Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Strasser, P.*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(7), p.3445 - 3450, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Chemistry, Analytical)Ichikawa, Tsubasa*; Hakoshima, Hideaki*; Inui, Koji*; Ito, Kosuke*; Matsuda, Ryo*; Mitarai, Kosuke*; Miyamoto, Koichi*; Mizukami, Wataru*; Mizuta, Kaoru*; Mori, Toshio*; et al.
Nature Reviews Physics (Internet), 6(6), p.345 - 347, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:99.15(Physics, Applied)Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Yamamoto, Koshi*; Asahara, Yoshihiro*; Maruyama, Ippei*; Karukaya, Koichi*; Saito, Akane*; Matsui, Hiroya; Mochizuki, Akihito; Jo, Mayumi*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.67_1 - 67_10, 2024/05
A capability to permanently seal fluid flow-paths through bedrock, like boreholes or underground tunnels, is needed to ensure the long-term safety and effectiveness of many underground activities e.g. CO storage, hydrocarbon field abandonment, and nuclear waste disposal. Commonly used cementitious seals may not be sufficiently durable due to chemical and physical degradation. Learning from natural calcite (CaCO
storage, hydrocarbon field abandonment, and nuclear waste disposal. Commonly used cementitious seals may not be sufficiently durable due to chemical and physical degradation. Learning from natural calcite (CaCO ) concretion formation, a more durable sealing method was developed using a "concretion-forming solvent". The method was tested by sealing flow-paths next to a tunnel in an underground research laboratory at 350 meters depth. The flow-paths initially sealed rapidly, then resealed after disturbance by earthquakes (M5.4). The treated rock recovered its very low natural permeability, demonstrating permanent sealing that is robust.
) concretion formation, a more durable sealing method was developed using a "concretion-forming solvent". The method was tested by sealing flow-paths next to a tunnel in an underground research laboratory at 350 meters depth. The flow-paths initially sealed rapidly, then resealed after disturbance by earthquakes (M5.4). The treated rock recovered its very low natural permeability, demonstrating permanent sealing that is robust.
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Chiu, I.-H.; Kudo, Takuto*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Sentoku, Sawako*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.1797_1 - 1797_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The amount of C in steel, which is critical in determining its properties, is strongly influenced by steel production technology. We propose a novel method of quantifying the bulk C content in steel non-destructively using muons. This revolutionary method may be used not only in the quality control of steel in production, but also in analyzing precious steel archaeological artifacts. A negatively charged muon forms an atomic system owing to its negative charge, and is finally absorbed into the nucleus or decays to an electron. The lifetimes of muons differ significantly, depending on whether they are trapped by Fe or C atoms, and identifying the elemental content at the muon stoppage position is possible via muon lifetime measurements. The relationship between the muon capture probabilities of C/Fe and the elemental content of C exhibits a good linearity, and the C content in the steel may be quantitatively determined via muon lifetime measurements. Furthermore, by controlling the incident energies of the muons, they may be stopped in each layer of a stacked sample consisting of three types of steel plates with thicknesses of 0.5 mm, and we successfully determined the C contents in the range 0.20 - 1.03 wt% depth-selectively, without sample destruction.
 evaluation tests in an Underground Research Laboratory, Horonobe, Japan
evaluation tests in an Underground Research Laboratory, Horonobe, JapanYoshida, Hidekazu*; Yamamoto, Koshi*; Asahara, Yoshihiro*; Maruyama, Ippei*; Karukaya, Koichi*; Saito, Akane*; Matsui, Hiroya; Mochizuki, Akihito; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Metcalfe, R.*
Powering the Energy Transition through Subsurface Collaboration; Proceedings of the 1st Energy Geoscience Conference (Energy Geoscience Conference Series, 1), 20 Pages, 2024/00
A capability to permanently seal fluid flow-paths in bedrock, such as natural faults/fractures, and damaged zones around boreholes/excavations, is needed to ensure the long-term safety and effectiveness of many underground activities. Cementitious materials are commonly used as seals, however these materials unavoidably undergo physical and chemical degradation, therefore potentially decreasing seal durability. In order to solve these problems, a more durable sealing method using concretion-forming resin has been developed by learning from natural calcite (CaCO ) concretion formation. The sealing capability of resin was tested by
) concretion formation. The sealing capability of resin was tested by  experiments on bedrock flow-paths in an underground research laboratory (URL), Hokkaido, Japan. The results showed a decrease the permeability rapidly down to 1/1,000 of the initial permeability due to calcite precipitation over a period of one year. During the experiment inland earthquakes occurred with foci below the URL (depths 2-7 km and maximum magnitude 5.4). Due to the earthquakes the hydraulic conductivities of the flow-paths sealed initially by concretion-forming resin increased. However, these flow-paths subsequently resealed rapidly, and within a few months recovered the same hydraulic conductivities as before the earthquakes. This new technique for rapidly producing long-lasting seals against fluid flow through rocks will be applicable to many kinds of underground activities.
