Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Kubo, Kenya*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Yoshida, Go*; Chiu, I.-H. ; Kudo, Takuto*; Asari, Shunsuke*; Sentoku, Sawako*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 14, p.1797_1 - 1797_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0The amount of C in steel, which is critical in determining its properties, is strongly influenced by steel production technology. We propose a novel method of quantifying the bulk C content in steel non-destructively using muons. This revolutionary method may be used not only in the quality control of steel in production, but also in analyzing precious steel archaeological artifacts. A negatively charged muon forms an atomic system owing to its negative charge, and is finally absorbed into the nucleus or decays to an electron. The lifetimes of muons differ significantly, depending on whether they are trapped by Fe or C atoms, and identifying the elemental content at the muon stoppage position is possible via muon lifetime measurements. The relationship between the muon capture probabilities of C/Fe and the elemental content of C exhibits a good linearity, and the C content in the steel may be quantitatively determined via muon lifetime measurements. Furthermore, by controlling the incident energies of the muons, they may be stopped in each layer of a stacked sample consisting of three types of steel plates with thicknesses of 0.5 mm, and we successfully determined the C contents in the range 0.20 - 1.03 wt% depth-selectively, without sample destruction.
Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Makoto*; Kishimoto, Tadafumi*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
From the viewpoint of energy security in Japan and reduction of the environmental load, continuous operation of light water reactors is essential. Since a pH adjuster with enriched Li-7 ions is required for water quality control on PWR, the development of Li-7 enrichment technology is one of the key issues. The multi-channel counter-current electrophoresis (MCCCE) method has been developed as the technology with a low environmental load. To put this method into practical use, it is necessary to understand Li-7 ion behavior in the channel flow and optimize the experimental condition to separate Li-7 and its isotope. In this paper, to understand Li-7 ion behavior in a single channel of the experimental apparatus, a numerical simulation method based on a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) code with a particle tracking method, TPFIT-LPT, was developed. In the method, the motion of multiple ions under the electric field was simulated as a particle with an added velocity by the electric field. The difference in the isotopes was represented by changing of the magnitude of the added velocity. We also considered that although it is impossible to measure the behavior of each ion, it is important to measure the flow velocity of the bulk fluid for the validation of the numerical simulation. We developed a lab-scale experimental apparatus in which the single channel of the actual apparatus was simplified to measure the flow velocity by Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV). We set a pulsation flow condition on the lab-scale experiment, which is one of difficult conditions for the numerical simulation, and measured the velocity. As the result, we confirmed that the pulsation flow was reproduced. We set the measured data as the inlet boundary condition of the numerical simulation and conducted it. As the numerical result, we confirmed the ions affected by the electric field moved upstream with pulsation. We also confirmed the effect of the electric field on the motion of the isotope.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Ishida, Taku*; Nakano, Keita; Abe, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Spina, T.*; Ammigan, K.*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2021-001, p.138 - 143, 2022/03
To predict the operating lifetime of materials in high-energy radiation environments at proton accelerator facilities, Monte Carlo code are used to calculate the number of displacements per atom (dpa). However, there is no experimental data in the energy region above 30 GeV. In this presentation, we introduce our experimental plan for displacement cross sections with 120-GeV protons at Fermilab Test Beam Facility. Experiments will be performed for the US fiscal year 2022. We developed the sample assembly with four wire sample of Al, Cu, Nb and W with 250- m diameter and 4-cm length. The sample assembly will be maintained at around 4 K by using a cryocooler in a vacuum chamber. Then, changes in the electrical resistivity of samples will be obtained under 120-GeV proton irradiation. Recovery of the accumulated defects through isochronal annealing, which is related to the defect concentration in the sample, will also be measured after the cryogenic irradiation.
