Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo mission
spp. under the ISS environmental conditions for performing exposure experiments of microbes in the Tanpopo mission河口 優子*; Yang, Y.*; 川尻 成俊*; 白石 啓祐*; 高須 昌子*; 鳴海 一成*; 佐藤 勝也; 橋本 博文*; 中川 和道*; 谷川 能章*; et al.
Origins of Life and Evolution of Biospheres, 43(4-5), p.411 - 428, 2013/10
被引用回数:41 パーセンタイル:80.34(Biology)In the Tanpopo mission, we have proposed to carry out experiments on capture and space exposure of microbes at the Exposure Facility of the Japanese Experimental Module of the International Space Station (ISS). Microbial candidates for the exposure experiments in space include  spp. We have examined the survivability of
spp. We have examined the survivability of  spp. under the environmental conditions in ISS in orbit. A One-year dose of heavy-ion beam irradiation did not affect the viability of
spp. under the environmental conditions in ISS in orbit. A One-year dose of heavy-ion beam irradiation did not affect the viability of  spp. within the detection limit. Exposure of various thicknesses of deinococcal cell aggregates to UV radiation revealed that a few hundred micrometer thick aggregate of deinococcal cells would be able to withstand the solar UV radiation on ISS for 1 year. We concluded that aggregated deinococcal cells will survive the yearlong exposure experiments. We propose that microbial cells can aggregate as an ark for the interplanetary transfer of microbes, and we named it "massapanspermia".
spp. within the detection limit. Exposure of various thicknesses of deinococcal cell aggregates to UV radiation revealed that a few hundred micrometer thick aggregate of deinococcal cells would be able to withstand the solar UV radiation on ISS for 1 year. We concluded that aggregated deinococcal cells will survive the yearlong exposure experiments. We propose that microbial cells can aggregate as an ark for the interplanetary transfer of microbes, and we named it "massapanspermia".
 to extreme environments
to extreme environments堀川 大樹*; 山口 理美*; 坂下 哲哉; 田中 大介*; 浜田 信行*; 行弘 文子*; 桑原 宏和*; 國枝 武和*; 渡邊 匡彦*; 中原 雄一*; et al.
Astrobiology, 12(4), p.283 - 289, 2012/04
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:68.76(Astronomy & Astrophysics)クマムシの乾燥休眠状態である卵の孵化率について、宇宙空間の特徴的な極限環境要因である放射線(Heイオン線),極低温,高真空に対する耐性を調べた。その結果、50%が孵化できない線量が約500Gy, -196度に曝されても70%以上が孵化し、6 10
10 Paの高真空においた後でも孵化することができることがわかった。以上の結果から、宇宙空間であってもクマムシの耐性能力により、乾眠状態であるならば、存在できる可能性が示唆された。
Paの高真空においた後でも孵化することができることがわかった。以上の結果から、宇宙空間であってもクマムシの耐性能力により、乾眠状態であるならば、存在できる可能性が示唆された。
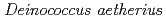 sp. nov., isolated from the stratosphere
sp. nov., isolated from the stratosphereYang, Y.*; 伊藤 隆*; 横堀 伸一*; 島田 治男*; 板橋 志保*; 佐藤 勝也; 大庭 寛史*; 鳴海 一成; 山岸 明彦*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 60, p.776 - 779, 2010/04
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:50.57(Microbiology)A pink pigmented, non-motile, coccoid bacterial strain, ST0316, was isolated from dust samples collected from the stratosphere in Japan. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that it belonged to the genus  . DNA G+C content, desiccation tolerance, and resistance to
. DNA G+C content, desiccation tolerance, and resistance to  -rays and UV radiation supported the affiliation of strain ST0316 to the genus
-rays and UV radiation supported the affiliation of strain ST0316 to the genus  . Strain ST0316 diverged from recognized species of the genus
. Strain ST0316 diverged from recognized species of the genus  , showing less than 93% similarity values to its closest relatives
, showing less than 93% similarity values to its closest relatives 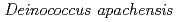 ,
, 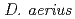 ,
,  and
and 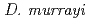 . We propose a new species of the genus
. We propose a new species of the genus  ,
, 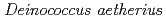 sp. nov.
sp. nov.
