Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Hikaru*; Suto, Masahito*; Otsuki, Kentaro*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Yoshida, Hiroko*
Japan Architectural Review (Internet), 6(1), p.e12353_1 - e12353_12, 2023/00
 (001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Takayanagi, Shuhei*; Ojima, Shoki*; Maeda, Motoyasu*; Origuchi, Naoki*; Ogawa, Arata*; Ikeda, Natsuki*; Aoyagi, Yoshihide*; Kabutoya, Yuito*; et al.
Langmuir, 37(42), p.12313 - 12317, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.51(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
(001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:96.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 decomposition on Si(110)
decomposition on Si(110)Yano, Masahiro; Uozumi, Yuki*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 16, p.370 - 374, 2018/08
 reduction reaction region at void periphery on Si(110)
reduction reaction region at void periphery on Si(110)Yano, Masahiro; Uozumi, Yuki*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Asaoka, Hidehito
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 57(8S1), p.08NB13_1 - 08NB13_4, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.89(Physics, Applied)Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Ogawa, Satoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yagi, Shinya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
The decontamination of radioactive Cs from the soil and the water has been required in Fukushima. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are attractive candidate for Cs adsorbent. AuNPs fabricated by solution plasma method is not covered by dispersant and is almost clean. It is known that L-cysteine rapidly adsorbs and exists with high density on the AuNPs surface. The electrostatic attractive force may be useful to induce interactions between -COO- of L-cysteine and Cs ion in aqueous solution. This study reveals the adsorption reaction between the Cs and the Cys/AuNP. Cys/AuNP has a peak and CsCl/Cys/AuNP has no peak in Na 1s spectra. Cys/AuNP has no peak and CsCl/Cys/AuNP has a peak for Cs 3
ion in aqueous solution. This study reveals the adsorption reaction between the Cs and the Cys/AuNP. Cys/AuNP has a peak and CsCl/Cys/AuNP has no peak in Na 1s spectra. Cys/AuNP has no peak and CsCl/Cys/AuNP has a peak for Cs 3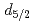 spectra. From these results, Na
spectra. From these results, Na on Cys/AuNP is replaced by Cs
on Cys/AuNP is replaced by Cs after reaction in CsCl aqueous solution. Cys/AuNP and CsCl/Cys/AuNP have a O 1s peak, where the peak position of CsCl/Cys/AuNP is higher than that ofCys/AuNP. This indicates the further polarization of -COO- by replacing Na
after reaction in CsCl aqueous solution. Cys/AuNP and CsCl/Cys/AuNP have a O 1s peak, where the peak position of CsCl/Cys/AuNP is higher than that ofCys/AuNP. This indicates the further polarization of -COO- by replacing Na by Cs
by Cs .
.
 -ray directional radiation dose detector with good efficiency for field survey
-ray directional radiation dose detector with good efficiency for field surveyYamamori, Ryo*; Kobayashi, Hikaru*; Honta, Shohei*; Yoshino, Hiroshi*; Nozaki, Atsuo*; Ichijo, Yusuke*; Hijikata, Yoshio*; Yoshida, Hiroko*; Furuta, Takuya
no journal, ,
Understanding radiation field is important to predict radiation dose rate in newly constructing buildings in an area widely contaminated by radioactive nuclei. Directional spectra of the radiations are important to consider the shielding effect of the building. We adopts a method to measure the directional spectra by adopting a plate of lead collimator in front of the scintillator and subtract the values from the spectra measured without lead collimator. We investigated a possible weight saving detection system having sufficient detection efficiency. The investigation was carried out for the condition of the collimator radius ( = 10, 15, 20 cm) and the distance between collimator and detector (
= 10, 15, 20 cm) and the distance between collimator and detector ( = 1, 3, 5 cm). We found that three combinations satisfied the 90
= 1, 3, 5 cm). We found that three combinations satisfied the 90 field view and the detection efficiency became better with larger collimator radius. On the other hand, larger collimator radius indicate heavier detection system. Therefore, we developed an optimum detection system for field survey with the 15 cm diameter plate (10kg), the scintillator (3.4kg), and the folder (1.0kg).
field view and the detection efficiency became better with larger collimator radius. On the other hand, larger collimator radius indicate heavier detection system. Therefore, we developed an optimum detection system for field survey with the 15 cm diameter plate (10kg), the scintillator (3.4kg), and the folder (1.0kg).
