Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 beam at J-PARC RCS
beam at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.59 - 63, 2023/11
 laser stripping at J-PARC RCS
laser stripping at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.272 - 276, 2023/01
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.656 - 660, 2021/10
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011026_1 - 011026_6, 2021/03
The charge-exchange multi-turn injection by using a carbon stripper foil is adopted in high-intensity proton ring accelerators worldwide. It is a beneficial method to compress the pulsed proton beam with high intensity but there are serious issues for high intensity. First issue is a short lifetime of the foil by deformation or breaking itself. Another issue is high radiation dose corresponding to the scattered particles on the foil. Therefore, a non-destructive stripping injection method is required for higher intensity proton beam. We newly propose a non-destructive method of H stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
stripping by using only laser. The new method is called "laser stripping injection". To establish our method, we are preparing for a POP (Proof-of-Principle) experiment of 400 MeV H- stripping to proton at J-PARC. In our presentation we will present the current status of laser system development for laser stripping injection at J-PARC.
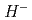 beam at J-PARC RCS
beam at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Liu, Y.*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011025_1 - 011025_7, 2021/03
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.441 - 445, 2020/09
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator. In order to realize higher intensity, new injection scheme of non-destructive type is needed instead of the foil. We newly propose laser stripping injection scheme by using laser pulse. We plan proof of principle experiment at J-PARC and are developing the laser system. In my presentation, we introduce the overview of laser stripping injection scheme and report the status of laser development.
 laser stripping at J-PARC
laser stripping at J-PARCSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.436 - 440, 2020/09
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Sato, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.841 - 845, 2019/07
 laser stripping at J-PARC 3-GeV RCS
laser stripping at J-PARC 3-GeV RCSSaha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Miura, Akihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Okabe, Kota; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Yamane, Isao*; Irie, Yoshiro*; Liu, Y.*; et al.
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.806 - 810, 2018/08
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Inoue, Shunsuke*; Sato, Atsushi*; Suganuma, Kazuaki; Yamane, Isao*; Kinsho, Michikazu; Irie, Yoshiro*
Proceedings of 15th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.811 - 815, 2018/08
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses occur by scattering at the foil. Additionally, the beam collision at the foil may cause the break itself. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. We newly propose and develop a laser stripping injection scheme. At the first step, we propose a proof-of-principle (POP) experiment of the scheme in J-PARC and develop a laser system. In this presentation, we will introduce the laser stripping injection scheme and describe an overview of a POP experiment. We will report a current status of the laser system.
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Miura, Akihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Irie, Yoshiro*; Yamane, Isao*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*
Proceedings of 61st ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams (HB 2018) (Internet), p.422 - 427, 2018/07
Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Iwamae, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 548(1), p.012038_1 - 012038_7, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.03(Physics, Applied)Polarization is a fundamental property of light, and the effective use provides us powerful tools for probing materials and for plasma diagnostics. In plasmas, alignment of emission shows the plasma anisotropy, and Zeeman splitting informs us the magnetic field strength. We took the plasma-based soft X-ray laser as an example and observed the Zeeman splitting under the external magnetic field. A grazing incidence spectrograph, HIREFS, with the resolution of 15000 was used to observe the X-ray laser line. A magnetic coil driven by an electrical pulsed power supply provided the external magnetic field of 10 35 T along the direction of the plasma column, and the left-handed and right-handed circular polarization components were obtained separately. The experimental result indicated that the magnetic field was larger by a factor of 4 than that of the applied field, which implied that the magnetic field compression occurred in the dynamics of the intense laser-plasma interaction.
35 T along the direction of the plasma column, and the left-handed and right-handed circular polarization components were obtained separately. The experimental result indicated that the magnetic field was larger by a factor of 4 than that of the applied field, which implied that the magnetic field compression occurred in the dynamics of the intense laser-plasma interaction.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sasaki, Akira; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Kishimoto, Maki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kunieda, Yuichi; Nagashima, Keisuke; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 163(1), p.012062_1 - 012062_4, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:66.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The precise knowledge about the wavelength and the spectral width of the lasing line is important for the applications of X-ray lasers, and especially for the spectral width, it is good benchmark of the atomic code because it depends on the electron collisional excitation and de-excitation rate coefficient. Only a few measurements of the spectral width of the laser line have been reported, because the spectral width of the X-ray laser is so narrow that the required spectral resolution is quite high. In this study, we took the nickel-like molybdenum X-ray laser as an example, and measure the spectral width by use of the high resolution spectrometer in order to compare it with a theoretical one.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Sasaki, Akira; Yamatani, Hiroshi; Kishimoto, Maki; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kunieda, Yuichi; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Yoneda, Hitoki*; et al.
