Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
岩本 修; 岩本 信之; 国枝 賢; 湊 太志; 中山 梓介; 安部 豊*; 椿原 康介*; 奥村 森*; 石塚 知香子*; 吉田 正*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
被引用回数:64 パーセンタイル:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)The fifth version of Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library, JENDL-5, was developed. JENDL-5 aimed to meet a variety of needs not only from nuclear reactors but also from other applications such as accelerators. Most of the JENDL special purpose files published so far were integrated into JENDL-5 with revisions. JENDL-5 consists of 11 sublibraries: (1) Neutron, (2) Thermal scattering law, (3) Fission product yield, (4) Decay data, (5) Proton, (6) Deuteron, (7) Alpha-particle, (8) Photonuclear, (9) Photo-atomic, (10) Electro-atomic, and (11) Atomic relaxation. The neutron reaction data for a large number of nuclei in JENDL-4.0 were updated ranging from light to heavy ones, including major and minor actinides which affect nuclear reactor calculations. In addition, the number of nuclei of neutron reaction data stored in JENDL-5 was largely increased; the neutron data covered not only all of naturally existing nuclei but also their neighbor ones with half-lives longer than 1 day. JENDL-5 included the originally evaluated data of thermal scattering law and fission product yield for the first time. Light charged-particle and photon induced reaction data were also included for the first time as the JENDL general purpose file.
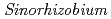 with
with 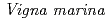 under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding
under high salt conditions using the ion beam mutation breeding丸山 雄大*; 武田 喜代子*; 友岡 憲彦*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 99, 2016/02
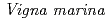 is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants.
is one of wild legumes, which called as Hamaazuki, are distributed at the vicinity of the coast from tropical to sub-tropical regions and have high salt tolerance among terrestrial plants. 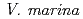 can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on
can grow at 400 mM NaCl condition. Furthermore, the root nodules on 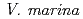 have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus
have a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia that related to the genus 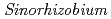 having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45
having high stress tolerance (500 mM NaCl, 45  C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however,
C, pH 10.5). Above both symbiotic partners showed extremely high salt tolerance, however, 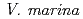 cannot develop root nodules with
cannot develop root nodules with 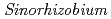 at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of
at over 80 mM NaCl conditions. To improve symbiotic performance of 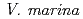 with
with 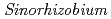 under high salt conditions,
under high salt conditions, 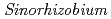 bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
bacterial cells were irradiated by carbon ion-beam at TIARA. However, so far, we could not obtain promising mutants having good symbiotic performance with Vigna marina under high salt conditions, yet.
 線3ミリメートル線量当量を測定・評価すべきか?
線3ミリメートル線量当量を測定・評価すべきか?赤羽 恵一*; 飯本 武志*; 伊知地 猛*; 岩井 敏*; 大口 裕之*; 大野 和子*; 川浦 稚代*; 黒澤 忠弘*; 立崎 英夫*; 辻村 憲雄; et al.
保健物理, 50(4), p.257 - 261, 2015/12
光子と 線の混合フィールドでは、皮膚に割り当てられた同じ線量は、
線の混合フィールドでは、皮膚に割り当てられた同じ線量は、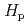 (3)の保守的な推定として水晶体への線量に一般に割り当てられる。しかしながら、線量限度と同じオーダーの非常に高い
(3)の保守的な推定として水晶体への線量に一般に割り当てられる。しかしながら、線量限度と同じオーダーの非常に高い 線量が与えられるかもしれない例外的なケースでは、その保守的にバイアスのかかった線量はあまりにも制限的であり、
線量が与えられるかもしれない例外的なケースでは、その保守的にバイアスのかかった線量はあまりにも制限的であり、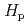 (3)の正確な評価は望ましい。この記事は、
(3)の正確な評価は望ましい。この記事は、 線
線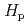 (3)の線量測定をどんなときに、どのようにしてなすべきかについて実用的な提案をする。
(3)の線量測定をどんなときに、どのようにしてなすべきかについて実用的な提案をする。
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大野 豊; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 120, 2015/03
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a viability loss of beneficial microorganisms in biofertilizers by high temperature stress during both storage and transportation. Therefore, we have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42
USDA110 using carbon-ion beams accelerated by an AVF cyclotron at TIARA. Consequently, we have obtained a high temperature tolerant mutant that can maintain a high survival rate at 42  C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
C for at least 7 days in yeast-mannitol broth medium, and named it as M14. The genome sequence of M14 was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to 18 base mutations and/or a large-scale inversion (1.27 Mb). In the future, we will conduct further analysis on these mutations in order to decipher the molecular mechanisms of high temperature tolerance of M14.