Ajikawa, Yusuke*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
A very small amount of gas control was indispensable for surface reaction experiments under ultrahigh vacuum conditions. Normally, it has been performed with a variable leak valve by the manual operation. However, the manual operation can not apply for advanced experiments such as multi-measurements. The automatic precise valve control would lead to the burden reduction and reproducible improvement. The antomatic control also has a metrit to avid the loss of control for the apparatus. In this conference, we will report recent developments of the automatic pressure control system and some results of precise pressure control from 10 to 10
to 10 Pa.
Pa.
Tsukada, Chie; Yoshida, Hikaru; Ogawa, Satoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yagi, Shinya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
We focus on the Au nanoparticle, which is fabricated by solution plasma method, as the adsorbent with high density and high efficiency of Cs in solution. To remove the Cs from the solution, we attempt two methods, which are the Cs adsorption on the Au nanoparticle surface and the interaction between the Cs and the L-cysteine on Au nanoparticle. Judging from the results of SR-XPS for the sample at the latter method, we suggest the interaction between the Cs and the COOH group of L-cysteine on Au nanoparticle.
in solution. To remove the Cs from the solution, we attempt two methods, which are the Cs adsorption on the Au nanoparticle surface and the interaction between the Cs and the L-cysteine on Au nanoparticle. Judging from the results of SR-XPS for the sample at the latter method, we suggest the interaction between the Cs and the COOH group of L-cysteine on Au nanoparticle.
 Pt(111)
Pt(111)Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
The oxidation with oxygen molecules is important in a metal corrosion process. In order to develop high noncorrosive materials, the understanding of oxidation processes is significant. In this study, the influence on oxidation reaction due to alloy ingredient difference was investigated by the comparison between Cu Au(111) and Cu
Au(111) and Cu Pt(111) surfaces. It was found that the Cu
Pt(111) surfaces. It was found that the Cu Pt(111) surface has lower reactivity than the Cu
Pt(111) surface has lower reactivity than the Cu Au(111) surface.
Au(111) surface.
Tsukada, Chie*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Ogawa, Satoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yagi, Shinya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
To recovery from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, the removal of radioactive Cs from the soil and cooling water is important. An absorbent and a removal procedure of Cs are required to have properties of effective separation ability, recyclable and energy saving. Here, we focus on the gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) fabricated by solution plasma method. The purpose of this study is to reveal the surface chemical states of the AuNPs fabricated by solution plasma method in CsCl aqueous solution. From the synchrotron light based analysis, it was found that the Cs-Cl-Au bondings form by the repeat of below two steps. (1) Cs and Cl atoms adsorb on AuNPs surface (Cs-Au and Cl-Au bondings). (2) Au atoms bonds around the AuNPs surface.
Katsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Takayanagi, Shuhei*; Ojima, Shoki*; Maeda, Motoyasu*; Yoshida, Hikaru*; Nishi, Shizuka*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abe, Masayuki*
no journal, ,
TiO has been extensively studied because of high photocatalytic activity. However, the basic reaction process of photocatalysis has not been understood yet. In this study, the difference in water adsorption reaction between rutile and anatase was clarified using synchrotron radiation soft X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The OH component observed at the higher binding energy side was clearly confirmed in the rutile type TiOTiO
has been extensively studied because of high photocatalytic activity. However, the basic reaction process of photocatalysis has not been understood yet. In this study, the difference in water adsorption reaction between rutile and anatase was clarified using synchrotron radiation soft X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The OH component observed at the higher binding energy side was clearly confirmed in the rutile type TiOTiO , suggesting that the rutile type is more reactive to water adsorption.
, suggesting that the rutile type is more reactive to water adsorption.
 H
H on Cu(410)
on Cu(410)Makino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
The de-hydrogenation reaction of hydrocarbon molecules at metal surface is important as an elementary process of graphene generation and various catalytic reactions. In order to investigate C H
H reactions at Cu(410) surface, C
reactions at Cu(410) surface, C H
H molecular beams and synchrotron radiation X-rays photoelectron spectroscopy was used. We found that the chemical species which became dehydrogenation adsorbs at the surface when C
molecular beams and synchrotron radiation X-rays photoelectron spectroscopy was used. We found that the chemical species which became dehydrogenation adsorbs at the surface when C H
H molecule has kinetic energy of 2 eV.
molecule has kinetic energy of 2 eV.
