として、NbTi短尺導体サンプル実験から得られた結果の解析を行った。特に、次の項目について検討を行った;(1)巻線内の導体ジョイントがクエンチする前に導体自身の分流開始温度Tcsを測定できる可能性に関する検討。(2)解析コードMithrandirを用いて短尺導体サンプルの実験結果を解析し、いわゆる突然の又は早期のクエンチの可能性に関する検討。(3)PFCI実験における熱量法によるACロス測定の可能性。検討の結果、Tcs及びACロスの測定は可能であることがわかった。しかし、突然のクエンチについては今後のこれらの検討が必要である。