m diameter and 4-cm length. The sample assembly will be maintained at around 4 K by using a cryocooler in a vacuum chamber. Then, changes in the electrical resistivity of samples will be obtained under 120-GeV proton irradiation. Recovery of the accumulated defects through isochronal annealing, which is related to the defect concentration in the sample, will also be measured after the cryogenic irradiation.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011050_1 - 011050_6, 2021/03
R&D of the beam window is crucial in the ADS, which serves as a partition between the accelerator and the target region. Although the displacement per atom (DPA) is used to evaluate the damage on the window, experimental data on the displacement cross section is scarce in the energy region above 20 MeV. We started to measure the displacement cross section for the protons in the energy region between 0.4 to 3 GeV. The displacement cross section can be derived by resistivity change divided by the proton flux and the resistivity change per Frankel pair on cryo-cooled sample to maintain damage. Experiments were conducted at the 3 GeV proton synchrotron at the J-PARC Center, and aluminum and copper was used as samples. As a result of comparison between the present experiment and the calculation of the NRT model, which is widely used for calculation of the displacement cross section, it was found that the calculation of the NRT model overestimated the experiment by about 3 times.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Shima, Tatsushi*
Materials Science Forum, 1024, p.95 - 101, 2021/03
To predict the lifetime of target materials in high-energy radiation environments at spallation neutron sources, radiation transport codes such as PHITS are used to calculate the displacements per atom (DPA) value. In this work, to validate calculated DPA values of tungsten, we implemented 0.25-mm-diameter wire sample of tungsten in a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler and measured the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the displacement cross section using 389-MeV protons at 10 K. As well as our previous results for aluminum and copper, calculated results with defect production efficiencies provided good agreements with experimental data. Based on measurements of recovery of the defects through annealing, about 85% of the damage remained at 60 K, and the same tendency is observed in other experimental result for reactor neutron irradiation.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(10), p.1141 - 1151, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:75.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)To estimate the structural damages of materials in accelerator facilities, displacement per atom (dpa) is widely employed as a damage index, calculated based on the displacement cross-section obtained using a calculation model. Although dpa is applied as standard, the experimental data of the displacement cross-section for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV are scarce. Among the calculation models, difference of about factor 8 exist, so that the experimental data of the cross-section are crucial to validate the model. To obtain the displacement cross-section, we conducted experiments at J-PARC. The displacement cross-section of copper and iron was successfully obtained for a proton projectile with the kinetic energies, 0.4 - 3 GeV. The results were compared with those obtained using the widely utilized Norgertt-Robinson-Torrens (NRT) model and the athermal-recombination-corrected (arc) model based on molecular dynamics. It was found that the NRT model overestimates the present displacement cross-section by 3.5 times. The calculation results obtained using with the arc model based on the Nordlund parameter show remarkable agreement with the experimental data. It can be concluded that the arc model must be employed for the dpa calculation for the damage estimation of copper and iron.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.06006_1 - 06006_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)R&D of the beam window is crucial in the ADS, which serves as a partition between the accelerator and the target region. Although the displacement per atom (DPA) is used to evaluate the damage on the window, experimental data on the displacement cross section is scarce in the energy region above 20 MeV. We started to measure the displacement cross section for the protons in the energy region between 0.4 to 3 GeV. The displacement cross section can be derived by resistivity change divided by the proton flux and the resistivity change per Frankel pair on cryo-cooled sample to maintain damage. Experiments were conducted at the 3 GeV proton synchrotron at the J-PARC Center, and copper was used as samples. As a result of comparison between the present experiment and the calculation of the NRT model, which is widely used for calculation of the displacement cross section, it was found that the calculation of the NRT model overestimated the experiment by about 3 times.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Kinomura, Atsushi*; Shima, Tatsushi*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.061003_1 - 061003_5, 2020/02