experiments on bedrock flow-paths in an underground research laboratory (URL), Hokkaido, Japan. The results showed a decrease the permeability rapidly down to 1/1,000 of the initial permeability due to calcite precipitation over a period of one year. During the experiment inland earthquakes occurred with foci below the URL (depths 2-7 km and maximum magnitude 5.4). Due to the earthquakes the hydraulic conductivities of the flow-paths sealed initially by concretion-forming resin increased. However, these flow-paths subsequently resealed rapidly, and within a few months recovered the same hydraulic conductivities as before the earthquakes. This new technique for rapidly producing long-lasting seals against fluid flow through rocks will be applicable to many kinds of underground activities.
Misaki, Satoshi*; Miwa, Hiroko*; Ito, Takashi; Yoshida, Takefumi*; Hasegawa, Shingo*; Nakamura, Yukina*; Tokutake, Shunta*; Takabatake, Moe*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Chun, W.-J.*; et al.
ACS Catalysis, 13(18), p.12281 - 12287, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:46.16(Chemistry, Physical)Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:75.48(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Nakae, Masanori*; Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Tsuji, Koichi*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 54, p.89 - 99, 2023/03
Fundamental research on X-ray absorption imaging for elemental identification was studied. A secondary target was applied to obtain X-ray absorption images above and below the X-ray absorption edge of the target element. X-rays from an X-ray tube were irradiated to the secondary target, where the characteristic X-rays were emitted that were irradiated to the sample. X-ray absorption images were acquired with an exposure time of a few seconds with an X-ray camera. In this technique, it is difficult to change the energy of X-rays as we want, however we can apply this technique for imaging the specific element. Metal foil sample composed of Al, Cu, and Ni was analyzed. To obtain an X-ray elemental image of Ni, two X-ray absorption images were taken using the X-rays above and below the Ni K-edge. X-rays of Cu K and Zn K
and Zn K were prepared by using Cu and Zn plates as the secondary target. Finally, the Ni elemental image was obtained by subtracting two images. Furthermore, the X-ray camera had a function of setting critical energies for imaging, thus it was demonstrated that an X-ray elemental image of Ni was obtained using a single secondary target without changing the secondary target.
were prepared by using Cu and Zn plates as the secondary target. Finally, the Ni elemental image was obtained by subtracting two images. Furthermore, the X-ray camera had a function of setting critical energies for imaging, thus it was demonstrated that an X-ray elemental image of Ni was obtained using a single secondary target without changing the secondary target.
Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Nakae, Masanori*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Tsuji, Koichi*
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 199, p.106593_1 - 106593_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:34.91(Spectroscopy)Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Fuchita, Tomoki*; Urata, Taisei*; Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Ueda, Akihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Sasaki, Toshiki; Tsuji, Koichi*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 53, p.77 - 87, 2022/03
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis is an analytical method to obtain elemental information by detecting fluorescence X-rays emitted from a sample irradiated with X-rays. It is possible to obtain two-dimensional elemental distribution images by scanning a sample with micro X-ray beam. In this study, we developed an XRF analytical instrument to rapidly obtain the elemental distributions for moving samples on a belt conveyor by applying the micro XRF technique. X-rays were widely irradiated to the belt conveyor. The elemental distributions were measured by scanning an X-ray detector, crossing above the belt conveyor. A collimator was attached to the top of the detector to limit the analyzing area. Both detection limit and spatial resolutions for moving directions of the detector and the belt conveyor were evaluated. Finally, it was demonstrated that the multi-elemental imaging was possible with the developed XRF instrument.