赤羽 恵一*; 飯本 武志*; 伊知地 猛*; 岩井 敏*; 大口 裕之*; 大野 和子*; 川浦 稚代*; 立崎 英夫*; 辻村 憲雄; 浜田 信行*; et al.
保健物理, 49(3), p.153 - 156, 2014/09
外部被ばくによる水晶体の線量測定に係る歴史と方法論について要約する。1989年の放射線防護関係法令の改正において、ICRP1977年勧告に基づいて導入された実効線量当量概念と水晶体の線量限度(150mSv/年)は、体幹部が不均一な放射線に曝される状況下における外部被ばくによる線量評価法を大きく変えた。そのような状況(鉛エプロンの着用によってしばしばもたらされる)では、作業者は、鉛エプロンの下側に一つ、鉛エプロンの上側(一般に上着の襟)にもう一つの個人線量計を着用する。後者の線量計は、実効線量当量評価のための線量分布を与えること、水晶体の線量当量を評価することの二つの役目をはたす。個人線量計によって指示された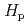 (10)と
(10)と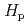 (0.07)のうち、値の大きな方又はより適切な値が、
(0.07)のうち、値の大きな方又はより適切な値が、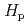 (3)の替わりに記録のため使用される。
(3)の替わりに記録のため使用される。
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2013-059, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2012, P. 114, 2014/03
With the aims of utilization as a biofertilizer inoculant and elucidation of high-temperature tolerance mechanism of soybean nodule bacteria, we had applied the ion beam breeding technology to a strain  (
(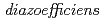 ) USDA110. Consequently, we obtained a mutant named M14 that was able to maintain high viable cell numbers under high-temperature (42
) USDA110. Consequently, we obtained a mutant named M14 that was able to maintain high viable cell numbers under high-temperature (42 C) for at least 7 days. Genome comparison with USDA110 revealed that (1) 1.27 Mbp inversion mutagenesis and (2) 84 single base mutations were occurred in M14. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to a large-scale inversion or small-scale mutations in the inverted region, or both.
C) for at least 7 days. Genome comparison with USDA110 revealed that (1) 1.27 Mbp inversion mutagenesis and (2) 84 single base mutations were occurred in M14. The acquirement of high temperature tolerance in M14 could be attributed to a large-scale inversion or small-scale mutations in the inverted region, or both.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 手島 光平*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 107, 2013/01
We have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43
USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43 C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30
C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30 C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
 -sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival
-sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival手島 光平*; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 112, 2013/01
Biofertilizer is a substance that holds beneficial microorganisms for plant growth in the carrier such as peat, perlite, charcoal and soil. To use biofertilizer more efficiently, it is necessary to keep the amount of viable inoculants in the biofertilizer for a definite period of time.  -irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of  -sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria
-sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria 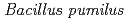 strain TUAT1 and
strain TUAT1 and 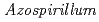 sp. strain MAFF210364.
sp. strain MAFF210364.
