Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Nakahara, Masaumi; Funakoshi, Tomomasa; Hoshino, Takanori; Takahatake, Yoko; Sakamoto, Atsushi; Aihara, Haruka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshida, Toshiki; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.168 - 174, 2025/05
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a project named "Systematic Treatment of RAdioactive liquid waste for Decommissioning (STRAD)" project since 2018 for fundamental and practical studies for treating radioactive liquid wastes with complicated compositions. Fundamental studies have been conducted using genuine liquid wastes accumulated in a hot laboratory of the JAEA called the Chemical Processing Facility (CPF), and treatment procedures for all liquid wastes in CPF were successfully designed on the results obtained. As the next phase of the project, new fundamental and practical studies on primarily organic liquid wastes accumulated in different facilities of JAEA are in progress. This paper reviews the representative achievements of the STRAD project and introduces an overview of ongoing studies.
Yoshida, Junya; Akaishi, Takaya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Kim, S.; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011112_1 - 011112_8, 2021/03
Kim, S. H.*; Ichikawa, Yudai; Sako, Hiroyuki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei*; Nanamura, Takuya*; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Yoshida, Junya; 11 of others*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 940, p.359 - 370, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)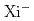 hyperon capture at rest in nuclear emulsion
hyperon capture at rest in nuclear emulsionTheint, A. M. M.*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Yoshida, Junya; 7 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.021D01_1 - 021D01_10, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Ashikaga, Sakiko; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Kimbara, Shinji*; Nanamura, Takuya; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.021D02_1 - 021D02_11, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:83.20(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kimbara, Shinji*; Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Yoshida, Junya; 12 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(1), p.011H01_1 - 011H01_9, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A development has been achieved in the identification method of the charges 1 to 5 of nuclides from the decay of double hypernuclei to be uniquely recognized by their nuclear species. The method is basically the measurement of track volume by the widths, depths, and angles of tracks of exposed nuclei of  H,
H,  He,
He,  Li,
Li,  Be, and
Be, and  B in nuclear emulsion at Riken Projectile-fragment Separator of RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. After their calibration by
B in nuclear emulsion at Riken Projectile-fragment Separator of RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. After their calibration by  particles, we obtained a quadric function to present a unified recognition of tracks with volume ratios of five nuclei to the
particles, we obtained a quadric function to present a unified recognition of tracks with volume ratios of five nuclei to the  particles. The function in the emulsion has been applied to a candidate event of a
particles. The function in the emulsion has been applied to a candidate event of a  hypernucleus for identification of the production and decay processes. We succeeded in recognizing a daughter nuclear fragment of a single-
hypernucleus for identification of the production and decay processes. We succeeded in recognizing a daughter nuclear fragment of a single- hypernucleus as
hypernucleus as  He with a likelihood ratio of 0.9; the process was then uniquely identified as
He with a likelihood ratio of 0.9; the process was then uniquely identified as 
 +
+  N
N 
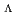
 Be +
Be + 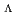
 He +
He +  .
.
Kawasaki, Masatsugu; Nakajima, Junya; Yoshida, Keisuke; Kato, Saori; Nishino, Sho; Nozaki, Teo; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Tsunoda, Junichi; Sugaya, Yuki; Hasegawa, Rie; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2017-004, 57 Pages, 2017/03
In emergency situation of nuclear facilities, we need to estimate the radiation dose due to radiation and radioactivity to grasp the influence range of the accident in the early stage. Therefore, we prepare the case studies of dose assessment for public exposure dose and personal exposure dose and contribute them to emergency procedures. This document covers about accidents of nuclear facilities in Nuclear Science Research Institute and past accident of nuclear power plant, and it can be used for inheritance of techniques of emergency dose assessment.
