Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Asamori, Koichi; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Nakajima, Toru; Ogata, Manabu; Uchida, Mao; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Tanaka, Kiriha; et al.
JAEA-Review 2024-035, 29 Pages, 2024/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2024. The objectives and contents of this research are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Sueoka, Shigeru; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*; Niwa, Masakazu; Kanno, Mizuho; Kohn, B. P.*; Kawamura, Makoto; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Ogita, Yasuhiro; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 75(1), p.177_1 - 177_24, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Fluid-inclusion and thermochronometric analyses have been applied to hydrothermal alteration zones and their host rocks outcropping in the Hongu area of the Kii Peninsula, southwestern Japan in an attempt to detect thermal anomalies related to hydrothermal events and quantify the thermal effects on the host rocks. Hydrothermal events at ca 150 deg. C and ca 200 deg. C were identified by fluid-inclusion microthermometry of quartz veins in the alteration zones. For the host rocks and alteration zones, in the youngest population zircon yielded U-Pb dates ranging between ca 74.7-59.2 Ma, fission-track dates of ca 27.2-16.6 Ma, and (U-Th)/He single-grain dates of ca 23.6-8.7 Ma. Apatite yielded pooled fission-track ages of ca 14.9-9.0 Ma. The zircon U-Pb dates constrain the maximum depositional ages of the sedimentary samples. However, the fission-track and (U-Th)/He dates show no clear trend as a function of distance from the alteration zones. Hence, no thermal anomaly was detected in the surrounding host rocks based on the thermochronometric data patterns. The fission-track and (U-Th)/He dates are rather thought to record regional thermal and exhumation histories rather than a direct thermal imprint of fluid flow, probably because the duration of such activity was too short or because fluid flow occurred before regional cooling events and were later thermally overprinted. Apatite fission-track ages of ca 10 Ma may reflect regional mountain uplift and exhumation related to the obduction of the SW Japan lithospheric sliver onto the Shikoku Basin, or the rapid subduction of the Philippine Sea slab associated with the clockwise rotation of the Southwest Japan Arc.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishihara, Takanori; Ogawa, Hiroki; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Tsuyoshi; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2023-005, 78 Pages, 2023/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
 Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Suyama, Kazuya*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Raymond, S.*; Steffens, P.*; Yamada, Akira*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kawasaki, Ikuto; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto*
International Handbook of Evaluated Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments (CD-ROM), p.ZPPR-LMFR-EXP-001, 002, 005, 006 - Appendix M, D, G, G, 2023/00
In the International Handbook of Evaluated Reactor Physics Benchmark Experiments (IRPhEP) edited by OECD/NEA, nine ZPPR experimental cores named ZPPR-9, 10A, 10B, 10C, 13A, 17A, 18A, 18C, and 19A, which are mock-up critical experiments for sodium-cooled MOX-fueled fast reactors in the JUPITER cooperative program, are included as reactor physics benchmarks. In order to build the as-built modeling of a ZPPR experimental core, the "all master model (AMM)" map and the drawer masters are used which are attached in the ZPPR benchmark as EXCEL files. Although these materials are usually enough to reproduce a complete ZPPR as-build modeling, there is one exception for several ZPPR cores with respect to special narrow drawers called "poison safety rods (PSR)" or "shim rods." These narrow drawers have a void region in the half part of the drawer to insert absorber materials in case of emergent shutdown or criticality adjustment. To get the exact direction of the narrow drawers, the direction of the void region (Right or Left, hereafter, R or L) must be designated in the AMM maps and the drawer masters. Unfortunately, those data of JUPITER-I series (ZPPR-9, 10A, 10B and 10C) did not distinguish the direction of the narrow drawers. JAEA has surveyed the narrow drawer directions of these four ZPPR cores from the original experimental core maps and the loading records which were made by ANL experimenters. New appendices for the four ZPPR core benchmarks are prepared as EXCEL files to summarize the narrow drawer directions obtained by JAEA survey, to make it possible to build the as-built modeling of the ZPPR experimental cores.