Yoshida, Shogo*; Koyama, Takehide*; Yamada, Haruhiko*; Nakai, Yusuke*; Ueda, Koichi*; Mito, Takeshi*; Kitagawa, Kentaro*; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review B, 103(15), p.155153_1 - 155153_5, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targets
Xe ions on proton, deuteron, and carbon targetsSun, X. H.*; Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Ahn, D. S.*; Aikawa, Masayuki*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; Kawakami, Shunsuke*; Koyama, Shumpei*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064623_1 - 064623_12, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:55.09(Physics, Nuclear)The spallation and fragmentation reactions of  Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
Xe induced by proton, deuteron and carbon at 168 MeV/nucleon were studied at RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory via the inverse kinematics technique. The cross sections of the lighter products are larger in the carbon-induced reactions due to the higher total kinetic energy of carbon. The energy dependence was investigated by comparing the newly obtained data with previous results obtained at higher reaction energies. The experimental data were compared with the results of SPACS, EPAX, PHITS and DEURACS calculations. These data serve as benchmarks for the model calculations.
 F from
F from  O
O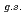 ?
?Tang, T. L.*; Uesaka, Tomohiro*; Kawase, Shoichiro; Beaumel, D.*; Dozono, Masanori*; Fujii, Toshihiko*; Fukuda, Naoki*; Fukunaga, Taku*; Galindo-Uribarri, A.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(21), p.212502_1 - 212502_6, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:72.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The structure of a neutron-rich  F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree (
F nucleus is investigated by a quasifree ( ) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of
) knockout reaction. The sum of spectroscopic factors of 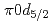 orbital is found to be 1.0
orbital is found to be 1.0  0.3. The result shows that the
0.3. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus, and the core consists of
O nucleus, and the core consists of  35%
35%  O
O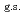 , and
, and  65% excited
65% excited  O. The result shows that the
O. The result shows that the  O core of
O core of  F nucleus significantly differs from a free
F nucleus significantly differs from a free  O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the
O nucleus. The result may infer that the addition of the  proton considerably changes the neutron structure in
proton considerably changes the neutron structure in  F from that in
F from that in  O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
O, which could be a possible mechanism responsible for the oxygen dripline anomaly.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Wada, Michiharu*; Iimura, Hideki; Sonnenschein, V.*; Iimura, Shun*; Takamine, Aiko*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Kojima, Takao*; Ahn, D. S.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(11), p.113D02_1 - 113D02_12, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An in-flight separator, BigRIPS, at RIBF in RIKEN provides each experiment with specific nuclides separated from many nuclides produced by projectile fragmentation or in-flight fission. In this process, nuclides other than separated ones are discarded on the slits in BigRIPS, although they include many nuclides interested from the view point of nuclear structure. In order to extract these nuclides for parasitic experiments, we are developing a method using laser ion-source (PALIS). A test experiment with 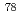 Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around
Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around  Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Wang, H.*; Otsu, Hideaki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Kawase, Shoichiro*; Takeuchi, Satoshi*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Koyama, Shumpei*; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Nakayama, Shinsuke; et al.
Communications Physics (Internet), 2(1), p.78_1 - 78_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.67(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Searching for effective pathways for the production of proton- and neutron-rich isotopes through an optimal combination of reaction mechanism and energy is one of the main driving forces behind experimental and theoretical nuclear reaction studies as well as for practical applications in nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste. We report on a study on incomplete fusion induced by deuteron, which contains one proton and one neutron with a weak binding energy and is easily broken up. This reaction study was achieved by measuring directly the cross sections for both proton and deuteron for  Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
Pd at 50 MeV/u via inverse kinematics technique. The results provide direct experimental evidence for the onset of a cross-section enhancement at high energy, indicating the potential of incomplete fusion induced by loosely-bound nuclei for creating proton-rich isotopes and nuclear transmutation of radioactive waste.
 , and COS
, and COSYoshida, Go*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Higemoto, Wataru; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Taichi*; Kubo, Kenya*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 320(2), p.283 - 289, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.76(Chemistry, Analytical)The role of valence electrons for the muon capture process by molecules is experimentally investigated with the aid of cascade calculations. Low-momentum muons are introduced to gas targets below atmospheric pressure. The initial states of captured muons are determined from the measured muonic X-ray structure of the Lyman and Balmer series. We propose that the lone pair electrons in the carbon atom of CO significantly contribute to the capture of a muon with large angular momenta.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Strasser, P.*; Abe, Mitsushi*; Aoki, Masaharu*; Choi, S.*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Higashi, Yoshitaka*; Higuchi, Takashi*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Ikedo, Yutaka*; Ishida, Katsuhiko*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 198, p.00003_1 - 00003_8, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:98.61(Quantum Science & Technology)Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.