 -sterilization of carrier materials made with different types of soils on the shelf life of biofertilizer containing
-sterilization of carrier materials made with different types of soils on the shelf life of biofertilizer containing  strain USDA110
strain USDA110手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 横山 正*; 鳴海 一成
Radioisotopes, 61(4), p.161 - 171, 2012/04
バイオ肥料とは、植物生育を促進する細菌をピートや土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材であり、施肥効果の高いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、保存中の接種菌数を長期間維持する技術が必要である。そこで、土着菌を 線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。担体として国内の代表的な土壌5種類を供試し、
線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。担体として国内の代表的な土壌5種類を供試し、 線滅菌(50kGy)及びオートクレーブ滅菌(121
線滅菌(50kGy)及びオートクレーブ滅菌(121 C, 40min)処理した後、ダイズ根粒菌
C, 40min)処理した後、ダイズ根粒菌 USDA110株を接種した。バイオ肥料を4
USDA110株を接種した。バイオ肥料を4 C及び30
C及び30 Cで1年間保存し、接種菌の生菌数の経時的推移を調べた。その結果、滅菌しない担体では接種菌が減少したが、滅菌した担体では接種菌の増加が見られた。供給安定性、低線量
Cで1年間保存し、接種菌の生菌数の経時的推移を調べた。その結果、滅菌しない担体では接種菌が減少したが、滅菌した担体では接種菌の増加が見られた。供給安定性、低線量 線照射での高い滅菌効果、接種菌密度の保持性を考慮すると、被検土壌の中でケト土がバイオ肥料担体として最も適していると考えられた。
線照射での高い滅菌効果、接種菌密度の保持性を考慮すると、被検土壌の中でケト土がバイオ肥料担体として最も適していると考えられた。
 USDA 110 obtained by ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 obtained by ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 110, 2012/01
In order to prevent deterioration in viability of inoculants in biofertilizers exposed to high temperature, we are trying to improve a phenotypic character concerning high temperature tolerance in  USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained 9 high temperature tolerant mutants that can survive at 45
USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained 9 high temperature tolerant mutants that can survive at 45 C for 5 days. These mutants were classified into 3 groups in terms of differences in colony morphology and colony size. We will carry out further characterization of those isolates in terms of temperature tolerant and symbiotic characters.
C for 5 days. These mutants were classified into 3 groups in terms of differences in colony morphology and colony size. We will carry out further characterization of those isolates in terms of temperature tolerant and symbiotic characters.
 -sterilized carriers
-sterilized carriers手島 光平; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 114, 2012/01
The inoculants survival in the biofertilizer could be affected by the physical and chemical properties of carrier materials and by the competition with native microbes in the carrier.  -irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In an effort to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In an effort to demonstrate the effectiveness of  -sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored to assess the shelf life of biofertilizer. The inoculants density after 12-month storage was greater than the initial density in biofertilizers made from sterilized carriers, while that was significantly decreased in biofertilizers made from non-sterilized carriers.
-sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored to assess the shelf life of biofertilizer. The inoculants density after 12-month storage was greater than the initial density in biofertilizers made from sterilized carriers, while that was significantly decreased in biofertilizers made from non-sterilized carriers.  -sterilization was superior to autoclave-sterilization in enhancing the survival of inoculants. Because of the stability of supply, the high sterilization effect with lower radiation doses, and the high performance in maintaining the inoculants density, "Keto-tsuchi" was selected as one of the most suitable for a biofertilizer's carrier.
-sterilization was superior to autoclave-sterilization in enhancing the survival of inoculants. Because of the stability of supply, the high sterilization effect with lower radiation doses, and the high performance in maintaining the inoculants density, "Keto-tsuchi" was selected as one of the most suitable for a biofertilizer's carrier.
 USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 75, 2011/01
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a serious deterioration of qualities in biofertilizers under both storage and transportation conditions. In order to prevent deterioration in variability of inoculants in biofertilizers exposed to high temperature, we are trying to improve a phenotypic character concerning high temperature tolerant in  USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained high temperature tolerant mutants of
USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained high temperature tolerant mutants of  USDA 110, which can survive at 45
USDA 110, which can survive at 45 C for 5 days. Now, we are characterizing these mutants in terms of differences in several phenotypic properties.
C for 5 days. Now, we are characterizing these mutants in terms of differences in several phenotypic properties.