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 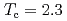 K for
K for 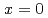 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 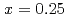 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 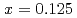 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 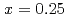 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 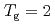 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 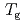 with a
with a 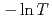 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
Higemoto, Wataru; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Ito, Takashi; Suzuki, Taiga*; Raymond, S.*; Yanase, Yoichi*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 119(49), p.e2209549119_1 - e2209549119_6, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:37.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; Ono, Koji*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Protection and Research, 47(1), p.1 - 7, 2022/03
Background: In Japan, new regulations that revise the dose limit for the lens of the eye (the lens), operational quantities, and measurement positions for the lens dose were enforced in April 2021. Based on the international safety standards, national guidelines, the results of the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund of the Nuclear Regulatory Authority, and other studies, the Working Group of Radiation Protection Standardization Committee, the Japan Health Physics Society (JHPS) developed a guideline for radiation dose monitoring for the lens. Materials and Methods: The Working Group of the JHPS discussed the criteria of non-uniform exposure and the management criteria set to not exceed the dose limit for the lens. Results and Discussion: In July 2020, the JHPS guideline was published. The guideline consists of three parts: main text, explanations, and 26 questions. In the questions, the corresponding answers were prepared, and specific examples were provided to enable similar cases to be addressed. Conclusion: With the development of guideline on radiation dose monitoring of the lens, radiation managers and workers will be able to smoothly comply with revised regulations and optimise radiation protection.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Iwai, Satoshi*; Tsujimura, Norio; Hashimoto, Makoto; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Kato, Masahiro*; Kurosawa, Tadahiro*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Sekiguchi, Hiroshi*; Koguchi, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-15) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 154, p.108100_1 - 108100_11, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the design of innovative nuclear reactors such as fast reactors, the improvement of the prediction accuracies for neutronics properties is an important task. The nuclear data adjustment is a promising methodology for this issue. The idea of the nuclear data adjustment was first proposed in 1964. Toward its practical application, however, a great deal of study has been conducted over a long time. While it took about 10 years to establish the theoretical formulation, the research and development for its practical application has been conducted for more than half a century. Researches in this field are still active, and the fact suggests that the improvement of the prediction accuracies is indispensable for the development of new types of nuclear reactors. Massimo Salvatores, who passed away in March 2020, was one of the first proposers to develop the nuclear data adjustment technique, as well as one of the great contributors to its practical application. Reviewing his long-time works in this area is almost the same as reviewing the history of the nuclear data adjustment methodology. The authors intend that this review would suggest what should be done in the future toward the next development in this area. The present review consists of two parts: a) the establishment of the nuclear data adjustment methodology and b) the achievements related to practical applications. Furthermore, the former is divided into two aspects: the study on the nuclear data adjustment theory and the numerical solution for sensitivity coefficient that is requisite for the nuclear data adjustment. The latter is separated to three categories: the use of integral experimental data, the uncertainty quantification and design target accuracy evaluation, and the promotion of nuclear data covariance development.
Shimizu, Yusei*; Miyake, Atsushi*; Maurya, A.*; Honda, Fuminori*; Nakamura, Ai*; Sato, Yoshiki*; Li, D.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; Yokoyama, Makoto*; Tokunaga, Yo; et al.
Physical Review B, 102(13), p.134411_1 - 134411_11, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:38.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Ishikawa, Makoto; Maruyama, Shuhei; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Jin, Tomoyuki*
JAEA-Research 2018-011, 556 Pages, 2019/03
We have developed a new unified cross-section set ADJ2017, which is an improved version of the unified cross-section set ADJ2010 for fast reactors. The unified cross-section set is used for reflecting information of C/E values (analysis / experiment values) obtained by integral experiment analyses; the values are stored in the standard database for FBR core design via the cross-section adjustment methodology, which integrates with the information such as uncertainty (covariance) of nuclear data, uncertainty of integral experiment / analysis, sensitivity of integral experiment with respect to nuclear data. The ADJ2017 is based on Japan's latest nuclear data library JENDL-4.0 as in the previous version of ADJ2010, and it incorporates more information on integral experimental data sets related to minor actinides (MAs) and degraded plutonium (Pu). In the creation of ADJ2010, a total of 643 integral experimental data sets were analyzed and evaluated, and 488 of the integral experimental data sets were finally selected to be used for the cross-section adjustment. In contrast, we have evaluated a total of 719 data sets, and eventually adopted 620 integral experimental data sets to create ADJ2017. ADJ2017 shows almost the same performance as ADJ2010 for the main neutronic characteristics of conventional sodium-cooled MOX-fuel fast reactors. In addition, for the neutronic characteristics related to MA and degraded Pu, ADJ2017 improves the C/E values of the integral experimental data sets, and reduces the uncertainty induced by the nuclear data. ADJ2017 is expected to be widely used in the analysis and design research of fast reactors. Moreover, it is expected that the integral experimental data sets used for ADJ2017 can be utilized as a standard database of FBR core design.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:98.03(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Pigni, M.*; Dunn, M.*; Leal, L.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.02001_1 - 02001_9, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:96.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides ( O,
O,  Fe,
Fe, 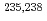 U and
U and  Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Pu) that significantly impact criticality in nuclear technologies with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality.