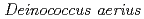 sp. nov., isolated from the high atmosphere
sp. nov., isolated from the high atmosphereYang, Y.*; 伊藤 隆*; 横堀 伸一*; 板橋 志保*; 島田 治男*; 佐藤 勝也; 大庭 寛史; 鳴海 一成; 山岸 明彦*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 59, p.1862 - 1866, 2009/00
被引用回数:32 パーセンタイル:56.58(Microbiology)日本の高度大気圏で収集した塵から、橙色の色素を持ち運動性のない球菌TR0125株が分離された。16S rRNA遺伝子をもとにした系統解析によってこの菌はデイノコッカス属細菌であることが示された。強い乾燥耐性,UV耐性, 線耐性及び高いGC含量は、この菌株がデイノコッカス属細菌であることを支持している。TR0125株は、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスの標準菌株の16S rRNA遺伝子配列と最も高い類似性(95.7%)をもち、系統解析の結果は、TR0125株が、デイノコッカス・ジオサーマリス以上に、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスと進化的に離れていることを示しており、このことは、TR0125株がこれら2種のデイノコッカス属細菌に属するものではないことを表している。他にも、TR0125株と上記2種のデイノコッカス属細菌の標準菌株との間には、幾つかの表現型に違いがあった。よって、われわれは今回分離した菌株に適合するものとして、新種デイノコッカス・アエリウスという名前を提案する。
線耐性及び高いGC含量は、この菌株がデイノコッカス属細菌であることを支持している。TR0125株は、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスの標準菌株の16S rRNA遺伝子配列と最も高い類似性(95.7%)をもち、系統解析の結果は、TR0125株が、デイノコッカス・ジオサーマリス以上に、デイノコッカス・アパチェンシスと進化的に離れていることを示しており、このことは、TR0125株がこれら2種のデイノコッカス属細菌に属するものではないことを表している。他にも、TR0125株と上記2種のデイノコッカス属細菌の標準菌株との間には、幾つかの表現型に違いがあった。よって、われわれは今回分離した菌株に適合するものとして、新種デイノコッカス・アエリウスという名前を提案する。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 藤崎 健太*; 河口 優子*; 小林 憲正*; 橋本 博文*; 河合 秀幸*; 三田 肇*; 鳴海 一成; 奥平 恭子*; et al.
no journal, ,
地球上に存在する生命の起源に関して、これまで多くの研究が行われてきた。地球における生命の起原を想定し、初期地球上での有機物の合成の可能性が検討されている。しかし、有機物の合成は地球上で進行した可能性と同時に、宇宙空間で合成された有機物が宇宙塵とともに初期地球に到達した可能性がある。一方、古くより生命が宇宙空間を移動するという仮説「パンスペルミア仮説」が提唱されていた。この仮説では地球外で誕生した生命が地球にやって来る可能性が想定されている。近年、火星由来隕石中での微生物様化石の発見を引き金に、隕石に載った微生物移動の可能性が議論されるに至っている。われわれは、これまで飛行機、大気球を用いた微生物採集を行い、成層圏から微生物を採集してきた。そこから、さらに上空でも微生物が到達している可能性に思い至った。真空中での微生物採集はこれまで試みられたことがない。われわれは、宇宙空間でデブリや宇宙塵採集に用いられてきた超低密度エアロゲルを微生物の採集に用いる可能性の検討を行った。また、エアロゲルを受動的な微生物捕集装置とする場合、他の宇宙塵等も合わせて捕集される。これらの宇宙塵には微生物が付着していなくとも有機物を含有している可能性がある。そのような宇宙塵が地球に有機物をもたらしたと考えると、それらの宇宙塵の有機物の解析を行うことも重要である。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 藤崎 健太*; 河口 優子*; 橋本 博文*; 山下 雅道*; 矢野 創*; 奥平 恭子*; 吉村 義隆*; 鳴海 一成; et al.