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea, 13(1), p.60 - 64, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:29.51(Optics)The precise knowledge about the spectral width of the X-ray laser line is important to generate the circularly polarized X-ray laser. There are three magnetic sub-levels at lower state of the collisional excitation X-ray laser transition of the nickel-like ion X-ray laser medium. The polarization of each transition is circular or linear. Therefore the circularly polarized X-ray laser could be extracted by the influence of the Zeeman effect if the X-ray laser medium was under the external magnetic field. The strength of the magnetic field required for the circularly polarized X-ray laser is determined by the spectral width of the X-ray laser. Only a few measurements of the spectral width of the laser line have been reported, because the spectral width of the X-ray laser is so narrow that the required spectral resolution is quite high. In this study, we took the nickel-like molybdenum X-ray laser as an example and succeeded the measurement of the spectral width of the X-ray laser.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sasaki, Akira; Kishimoto, Maki; Tanaka, Momoko; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kunieda, Yuichi; Iwamae, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*
no journal, ,
We tried to generate the circularly polarized X-ray laser by use of the high power pulse magnet system. There are three magnetic sub-levels at lower state of the collisional excitation X-ray laser transition. For example, nickel-like X-ray laser transition (4d (m = 0) - 4p (m = -1, 0, +1)), the polarization from each transitions are right-handed circular ( m = -1), left-handed circular (
m = -1), left-handed circular ( m = +1), and linear (
m = +1), and linear ( m = 0) along to the quantization axis. If the quantization axis were decided by the magnetic field from the outside of the X-ray laser medium, the circularly polarized X-ray laser can be extracted. In this study, we tried to generate the circularly polarized X-ray laser by using the nickel-like molybdenum X-ray laser medium (18.9 nm) with 20 Tesla magnetic field generated by the pulse power magnet system.
m = 0) along to the quantization axis. If the quantization axis were decided by the magnetic field from the outside of the X-ray laser medium, the circularly polarized X-ray laser can be extracted. In this study, we tried to generate the circularly polarized X-ray laser by using the nickel-like molybdenum X-ray laser medium (18.9 nm) with 20 Tesla magnetic field generated by the pulse power magnet system.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sasaki, Akira; Kishimoto, Maki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yoneda, Hitoki*
no journal, ,
We proposed and demonstrated the polarization control method of an X-ray laser using the magnetic field for the first time. The line of nickel-like molybdenum X-ray laser was separated using a high-resolution spectrometer with strong magnetic field. The result of this experiments implied the left and right handed circularly polarized X-ray laser were generated at the same time. It is very applicable for a circular dichroism measurement.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme can realize high intensity proton beam but the uncontrolled beam losses are caused by scattering between beams and the foil. Additionally, the collision may occur the foil beak. Therefore, a new injection scheme for higher intensity is needed as an alternative to the foil. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme by using a laser and develop the laser system for a test. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection and report the status of the development.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection. Additionally, we report the status of the development and the schedule of the experiment.
Fuchi, Aoi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In the J-PARC as high-intensity proton accelerator, beam injection into a synchrotron uses for charge exchange process from hydrogen to proton. For higher intensity beam, we study laser development and POP experiment for charge exchange by using laser. In our method, we consider doppler shift and multi process of electron stripping. Therefore, we are developing high power laser and the 5th harmonics. In order to reduce laser power, we must increase the utilization rate of laser. So, we develop multi-pass cavity and beam shaper. In our presentation, we will report about a status of high-repetition laser and optics devices under developing.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection. Additionally, we report the status of the development and the results of the first experiment (day-1).