 -sterilization of carrier materials on the shelf life of biofertilizer
-sterilization of carrier materials on the shelf life of biofertilizer手島 光平; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 83, 2011/01
バイオ肥料とは、窒素固定細菌や植物生長を促進する菌を泥炭(ピート)や土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材であり、施肥効果の高いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、保存中における接種菌(原体微生物)の生存数を長期間維持する技術が必要である。そこで、土着の微生物を 線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。非滅菌担体では接種菌の密度は保存期間とともに低下していたが、30
線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。非滅菌担体では接種菌の密度は保存期間とともに低下していたが、30 C保存に比べ4
C保存に比べ4 C保存の方が緩やかに減少していた。一方、滅菌担体の接種菌密度は2か月目までは増加し、その後減少に転ずる傾向が見られた。特に、30
C保存の方が緩やかに減少していた。一方、滅菌担体の接種菌密度は2か月目までは増加し、その後減少に転ずる傾向が見られた。特に、30 C保存の
C保存の 線滅菌担体ではオートクレーブ滅菌担体よりも接種菌密度の増加量が大きかった。以上の結果から、バイオ肥料を低温で保存できない場合、滅菌処理した担体が接種菌の密度を維持するために有効であることが示された。また、
線滅菌担体ではオートクレーブ滅菌担体よりも接種菌密度の増加量が大きかった。以上の結果から、バイオ肥料を低温で保存できない場合、滅菌処理した担体が接種菌の密度を維持するために有効であることが示された。また、 線滅菌がより有効であることが示された。
線滅菌がより有効であることが示された。
横山 博巨*; 金沢 俊夫*; 福間 忠士*; 為清 好三*; 柳田 甲二*; 降矢 喬*; 河野 弘志*; 伊藤 圭二*; 白倉 貴雄*; 柏原 晋一郎*; et al.
PNC TN8410 87-086VOL2, 944 Pages, 1986/09
None
横山 博巨*; 金沢 俊夫*; 福間 忠士*; 為清 好三*; 柳田 甲二*; 降矢 喬*; 河野 弘志*; 伊藤 圭二*; 白倉 貴雄*; 柏原 晋一郎*; et al.
PNC TN8410 87-086VOL1, 1037 Pages, 1986/09
動燃再処理工場に設置されている既設蒸発缶(ステンレス綱製)を新材料製蒸発缶と交換 設置することを前提として、それに必要な詳細設計を実施した。すでに実施されている新型酸回収蒸発缶基本設計(2)ならびに小型モックアップ試験設備の設計、製作、異材継手・開発の成果を参考にした。蒸発缶の詳細設計、性能計算、耐震設計、板取り設計、異材継手設計、セル内配管設計、蒸発缶撤去、設置工事設計、蒸発缶の点検、保守設計、蒸発缶試運転計画、製作技術仕様書の検討、作業工程検討等を行った。
武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では、作物生産に根粒菌等を用いたバイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、輸送や保存時の高温・乾燥によるバイオ肥料の品質低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。そこで、炭素イオンビーム照射による高温耐性ダイズ根粒菌の作出を試みた。ダイズ根粒菌 USDA110株を供試菌株とし、原子力機構高崎量子応用研究所のイオンビーム照射施設(TIARA)にて炭素イオンビームを凍結乾燥菌体に照射した。照射菌体をYM寒天培地で28
USDA110株を供試菌株とし、原子力機構高崎量子応用研究所のイオンビーム照射施設(TIARA)にて炭素イオンビームを凍結乾燥菌体に照射した。照射菌体をYM寒天培地で28 C・4日間培養した後、菌体をYM寒天培地に塗抹して45
C・4日間培養した後、菌体をYM寒天培地に塗抹して45 Cで14日間静置、又はYM液体培地に懸濁して45
Cで14日間静置、又はYM液体培地に懸濁して45 Cで5日間静置し、それぞれ28
Cで5日間静置し、それぞれ28 Cで4日間再び培養して生存する菌を高温耐性獲得変異株として選抜した。その結果、照射した菌体から、45
Cで4日間再び培養して生存する菌を高温耐性獲得変異株として選抜した。その結果、照射した菌体から、45 Cで5日間生存可能な高温耐性獲得変異株が得られた。