no journal, ,
火星起源隕石に微小化石様構造が発見されてから、パンスペルミア(胚種広布説)仮説は生命の起源を議論するうえで無視することはできなくなってきた。われわれが国際宇宙ステーション(ISS)の日本棟きぼうの曝露部で行う実験として提案した「たんぽぽ」ミッションは、さまざまな意味でパンスペルミアの現実性について検討し、テストするための実験計画である。この計画では、6種類の実験を平行して行うことを計画している。そのうち2つが宇宙における微小生物の製造可能性に関する実験である。1つはISS高度で直接微小生物の捕集を試みるものである。もう1つは、さまざまな微小生物の宇宙に対する長期の曝露実験である。後者の実験は、地球由来の微小生物が地球と他の地球外天体との間を移動することが可能であるか、微小生物を実際に宇宙空間に曝露することで検証しようというものである。われわれは、ISS高度で微小生物が長期に渡って生存するためには、惑星間塵等の内部の間隙に微小生物が入り込んで、紫外線や宇宙線から護られることが必要であろうと考えている。そこで、われわれは微小生物と模擬惑星間塵(粘土鉱物等)とを混合したものを、曝露実験に供することを計画している。
横堀 伸一*; 藤崎 健太*; 河口 優子*; Yang, Y.*; 伏見 英彦*; 橋本 博文*; 山下 雅道*; 矢野 創*; 奥平 恭子*; 林 宣宏*; et al.
no journal, ,
ISS-JEM「きぼう」曝露部での微生物の採集/宇宙空間への直接曝露実験を計画している(プロジェクト名「たんぽぽ」)。そこでは、微生物を直接採取することを目指すとともに、1から5年以上、微生物を宇宙空間に曝露し、その生存可能性を検証することを計画している。また、その際には、粘土鉱物による微生物の保護効果も検証する予定である。そのため、上記の宇宙曝露実験を行うにあたり、重粒子線の微生物生存に与える効果と、粘土鉱物の重粒子線に対する遮蔽効果を現在検討した。また、種々の紫外線/放射線耐性の高い微生物を実験対象とすることで、重粒子線耐性がそれらの耐性の高さと相関するのかなどについても検討した。微生物培養液を単独又は粘土鉱物と混合して乾燥したサンプルに、室温で、Ar線,He線,C線の照射を行った。これらの重粒子線を照射した微生物サンプルと非照射の対照サンプルについて、コロニー計数法等により、生存率を求めた。さらに、粘土鉱物(合成スクメタイトの一種ルーセンタイトを使用)の有無による生存率の違いについて検証を行った。その結果、粘土鉱物がAr線及びC線から微生物を遮蔽し、保護する働きをすることが示唆された。すなわち、微生物が宇宙空間に単独で存在せず、粘土鉱物内部の間隙などに存在するのなら、重粒子線の影響が軽減されることを示唆する。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 板橋 志保*; 藤崎 健太*; 伏見 英彦*; 長谷川 直*; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; et al.
no journal, ,
We isolated two novel species of the genus  , one from top of troposphere (
, one from top of troposphere (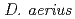 ) and the other from bottom of stratosphere (
) and the other from bottom of stratosphere (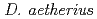 ). Can these newly isolated bacterial species and strains survive harsher environment such as space environment and/or other astronomical objects such as Mars? To address these questions, we have analyzed the survival of these microbial species and strains under the extreme conditions. Environment at high altitude is extreme for microorganisms not only because of high UV radiation, but also other stresses such as extreme dryness. To clarify how dryness affects to the survivability of microorganisms, we examined the effects of desiccation and high humidity on survival and DNA double strand breaks (DSB) of
). Can these newly isolated bacterial species and strains survive harsher environment such as space environment and/or other astronomical objects such as Mars? To address these questions, we have analyzed the survival of these microbial species and strains under the extreme conditions. Environment at high altitude is extreme for microorganisms not only because of high UV radiation, but also other stresses such as extreme dryness. To clarify how dryness affects to the survivability of microorganisms, we examined the effects of desiccation and high humidity on survival and DNA double strand breaks (DSB) of  ,
,  and spores of
and spores of 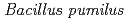 . They exhibited different survival rates and DSB patterns under desiccation and high humidity. Higher survival and less DSB occurred at lower temperatures. Spores of
. They exhibited different survival rates and DSB patterns under desiccation and high humidity. Higher survival and less DSB occurred at lower temperatures. Spores of 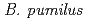 showed the highest survivability at each condition. Survivability of
showed the highest survivability at each condition. Survivability of  at desiccation condition is higher than that at the humid condition, although survivability of
at desiccation condition is higher than that at the humid condition, although survivability of  at desiccation condition is lower than that at the humid condition. We also tested the effects of various factors on survivability of
at desiccation condition is lower than that at the humid condition. We also tested the effects of various factors on survivability of  spp. Together with tests under desiccation condition, these test results suggested that
spp. Together with tests under desiccation condition, these test results suggested that  spp. which we tested can survive in space for years.