Yamada, Katsunori; Fujii, Katsutoshi; Kanda, Hiroshi; Higashi, Daisuke; Kobayashi, Toshiaki; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Fukami, Tomoyo; Yoshida, Keisuke; Ueno, Yumi; Nakajima, Junya; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-033, 51 Pages, 2013/12
After the accident at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant, various numerical criteria relevant to radiation protection were defined. We surveyed these criteria through internet. As a result of survey, the following 13 items were identified: (1) criteria for taking stable iodine tablets, (2) criteria for the screening of surface contamination, (3) evacuation area, sheltering area, etc., (4) activity concentrations in food, drinking water, etc., (5) dose limit for radiation workers engaged in emergency work, (6) guideline levels of radioactive substances in bathing areas, (7) criteria for use of school buildings and schoolyards, (8) restriction on planting rice, (9) acceptable activity concentrations in feedstuff, (10) acceptable activity concentrations in compost, (11) criteria for export containers and ships, (12) criteria for contaminated waste, (13) standards for radiation workers engaged in decontamination work. In this report, the basis of and issues on these criteria are summarized.
Shiraishi, Junya; Yoshida, Zensho*; Furukawa, Masaru*
Astrophysical Journal, 697(1), p.100 - 105, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.30(Astronomy & Astrophysics)A thin disk accompanied by spindle-like jet, created commonly near massive central objects, exhibits a topologically singular aspect when viewed from an ideal macroscopic theory. The accreting inflow and jet's outflow are "singular perturbation" on the ambient Keplerian rotation, which are generated by some non-ideal higher-order (in the order of derivatives) effect. The Hall effect can generate such a structure in a weakly ionized plasma of a protostellar disk. Numerical estimate of the characteristic length scale defined by the singular perturbation justifies the precedence of the Hall effect.
Katayama, Hisato*; Kitamura, Harushige*; Mori, Mari*; Nakagawa, Junya*; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Kawai, Toshihiko*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 94, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Junya
no journal, ,
J-PARC E07 is a unique experiment at J-PARC to investigate double strangeness nuclei with hybrid emulsion method. It was designed to obtain ten times more double strangeness nuclei than that obtained by previous experiments. Moreover, it aims the first measurement of X-ray from 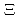 -atom by Germanium detector. Beam exposure of E07 and photographic development of emulsion sheets are successfully completed. Several double strangeness events are found through searching work. I will report the present status, analysis of detected events, and the prospect of the experiment.
-atom by Germanium detector. Beam exposure of E07 and photographic development of emulsion sheets are successfully completed. Several double strangeness events are found through searching work. I will report the present status, analysis of detected events, and the prospect of the experiment.
Kitamura, Harushige*; Katayama, Hisato*; Mori, Mari*; Nakagawa, Junya*; Yoshida, Takahiro*; Kawai, Toshihiko*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
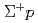 scattering events in the J-PARC E40 experiment
scattering events in the J-PARC E40 experimentNanamura, Takuya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Yoshida, Junya; Miwa, Koji*; Honda, Ryotaro*; Akazawa, Yuya*; Yamamoto, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Hyperon-nucleon scattering experiment is one of the powerful methods for studying YN interaction. However, it is difficult due to short lifetime of hyperon. 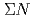 scattering experiments were performed as KEK E251 and KEK E289 in order to measure the differential cross sections. In these experiments, statistics were limited to less than 100 events and differential cross section had too large statistical errors to restrict baryon-baryon interaction models. J-PARC E40 experiment aims for measuring cross sections of
scattering experiments were performed as KEK E251 and KEK E289 in order to measure the differential cross sections. In these experiments, statistics were limited to less than 100 events and differential cross section had too large statistical errors to restrict baryon-baryon interaction models. J-PARC E40 experiment aims for measuring cross sections of 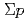 scatterings with high statistics (
scatterings with high statistics (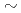 10000 events) by overcoming difficulties of hyperon-nucleon scattering experiment. By using high rate (
10000 events) by overcoming difficulties of hyperon-nucleon scattering experiment. By using high rate ( 19M /spill)
19M /spill)  beam and large acceptance spectrometer, we can produce and tag large amount of
beam and large acceptance spectrometer, we can produce and tag large amount of  beam. LH
beam. LH target and surrounding detector system CATCH enable us to reconstruct reactions from two body kinematics. Our experimental group completed
target and surrounding detector system CATCH enable us to reconstruct reactions from two body kinematics. Our experimental group completed 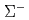 data taking and about half of
data taking and about half of 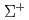 data taking by 2019 Apr. Left data taking will be performed in the end of this fiscal year.
data taking by 2019 Apr. Left data taking will be performed in the end of this fiscal year.