Yamamori, Ryo*; Kobayashi, Hikaru*; Honta, Shohei*; Yoshino, Hiroshi*; Nozaki, Atsuo*; Ichijo, Yusuke*; Yoshida, Hiroko*; Furuta, Takuya
no journal, ,
Understanding radiation field is important to predict radiation dose rate in newly constructing buildings in an area widely contaminated by radioactive nuclei. Radiation dose rate at the site is not sufficient, and directional spectra of the radiations are important to consider the shielding effect of the building. Radiation directional spectra can be measured by scintillator partially shielded by lead collimators but the angle of view highly depends on the combination of the scintillator and the collimators. We adopts a method to measure the directional spectra by adopting 3 inch scintillator with placing a plate of lead collimator in front of the scintillator and subtract the values from the spectra measured without lead collimator. We simulates the optimal size of the lead collimator and found that the 15 cm diameter plate placing at 3 cm from the scintillator is the best for our purpose, 90 degree angle of view.
Tsuda, Yasutaka*; Makino, Takamasa*; Yoshida, Hikaru; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Fukuyama, Tetsuya*; Okada, Michio*
no journal, ,
Initial stage of corrosion is one of the central topics in material science. In the present study, we report the results of oxidation on Cu Pd(111) and Cu
Pd(111) and Cu Pt(111) with a hyperthermal O
Pt(111) with a hyperthermal O molecular beam (HOMB) with variable incident energies, using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. All experiments were performed using the Surface Reaction Analysis Apparatus constructed in BL23SU at SPring-8. The Cu
molecular beam (HOMB) with variable incident energies, using X-ray photoemission spectroscopy in conjunction with synchrotron radiation. All experiments were performed using the Surface Reaction Analysis Apparatus constructed in BL23SU at SPring-8. The Cu Pd(111) and Cu
Pd(111) and Cu Pt(111) samples were cleaned by Ar+ sputtering and annealing. The kinetic energy of the HOMB was set to be 2.3 eV. From the uptake curves, it was found that the oxidation of Cu
Pt(111) samples were cleaned by Ar+ sputtering and annealing. The kinetic energy of the HOMB was set to be 2.3 eV. From the uptake curves, it was found that the oxidation of Cu Pt is less effective than that on Cu
Pt is less effective than that on Cu Au and Cu
Au and Cu Pd. This suppression of the surface reactivity may be caused by the Pt-rich subsurface layer.
Pd. This suppression of the surface reactivity may be caused by the Pt-rich subsurface layer.
Chen, B.*; Yoshida, Takehito*; Yokomura, Ryota*; Terashima, Hikaru*; Hanari, Toshihide; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Fukui, Rui*
no journal, ,
In the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the modularized rail structure, "Rail DRAGON" has been developed to observe inside the PCV for avoiding the troubles of robot teleoperation. Because there are obstacles on the path of the extending rail, the operators need to control the joint angles and avoid them. In this research, we propose "wire switch method" to concurrently execute the module connection and the control of joint angles. By setting up a detour of the power line and automatically judging the suitable moment that the fluctuation of angle signals is small, we proved that joint control can be maintained during the wire switching.
Kobayashi, Kensei*; Kawamoto, Yukinori*; Sarker, P. K.*; Ono, Keisuke*; Kuwahara, Hideharu*; Obayashi, Yumiko*; Kaneko, Takeo*; Mita, Hajime*; Yabuta, Hikaru*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
Kobayashi, Kensei*; Kawamoto, Yukinori*; Sarker, P. K.*; Kuwahara, Hideharu*; Obayashi, Yumiko*; Kaneko, Takeo*; Mita, Hajime*; Yabuta, Hikaru*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Narumi, Issei; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yokobori, Shinichi*; Kawaguchi, Yuko*; Yang, Y.*; Kawashiri, Narutoshi*; Shiraishi, Keisuke*; Shimizu, Yasuyuki*; Takahashi, Yuta*; Sugino, Tomohiro*; Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English