spp. which we tested can survive in space for years.
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 伏見 英彦*; 鳴海 一成; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; 河合 秀幸*; 小林 憲正*; et al.
no journal, ,
To explain how organisms on the Earth were originated at the quite early stage of the history of Earth, Panspermia hypothesis was proposed. Recent findings of the Martian meteorite suggested possible existence of extraterrestrial life, and interplanetary migration of life as well. On the other hand, microbes have been collected from high altitude using balloons, aircraft and meteorological rockets since 1936, though it is not clear how could those microbes be ejected up to such high altitude. Spore forming fungi and Bacilli, and Deinococci have been isolated in these experiments. If microbes could be found present even at the higher altitude of low earth orbit (400 km), the fact would endorse the possible interplanetary migration of terrestrial life. We proposed the "Tanpopo" mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes on Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS). In our proposal, microorganisms will be exposed to the space environment with/without model-clay materials that might protect microorganisms from vacuum UV and cosmic rays. Spore of 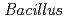 sp., and vegetative cells of
sp., and vegetative cells of  and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In preliminary experiments, clay-materials tend to increase survivability of microorganisms under irradiation of heavy ion beam and other radiation. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission.
and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In preliminary experiments, clay-materials tend to increase survivability of microorganisms under irradiation of heavy ion beam and other radiation. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission.
小林 憲正*; 三田 肇*; 中嶋 悟*; 薮田 ひかる*; 横堀 伸一*; 鳴海 一成; 長沼 毅*
no journal, ,
地球上の生命起源に関しては、地球起源説と地球外起源説がある。通常、前者が多くの支持を得ているが、後者(パンスペルミア説)の可能性は否定できない。微生物の惑星間移動の可能性を考えるうえでは、微生物の宇宙での生存可能性の検証が必要である。われわれは、惑星間塵中の有機物や微生物の耐性を調べ、パンスペルミアの可能性を検証している。具体的には、地球から脱出した微生物に、宇宙線を模した高エネルギー重粒子線や種々の波長の紫外線を照射し、微生物の生存率や変異を評価した。 等の放射線抵抗性細菌や胞子を形成する微生物は粒子線や紫外線に対して強い耐性を示した。一方、地球の場合、約40億年前にパンスペルミアもしくは化学パンスペルミアが起きたと考えられる。その場合、惑星間塵等がどの程度の太陽紫外線や銀河宇宙線・太陽フレア粒子・太陽風の照射を受けたかが問題となる。これらの評価を行ううえで、過去の太陽活動に関する情報が必要となる。このような研究においては、化学や微生物の研究者と太陽研究者との協力が不可欠である。
等の放射線抵抗性細菌や胞子を形成する微生物は粒子線や紫外線に対して強い耐性を示した。一方、地球の場合、約40億年前にパンスペルミアもしくは化学パンスペルミアが起きたと考えられる。その場合、惑星間塵等がどの程度の太陽紫外線や銀河宇宙線・太陽フレア粒子・太陽風の照射を受けたかが問題となる。これらの評価を行ううえで、過去の太陽活動に関する情報が必要となる。このような研究においては、化学や微生物の研究者と太陽研究者との協力が不可欠である。
河口 優子*; 杉野 朋弘*; Yang, Y.*; 高橋 勇太*; 吉村 義隆*; 辻 尭*; 小林 憲正*; 田端 誠*; 橋本 博文*; 鳴海 一成; et al.