Yoshida, Junya; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Ekawa, Hiroyuki*; Yoshimoto, Masahiro*; Kasagi, Ayumi*; Lin, P. M.*; Nyaw, A. N. L.*; Nakazawa, Kazuma*
no journal, ,
J-PARC E07 is an experiment with the photographic emulsion technique to detect 10 times higher statistics of double hypernuclei compared to the past experiments. This experiment aims to obtain quantitative data on  -
- and
and  -nucleon interaction, by the mass measurement of various double hypernuclei. As of July 2019, we have scanned about 53% of 1300 emulsion sheets at least once and detected about 30 candidate events of double hypernuclei. We start a study of the branching ratio of the decay mode with the accumulating data. However, the detection efficiency is about half of the designed value. It is due to the rugged surface position of emulsion module. We are developing the correction method to reconstruct its original geometry by using proton tracks which punch through SSD and emulsion sheets.
-nucleon interaction, by the mass measurement of various double hypernuclei. As of July 2019, we have scanned about 53% of 1300 emulsion sheets at least once and detected about 30 candidate events of double hypernuclei. We start a study of the branching ratio of the decay mode with the accumulating data. However, the detection efficiency is about half of the designed value. It is due to the rugged surface position of emulsion module. We are developing the correction method to reconstruct its original geometry by using proton tracks which punch through SSD and emulsion sheets.
Yoshida, Junya
no journal, ,
J-PARC E07, the largest experiment with Double Lambda hypernucleus thus far at J-PARC was designed and performed. Double  hypernuclei, rare nuclei containing 2 Lambda particles is one of the important subjects in modern hadron nuclear physics. The experiment is unique in that photographic emulsion sheets are employed as the main detector for Double
hypernuclei, rare nuclei containing 2 Lambda particles is one of the important subjects in modern hadron nuclear physics. The experiment is unique in that photographic emulsion sheets are employed as the main detector for Double  hypernuclei. We performed the physics-run in the J-PARC hadron facility in 2016-17. One of the observed events was identified as a beryllium 11 double Lambda. We measured the strength of Lambda-Lambda interaction through the event. Moreover, we detected several
hypernuclei. We performed the physics-run in the J-PARC hadron facility in 2016-17. One of the observed events was identified as a beryllium 11 double Lambda. We measured the strength of Lambda-Lambda interaction through the event. Moreover, we detected several  hypernuclei events which suggest multiple bound levels of
hypernuclei events which suggest multiple bound levels of  particle in the nucleus. Further event search is ongoing.
particle in the nucleus. Further event search is ongoing.
Yoshida, Hiroko*; Nomura, Naoki*; Kono, Takahiko; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kuroda, Yujiro*; Naito, Wataru*; Hirota, Seiko*; Kudo, Shinichi*; Takahara, Shogo; Etani, Reo*; et al.
no journal, ,
The WG has translated the "Practical Guidance for Engagement with the Public on Radiation and Risk" ("IRPA Guidance") issued by the International Radiation Protection Association ("IRPA") to its member societies in 2020. "Practical Guidance for Engagement with the Public on Radiation and Risk" (hereinafter referred to as "IRPA Guidance") published by the International Radiological Protection Association (hereinafter referred to as "IRPA") in 2020 for its member societies, and to provide the information to radiation protection experts and other interested.
Yoshida, Hiroko*; Nomura, Naoki*; Kono, Takahiko; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kuroda, Yujiro*; Naito, Wataru*; Hirota, Seiko*; Kudo, Shinichi*; Kawaguchi, Isao*; Etani, Reo*; et al.
no journal, ,
The WG has translated the "Practical Guidance for Engagement with the Public on Radiation and Risk" ("IRPA Guidance") issued by the International Radiation Protection Association ("IRPA") to its member societies in 2020. "The content of the IRPA guidance was presented at a symposium organized by the Health Physics Society of Japan in June 2020. The content of the IRPA guidance was presented at the Health Physics Society planning symposium held in June 2020, where many experts attended and provided feedback. In this planning session, we will focus on public engagement and related specific examples and situations related to public engagement.