To predict the lifetime of target materials in high-energy radiation environments at spallation neutron sources, radiation transport codes such as PHITS are used to calculate the displacements per atom (DPA) value. In this work, to validate calculated DPA values of tungsten, we implemented 0.25-mm-diameter wire sample of tungsten in a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler and measured the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the displacement cross section using 389-MeV protons at 10 K. In comparison with experimental data under 1.1 and 1.9 GeV proton irradiation, we found that damage rate of tungsten increases with proton energy due to increase the number of secondary particle s produced by nuclear reactions.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 28, p.061004_1 - 061004_6, 2020/02
no abstracts in English
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2130, p.050001_1 - 050001_8, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.09(Physics, Nuclear)We find a novel phenomenon induced by the interplay between a strong magnetic field and finite orbital angular momenta in hadronic systems, which is analogous to the Paschen-Back effect observed in the field of atomic physics. This effect allows the wave functions to drastically deform. We discuss anisotropic decay from the deformation as a possibility to measure the strength of the magnetic field in heavy-ion collision at LHC, RHIC and SPS, which has not experimentally been measured. As an example we investigate charmonia with finite orbital angular momentum in a strong magnetic field. We calculate the mass spectra and mixing rate. To obtain anisotropic wave functions, we apply the cylindrical Gaussian expansion method, where the Gaussian bases to expand the wave functions have different widths along transverse and longitudinal directions in the cylindrical coordinate.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
International Journal of Modern Physics; Conference Series (Internet), 49, p.1960002_1 - 1960002_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.09(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The hadronic Paschen-Back effects in P-wave charmonia are analyzed using the constituent quark models in strong magnetic field.
 , and COS
, and COSYoshida, Go*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Inagaki, Makoto*; Higemoto, Wataru; Strasser, P.*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Taichi*; Kubo, Kenya*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 320, p.283 - 289, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:41.24(Chemistry, Analytical)The role of valence electrons for the muon capture process by molecules is experimentally investigated with the aid of cascade calculations. Low-momentum muons are introduced to gas targets below atmospheric pressure. The initial states of captured muons are determined from the measured muonic X-ray structure of the Lyman and Balmer series. We propose that the lone pair electrons in the carbon atom of CO significantly contribute to the capture of a muon with large angular momenta.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
Physics Letters B, 790, p.71 - 76, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:71.88(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We find a novel phenomenon induced by the interplay between a strong magnetic field and finite orbital angular momenta in hadronic systems, which is analogous to the Paschen-Back effect observed in the field of atomic physics. This effect allows the wave functions to drastically deform. We discuss anisotropic decay from the deformation as a possibility to measure the strength of the magnetic field in heavy-ion collision at LHC, RHIC and SPS, which has not experimentally been measured. As an example we investigate charmonia with finite orbital angular momentum in a strong magnetic field. We calculate the mass spectra and mixing rate. To obtain anisotropic wave functions, we apply the cylindrical Gaussian expansion method, where the Gaussian bases to expand the wave functions have different widths along transverse and longitudinal directions in the cylindrical coordinate.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; Satoh, Daiki; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Shima, Tatsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 508, p.195 - 202, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.7(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To validate the displacement damage model in radiation transport codes used for the estimation of radiation damages at accelerator facilities, we measured electrical resistance increase of aluminum and copper induced by radiation defects under the cryogenic 200 MeV proton irradiation. The irradiation device had the structure to cool two irradiation samples at same time using thermal conductance. The aluminum and copper wire with 250  m diameter was sandwiched between two AlN plates with excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. As a result, temperature of irradiation samples was kept at below 5 K under proton irradiation with beam intensity below 3 nA. The experimental displacement cross section agreed with calculated results with defect production efficiency.
m diameter was sandwiched between two AlN plates with excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. As a result, temperature of irradiation samples was kept at below 5 K under proton irradiation with beam intensity below 3 nA. The experimental displacement cross section agreed with calculated results with defect production efficiency.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; et al.