no journal, ,
われわれは、地球低軌道を周回する国際宇宙ステーション日本棟曝露部を利用する「微生物・有機物の宇宙曝露と微生物・宇宙塵の捕集実験」(たんぽぽ計画)を提案している。この計画では、微生物と生命の材料となり得る有機化合物が天体間を移動する可能性の検討と微小隕石の検出及び解析実験を行う予定である。超低密度シリカエアロゲルを一定期間軌道上に曝露し、衝突する微粒子内に含まれる微生物の捕集を行うとともに、地球低軌道上での微生物の生存可能性を検証するために、微生物曝露実験を行う。本発表では、捕集する微生物を解析するうえで障害となり得る点について検討した結果について報告する。また、微生物の曝露実験については、さまざまな 属細菌について、宇宙環境を模擬した条件下(紫外線,放射線等)での生存を検討した結果を報告する。
属細菌について、宇宙環境を模擬した条件下(紫外線,放射線等)での生存を検討した結果を報告する。
横堀 伸一*; 春山 純一*; 矢野 創*; 鳴海 一成; 三田 肇*; 高橋 淳一*
no journal, ,
地球では既に失われてしまった生命の起源に関連する物質や生命の痕跡が、地球に最も近い天体である月で見つかる可能性について、宇宙環境利用科学委員会「月における生命探査の可能性の検討」研究チームで検討した。月の表面では、生命の生存はおろか、生命の起源に関連する物質でさえ、紫外線暴露や極度の温度変化等で変性・分解してしまうので、生命の痕跡が検出される可能性は極めて低い。しかし、月に複数個存在が確認されている溶岩チューブ孔及び極域永久陰は、太陽放射暴露や温度変化が少ないため、宇宙塵由来の生命起源関連物質や地球からの飛来物質が保存されている可能性がある。したがって、地球由来物質が月面に到達するかのシミュレーション,溶岩チューブ孔の形成時期の推定,模擬環境下での標的物質検出の検証などの研究とともに、in situ解析やサンプルリターンを前提とした月における生命探査は必要と結論づけられる。
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 河口 優子*; 杉野 朋弘*; 高橋 勇太*; 鳴海 一成; 高橋 裕一*; 林 宣宏*; 吉村 義隆*; 田端 誠*; et al.
no journal, ,
生物にはさまざまな極限環境に存在するものがあり、生命の起原、Astrobiology研究の重要な研究対象として、それらの研究が進んでいる。高層大気圏も極限環境であり、そこでどのような生物が存在するのか研究が行われてきた。一方、生命の起源を考えるうえで、地球外に生命の起源を求める「パンスペルミア仮説」が古くから議論されてきた。これらのことを踏まえ、われわれのグループは、国際宇宙ステーション(ISS)上で、微生物や生命の材料になりうる有機化合物が天体間で移動可能かについての検証と、微小隕石の検出及び解析実験を行うことの提案と準備を行っている。そこでは、ISS外部に一定期間曝露した超低密度エアロゲルを用いて微小隕石やその他の微粒子を捕集し、エアロゲルの回収後にその表面と衝突トラックの顕微鏡観察等のさまざまな解析を行う。ISS軌道は強力な紫外線や放射線が降り注ぐ過酷な環境下であり、微生物は長期に生存するためには宇宙塵や粘土鉱物などの微粒子の内部に存在すると考えられる。そこで捕集した微粒子にDNA特異的な蛍光染色を行い、微生物の検出を行う。本発表では、上記のような微粒子を模した微生物と粘土鉱物の混合サンプルを用いた蛍光染色やPCRによる微生物の検出についての地上模擬実験の現状について報告する。また、宇宙曝露を予定している微生物の紫外線,放射線,真空,温度などに対する耐性について、地上対照実験を進めている。これについても併せて報告し、たんぽぽ計画の進行状況を報告する。
杉野 朋弘*; 横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 河口 優子*; 長谷川 直*; 橋本 博文*; 今井 栄一*; 奥平 恭子*; 河合 秀幸*; 田端 誠*; et al.