Yoshida, Junya
no journal, ,
The studies of double strangeness nuclei play an important role for modern hadron physics because they have been providing information about Lambda-Lambda and Xi-Nucleon interaction as extensions of nuclear force. J-PARC E07 is a unique experiment at J-PARC to investigate double strangeness nuclei with hybrid emulsion method. This experiment was designed to obtain ten times more double strangeness nuclei than that obtained by previous experiments. Moreover, it aims the first measurement of X-ray from Xi-atom by Germanium detector. The beam exposure of E07 was successfully completed in 2016 and 2017. New double strangeness nuclear events will be detected in the near future through the analysis of emulsion sheet. I will report the present status and the future prospect of the experiment.
Kimura, Daisuke; Hikinuma, Yuichi; Tanabe, Masanori; Makino, Tatsuya; Maegawa, Yoshiharu; Hayata, Kenichi*; Shiotani, Junya*; Nohara, Naofumi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -
- N interaction by measurement of twin hypernuclei with hybrid emulsion method at J-PARC
N interaction by measurement of twin hypernuclei with hybrid emulsion method at J-PARCHayakawa, Shuhei; Yoshida, Junya
no journal, ,
The studies of hyperon-nucleon and hyperon-hyperon interactions are necessary for the understanding of general baryon-baryon interaction. Even in the  = -1 sector such as
= -1 sector such as 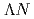 and
and 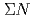 , the available data is limited. As for the
, the available data is limited. As for the  = -2 sector such as
= -2 sector such as 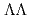 and
and 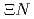 , there are few experimental data. The J-PARC E07 experiment was performed to investigate
, there are few experimental data. The J-PARC E07 experiment was performed to investigate  = -2 hypernuclei at J-PARC K1.8 beam line. Using a K- meson beam with the momentum of 1.81 GeV/c,
= -2 hypernuclei at J-PARC K1.8 beam line. Using a K- meson beam with the momentum of 1.81 GeV/c,  - hyperons are produced in the quasi-free
- hyperons are produced in the quasi-free 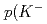 , K
, K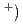
 - reaction at a diamond target. A method using combined information between two spectrometers and nuclear emulsion, called hybrid emulsion method, was conducted by using silicon-strip detectors and one hundred eighteen emulsion modules. A twin
- reaction at a diamond target. A method using combined information between two spectrometers and nuclear emulsion, called hybrid emulsion method, was conducted by using silicon-strip detectors and one hundred eighteen emulsion modules. A twin  hypernuclear event, named IBUKI event, was observed with a newly developed scanning system. At the
hypernuclear event, named IBUKI event, was observed with a newly developed scanning system. At the  - capture point, two
- capture point, two  hypernuclei of
hypernuclei of 
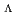 Be and
Be and 
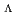 He were the most likely to be produced by the conservation laws of energy and momentum. The reaction process of the IBUKI event was identified as
He were the most likely to be produced by the conservation laws of energy and momentum. The reaction process of the IBUKI event was identified as  - +
- +  N
N 

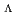 Be +
Be + 
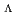 He. The binding energy of
He. The binding energy of  - +
- +  N system was determined to be 1.27
N system was determined to be 1.27  0.21 MeV. From the consideration of an excited state, the energy level for
0.21 MeV. From the consideration of an excited state, the energy level for 
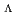 Be was interpreted to be the ground state (2-) or the other state of the spin doublet (1-). The IBUKI event was the first event whose binding energy was determined with a little ambiguity. The binding energy indicates a bound state of the
Be was interpreted to be the ground state (2-) or the other state of the spin doublet (1-). The IBUKI event was the first event whose binding energy was determined with a little ambiguity. The binding energy indicates a bound state of the  -
- N system by an attractive
N system by an attractive 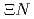 interaction. In this talk, we would like to report the above result of the IBUKI event.
interaction. In this talk, we would like to report the above result of the IBUKI event.