Cで5日間生存可能な高温耐性獲得変異株が得られた。
 -irradiation of biofertilizer's carrier in bacterial inoculants survival
-irradiation of biofertilizer's carrier in bacterial inoculants survival手島 光平; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
バイオ肥料とは、窒素固定細菌や植物生長を促進する菌を泥炭(ピート)や土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材であり、農業生産における普及が期待されている。しかし、土着菌との競合が弱い場合などを除けば、安定した顕著な効果を示す実用技術は確立されていない。効率の良いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、接種菌の生存数を維持した状態で比較的長期間保存できることが必要不可欠である。バイオ肥料の保存中における接種菌密度の低下は、担体中に存在する微生物との競合も要因のひとつと考えられる。そこで、土壌を母材とした担体を用い、 線滅菌により競合相手となり得る微生物の密度を低下させた場合のバイオ肥料中での接種菌密度の変化を調べ、オートクレーブ滅菌及び非滅菌と比較した。
線滅菌により競合相手となり得る微生物の密度を低下させた場合のバイオ肥料中での接種菌密度の変化を調べ、オートクレーブ滅菌及び非滅菌と比較した。
 USDA110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
炭素イオンビーム照射による高温耐性ダイズ根粒菌の作出を試みた。はじめに、イオンビーム照射菌株の生存率、及びリファンピシン耐性をマーカーとした突然変異率を指標として、変異誘発に最適な炭素イオンビーム線量を決定した。その結果、100Gy 400Gy程度のエネルギー量が突然変異誘発に適した条件であると考えられた。次に、イオンビーム照射菌株を45
400Gy程度のエネルギー量が突然変異誘発に適した条件であると考えられた。次に、イオンビーム照射菌株を45 Cで5日間静置し、生存している菌株の選抜を行った。その結果、300Gy及び400Gy照射区から生存する菌株を6株取得した。得られた株を16S-rRNAのシークエンスの比較により同定した結果、すべての株がUSDA110株からの変異株と判定された。
Cで5日間静置し、生存している菌株の選抜を行った。その結果、300Gy及び400Gy照射区から生存する菌株を6株取得した。得られた株を16S-rRNAのシークエンスの比較により同定した結果、すべての株がUSDA110株からの変異株と判定された。
中嶋 悟*; 桐野 祐介*; 西山 直毅*; 塔ノ上 亮太*; 横山 正*; 永澤 眞*; 春井 里香*; Walker, C.; 笹本 広
no journal, ,
高レベル放射性廃棄物の地層処分において、坑道内への湧水量を低減させるため、セメント系のグラウト材料が用いられることが想定される。セメント系グラウト材料から生じる高pH溶液は、岩盤と反応し、長期的には岩盤を変質させることが懸念される。核種移行評価において、核種移行の場となる岩盤がどのように変質したかを把握することは、核種の移行挙動(拡散・収着等)に影響を与える可能性があるため重要である。本報では、高pH溶液と岩石(花崗岩質岩石)が反応したときに生じた微量の二次鉱物(変質生成物)を(顕微)赤外分光測定により推定するとともに、その生成反応を速度論的に評価した結果について報告する。
横山 正*; 武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では、作物生産に根粒菌等を用いたバイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、輸送や保存時の高温・乾燥によるバイオ肥料の品質低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。そこで、炭素イオンビーム照射による高温耐性ダイズ根粒菌の作出を試みた。現在までに、300及び400Gy照射区から45 Cで生存する菌株を6株取得した。今後は、これらの変異株の根粒形成能力を調べる予定である。また、変異の原因遺伝子を同定するため、野生株のmRNAと変異株のmRNAの網羅的な比較解析を次世代シークエンサーにより開始している。
Cで生存する菌株を6株取得した。今後は、これらの変異株の根粒形成能力を調べる予定である。また、変異の原因遺伝子を同定するため、野生株のmRNAと変異株のmRNAの網羅的な比較解析を次世代シークエンサーにより開始している。