Proceedings of 61st ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High-Intensity and High-Brightness Hadron Beams (HB 2018) (Internet), p.116 - 121, 2018/07
The radiation damage model in the radiation transport code PHITS has been developed to calculate the basic data of the radiation damage including the energy of the target Primary Knock on Atom (PKA). For the high-energy proton incident reactions, a target PKA created by the secondary particles was more dominant than a target PKA created by the projectile. To validate the radiation damage model in metals irradiated by  100 MeV protons, we developed a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler to cryogenically cool wire samples. By using this device, the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the DPA cross section of copper and aluminum were measured under irradiation with 125 and 200 MeV protons at cryogenic temperature. A comparison of the experimental data with the calculated results indicates that the DPA cross section with defect production efficiencies provide better quantitative descriptions.
100 MeV protons, we developed a proton irradiation device with a Gifford-McMahon cryocooler to cryogenically cool wire samples. By using this device, the defect-induced electrical resistivity changes related to the DPA cross section of copper and aluminum were measured under irradiation with 125 and 200 MeV protons at cryogenic temperature. A comparison of the experimental data with the calculated results indicates that the DPA cross section with defect production efficiencies provide better quantitative descriptions.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Yoshida, Makoto*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.499 - 501, 2018/06
no abstracts in English
Hosaka, Atsushi; Hiyama, Emiko; Kim, S.-H.*; Kim, H.-C.*; Nagahiro, Hideko*; Noumi, Hiroyuki*; Oka, Makoto; Shirotori, Kotaro*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Nuclear Physics A, 954, p.341 - 351, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.8(Physics, Nuclear)In this paper, we discuss reactions involving charmed baryons to explore their unique features. A well known phenomenon, the separation of the two internal motions of the  and
and  types of a three-quark system is revisited. First we discuss the mass spectrum of low-lying excitations as functions of the heavy quark mass, smoothly connecting the
types of a three-quark system is revisited. First we discuss the mass spectrum of low-lying excitations as functions of the heavy quark mass, smoothly connecting the 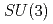 and heavy quark limits. The properties of these modes can be tested in the production and decay reactions of the baryons. For the productions, we consider a one step process which excites dominantly
and heavy quark limits. The properties of these modes can be tested in the production and decay reactions of the baryons. For the productions, we consider a one step process which excites dominantly  mode excitations. We find abundant production rates for some of excited states. For decays, we study pion emission process, which provides a clean tool to test the structure of heavy quark systems due to well controlled low energy dynamics of the pion and quark. Both productions and decays of the charmed baryons are the issues of the future experiments at J-PARC.
mode excitations. We find abundant production rates for some of excited states. For decays, we study pion emission process, which provides a clean tool to test the structure of heavy quark systems due to well controlled low energy dynamics of the pion and quark. Both productions and decays of the charmed baryons are the issues of the future experiments at J-PARC.
Yoshida, Masahiro*; Ishii, Kenji; Naka, Makoto*; Ishihara, Sumio*; Jarrige, I.*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Kudo, Kazutaka*; Koike, Yoji*; Nagata, Tomoko*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.23611_1 - 23611_8, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Kojima, Keiji*; Onishi, Yuzo*; Aoki, Kenji*; Tochiyama, Osamu*; Nishigaki, Makoto*; Tosaka, Hiroyuki*; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Murakami, Hiroaki; Sasao, Eiji
JAEA-Research 2015-017, 54 Pages, 2015/12
This report is concerned with research to reconstruct more realistic near-field (NF) concept for the geological disposal of radioactive waste. This year is the final year of this committee activities. So we have carried out the summary on Re-thinking of NF concept and its technical basis. Cooperation between the study fields and combination of various science and technology and evaluation methods are one of the important technical bases of NF concept. In addition, since the "Great East Japan Earthquake 2011", the safety paradigm has shifted dramatically. In the reconstruction of realistic NF concept, it is necessary to analyze what security matters whether society has become unacceptable for geological disposal. Committee, we also exchange views on such matters and presented the direction of future research and development for geological disposal.