no journal, ,
In this report, we will report whether aerogel that have been used for the collection of space debris and cosmic dusts can be used for microbe sampling in space. We will discuss how captured particles by aerogel can be detected with DNA-specific fluorescence dye, and how to distinguish microbes from other materials (i.e. aerogel and particles such as clay). The surface of microparticles captured by aerogel is often vitrified. The non-specific fluorescent light is often observed from vitrified materials. Therefore, we need to distinguish fluorescent light of stained microbes from that of spectral characteristics of vitrified materials and bleaching rate are going to be need to distinguish stained microbes with DNA-specific fluorescence dye and other materials such as clay and aerogel. We simulated the high-speed collision of micro-particles to the aerogel with the two stage light gas gun (ca. 4 km/s). The micro-particles containing dried cells of  mixed with clay material were used for the collision experiment, and the captured particles, which was stained after collision experiment, were observed with a fluorescence microscope. This experiment suggests that the captured microbes can be detected and be distinguished from clay materials.
mixed with clay material were used for the collision experiment, and the captured particles, which was stained after collision experiment, were observed with a fluorescence microscope. This experiment suggests that the captured microbes can be detected and be distinguished from clay materials.
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 杉野 朋弘*; 河口 優子*; 高橋 勇太*; 鳴海 一成; 橋本 博文*; 林 宣宏*; 今井 栄一*; 河合 秀幸*; et al.
no journal, ,
We proposed the "Tanpopo" mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes, and organic compounds on Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS). Tanpopo consists of six subthemes. Two of them are on the possible interplanetary migration of microbes capture experiment of microbes at the ISS orbit and space exposure experiment of microbes. In this paper, we focus on the space exposure experiment of microbes. Microbes in space are assumed be exposed to the space environment with a kind of clay materials that might protect microbes from vacuum UV and cosmic rays, or exposed as the aggregates of which outer cells might protect inner cells from vacuum UV and cosmic rays. Dried vegetative cells of  and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In addition, we are planning to perform another space exposure experiments of microbes. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission and others.
and our novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude are candidates for the exposure experiment. In addition, we are planning to perform another space exposure experiments of microbes. In this paper, we discuss current status of exposure experiment of microorganisms defined for the Tanpopo mission and others.
横堀 伸一*; Yang, Y.*; 河口 優子*; 杉野 朋弘*; 高橋 勇太*; 鳴海 一成; 中川 和道*; 田端 誠*; 小林 憲正*; 丸茂 克美*; et al.
no journal, ,
We propose a mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes, organic compounds and meteoroids on Japan Experimental Module (JEM) of the International Space Station (ISS) - Tanpopo mission. Ultra low-density aerogel (ca. 0.01 g/cm ) will be used to capture micrometeoroid and space debris. Particles captured by aerogel will be analyzed after the initial inspection of the gel and tracks. The particles will be characterized in terms of mineralogical, organic and microbiological properties. In addition to particle-capture experiment on ISS, we also proposed to perform direct exposure experiments of microorganisms and organic compounds. Several deinococcal species (and strains) including our high-altitude isolates, and some other microbes are candidates for exposure.
) will be used to capture micrometeoroid and space debris. Particles captured by aerogel will be analyzed after the initial inspection of the gel and tracks. The particles will be characterized in terms of mineralogical, organic and microbiological properties. In addition to particle-capture experiment on ISS, we also proposed to perform direct exposure experiments of microorganisms and organic compounds. Several deinococcal species (and strains) including our high-altitude isolates, and some other microbes are candidates for exposure.