Palmiotti, G.*; Salvatores, M.*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Ishikawa, Makoto
NEA/NSC/R(2016)6 (Internet), 42 Pages, 2017/05
Ohgama, Kazuya; Ikeda, Kazumi*; Ishikawa, Makoto; Kan, Taro*; Maruyama, Shuhei; Yokoyama, Kenji; Sugino, Kazuteru; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Oki, Shigeo
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2017/04
 I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts applied by determination of passing-through time of plume using noble gas counts
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts applied by determination of passing-through time of plume using noble gas countsYamada, Junya; Hashimoto, Makoto; Seya, Natsumi; Haba, Risa; Muto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Shimo, Michikuni*
Hoken Butsuri, 52(1), p.5 - 12, 2017/03
The purpose of this study is to improve a quick method for estimation of  I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts in case that a nuclear disaster occurs. In this method,
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts in case that a nuclear disaster occurs. In this method,  I concentrations were estimated by multiplying
I concentrations were estimated by multiplying  I count rates of cloud-shine measured with NaI (Tl) detector by concentration conversion factor. A previous study suggested that it was difficult to determine passing-through time of plume from temporal change of
I count rates of cloud-shine measured with NaI (Tl) detector by concentration conversion factor. A previous study suggested that it was difficult to determine passing-through time of plume from temporal change of  I count rates or dose rate. Our study applies the method for estimating passing-through time of plume from temporal change of noble gas counts. The
I count rates or dose rate. Our study applies the method for estimating passing-through time of plume from temporal change of noble gas counts. The  I concentrations in the air at Oarai center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency resulting from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were estimated by proposal technique. The result of comparison of this method with sampling method for
I concentrations in the air at Oarai center, Japan Atomic Energy Agency resulting from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were estimated by proposal technique. The result of comparison of this method with sampling method for  I concentrations in the air were within factor 3.
I concentrations in the air were within factor 3.
 La
La RuO
RuO studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopy
studied by soft X-ray photoemission spectroscopyKawasaki, Ikuto*; Sakon, Yumi*; Fujimori, Shinichi; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Tenya, Kenichi*; Yokoyama, Makoto*
Physical Review B, 94(17), p.174427_1 - 174427_7, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) I concentrations in the air from pulse-height distribution observed by NaI(Tl) detector in monitoring posts
I concentrations in the air from pulse-height distribution observed by NaI(Tl) detector in monitoring postsYamada, Junya; Hashimoto, Makoto; Seya, Natsumi; Haba, Risa; Muto, Yasunobu; Shimizu, Takehiko; Takasaki, Koji; Yokoyama, Sumi*; Shimo, Michikuni*
Radioisotopes, 65(10), p.403 - 408, 2016/10
The purpose of this study is to develop a quick method for estimation of  I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts. In this method,
I concentrations in the air using data measured by monitoring posts. In this method,  I concentrations were estimated by multiplying
I concentrations were estimated by multiplying  I count rates at the full-energy peak measured with a NaI(Tl) detector by a concentration conversion factor. The concentration conversion factor for monitoring posts in JAEA Oarai Center was calculated with an EGS5 Monte Carlo code. As a result, the concentration conversion factor for an infinite-air-source was 25.7 Bq/m
I count rates at the full-energy peak measured with a NaI(Tl) detector by a concentration conversion factor. The concentration conversion factor for monitoring posts in JAEA Oarai Center was calculated with an EGS5 Monte Carlo code. As a result, the concentration conversion factor for an infinite-air-source was 25.7 Bq/m /cps.
/cps.