小林 憲正*; 川本 幸徳*; Sarker, P. K.*; 小野 恵介*; 桑原 秀治*; 大林 由美子*; 金子 竹男*; 三田 肇*; 薮田 ひかる*; 吉田 聡*; et al.
no journal, ,
A wide variety of complex organic compounds including precursors of amino acids have been detected in carbonaceous chondrites and comets. It was suggested that organics in them were formed in quite cold environments, such as interstellar space. Irradiation of frozen mixture of possible interstellar molecules with high-energy particles gave complex amino acid precursors with high molecular weights. Such interstellar complex molecules would be altered by cosmic rays and solar light in proto-solar nebula and interplanetary space before the delivery to the Earth by such extraterrestrial bodies as space dusts. We examined possible alteration of amino acids and their precursors by irradiation with photons and heavy ions. Complex amino acid precursors with high molecular weights could be formed in simulated dense cloud environments, and they were much more stable than free amino acids against radiation. They could have been delivered to the Earth by space dusts. We are planning to collect space dusts and expose amino acids and their precursors in the Japan Experimental Module / Exposed Facility (JEM/EF) of the ISS in the Tanpopo Mission.
横堀 伸一*; 春山 純一*; 矢野 創*; 鳴海 一成; 三田 肇*; 高橋 淳一*
no journal, ,
月は長期に渡り大きな地殻変動が起きておらず、過去に起きた惑星間塵の飛来などのイベントの痕跡が、いわばタイムカプセルのように保存されているかも知れないと期待されている。月の表面ではDNAやタンパク質などの生体高分子の残存が困難と予想されるが、太陽紫外線や極端な温度変化を免れる溶岩チューブ孔や極域永久陰孔のような環境があれば、生体高分子が保存される可能性もある。放射線抵抗性細菌 は、放射線や真空乾燥にも強い耐性を持つので、もし過去に地球から月に飛来したものがあれば、その痕跡が残っているかも知れない。月を宇宙生物学研究の対象とするためには、疑似環境可での生体高分子の保存可能性の実験的検証や、月からの岩石等のサンプルを採取・分析するための研究体制を構築することなどが必要である。
は、放射線や真空乾燥にも強い耐性を持つので、もし過去に地球から月に飛来したものがあれば、その痕跡が残っているかも知れない。月を宇宙生物学研究の対象とするためには、疑似環境可での生体高分子の保存可能性の実験的検証や、月からの岩石等のサンプルを採取・分析するための研究体制を構築することなどが必要である。
河口 優子*; Yang, Y.*; 川尻 成俊*; 白石 啓祐*; 杉野 朋弘*; 高橋 勇太*; 谷川 能章*; 鳴海 一成; 佐藤 勝也; 橋本 博文*; et al.
no journal, ,
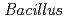 spores and
spores and 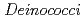 are known by their extremely high resistance against UV,
are known by their extremely high resistance against UV,  rays and other radiations.
rays and other radiations. 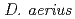 and
and 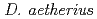 , that were novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude, showed higher resistance to UV and ionizing radiations than
, that were novel deinococcal species isolated from high altitude, showed higher resistance to UV and ionizing radiations than  . If microbes could be found present even at the higher altitude of low earth orbit, the fact would endorse the possible interplanetary migration of terrestrial life. We proposed the Tanpopo mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes on Japan Experimental Module of the International Space Station (ISS). Dried vegetative cells of
. If microbes could be found present even at the higher altitude of low earth orbit, the fact would endorse the possible interplanetary migration of terrestrial life. We proposed the Tanpopo mission to examine possible interplanetary migration of microbes on Japan Experimental Module of the International Space Station (ISS). Dried vegetative cells of  and our novel deinococcal species are candidates for the exposure experiment. We are now testing survivals of deinococcal species under the harsh environmental conditions simulating ISS environmental conditions.
and our novel deinococcal species are candidates for the exposure experiment. We are now testing survivals of deinococcal species under the harsh environmental conditions simulating ISS environmental conditions.
金澤 真吾; 大杉 武史; 中塩 信行; 石原 圭輔; 横堀 智彦; 大越 実; 時澤 孝之; 中山 真一; 木村 武*
no journal, ,
農地等の除染作業から発生する植物や土壌等の除染廃棄物を減容処理することを目的として、パイロットスケールのロータリーキルン型熱分解炉を製作し、処理試験を行った。処理試験の概要及び製作した熱分解炉の概要について報告する。