Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Yamashita, Susumu; Sano, Yoshihiko*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(6), p.523 - 541, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a numerical method with the JUPITER code with a porous medium model to calculate the thermal behavior in PCVs of 1F. In this study, we performed an experiment and numerical simulation of the natural convective heat transfer with the porous medium to validate JUPITER with the porous medium model. In comparison of the temperature and velocity distributions between the experiment and simulation, the temperature distribution in the simulation was in good agreement with the distribution in the experiment except the temperature near the top surface of the porous medium. The velocity distribution also agreed qualitatively with the experimental result. In addition, we also performed the numerical simulations with various effective thermal conductivity models to discuss the effect of the conductivity based on the internal structure of porous media on the natural convective heat transfer. The result indicated that the temperature distribution in the porous medium and the velocity distribution of the natural convection were significantly different for each model, and thus the conductivity of the fuel debris was one of the key parameters of in the thermal behavior analysis in 1F.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Nagatake, Taku; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.432 - 456, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We performed electrostatic simulations of a wire-mesh sensor (WMS) for a single spherical bubble and bubbly flow to clarify the accuracy of the WMS. The electrostatic simulation for the single bubble showed the electric current density distribution and the electric current path from the excited transmitter to receivers for various bubble locations. It indicated systematic errors based on the nonuniform current density distribution around the WMS. The electrostatic simulation for the bubbly flow calculated by the computational fluid dynamics code, JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER), indicated that the WMS had difficulty in quantitatively measuring the intermediate values of the instantaneous void fraction between 0 and 1 because they cannot be estimated by previous transformation methods from the WMS signal to the void fraction, such as linear approximation or Maxwell's equation, and have a significant deviation of the void fraction of  0.2 for the WMS signal. However, the electrostatic simulation indicated that the time-averaged void fractions around the center of the flow channel can be estimated using linear approximation, and the time-averaged void fraction near the wall of the flow channel can be estimated using Maxwell's equation.
0.2 for the WMS signal. However, the electrostatic simulation indicated that the time-averaged void fractions around the center of the flow channel can be estimated using linear approximation, and the time-averaged void fraction near the wall of the flow channel can be estimated using Maxwell's equation.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 13th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS13) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/11
A conductance-typed wire-mesh sensor (WMS), utilizing the difference in conductivity between gas and liquid phases between the electrodes, is one of the practical measurement techniques of a cross-sectional void fraction distribution in a flow path. In this study, we performed two-phase computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and electrostatic simulations around a WMS for a single spherical bubble and bubbly flow to clarify the systematic error in the WMS. The results for the single bubble indicated that there were systematic errors based on the non-uniform current density distribution around the WMS. The correlation between instantaneous void fractions and WMS signals is not uniquely determined for positions of the single bubble moving across the WMS, even for the same bubble. Moreover, the correlation between the instantaneous void fractions and the WMS signals did not fit in a linear approximation and Maxwell's equation, which traditionally used transformation methods from the WMS signal to the void fraction. The results for the bubbly flow indicated that the WMS had difficulty in quantitative measurements of the instantaneous void fraction because the values had a significant deviation of the void fraction of approximately  0.2. On the other hand, time-averaged void fraction values had relatively small deviation. Thus, we concluded that the WMS, using existing transformation methods, can measure time-averaged void fractions, but it is difficult to measure quantitatively instantaneous void fractions.
0.2. On the other hand, time-averaged void fraction values had relatively small deviation. Thus, we concluded that the WMS, using existing transformation methods, can measure time-averaged void fractions, but it is difficult to measure quantitatively instantaneous void fractions.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Fukuda, Takanari; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
The VOF method is a type of CFDs that is most widely applied to multiphase flow analysis involving advective interfaces, and several interface-capturing schemes have been developed for an accurate advection of VOF values. However, the performance of these schemes has typically been evaluated only for limited numerical problems where velocity fields are spatially orderly and fixed in time. Few studies have been conducted to evaluate the performance of these schemes for more realistic and complex conditions, such as gas-liquid two-phase flows in nuclear reactors. Therefore, in this study, three-dimensional analysis of bubble flows has been conducted using the interface-capturing schemes of THINC and THINC/WLIC, which have been developed relatively recently. Evaluation is performed using more engineering indicators such as the number, volume, and trajectory of bubbles, which can influence the void fraction distribution in reactor cores. The results of these comparisons showed that the VOF value could be significantly diffused, leading to numerical brake-up and dissipation of the bubbles, with the influence of interface-capturing scheme.
Ono, Ayako; Sakashita, Hiroto*; Yamashita, Susumu; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(4), p.24-00188_1 - 24-00188_12, 2024/07
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is developing the evaluation method for a two-phase flow in the reactor core using simulation codes based on the Volume Of Fluid (VOF) method. JAEA started developing a Simplified Boiling Model (SBM) for the large-scale two-phase flow in the fuel assemblies. In the SBM, the motion and growth equations of the bubble are solved to obtain their diameter and time length at the detachment, of which size scale is within/around the calculation grid size of the numerical simulation. JUPITER calculates the bubble behavior with a scale of more than several  m. In this study, the convection boiling on a vertical heating surface is simulated using the developed SBM. The comparison between the simulation and experimental results showed good reproducibility of the heat flux and velocity dependency on the passage period of the bubble.
m. In this study, the convection boiling on a vertical heating surface is simulated using the developed SBM. The comparison between the simulation and experimental results showed good reproducibility of the heat flux and velocity dependency on the passage period of the bubble.
Yamashita, Susumu; Kondo, Nao; Sugawara, Takanori; Monji, Hideaki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.740 - 761, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To confirm the validity of the thermal-hydraulics design tool based on the Ansys Fluent, we used a detailed computational fluid dynamics code named JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER) for the thermal-hydraulics around the beam window (BW) of the Accelerator-Driven System (ADS). The Fluent uses the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) model and can quickly calculate the turbulent flow around the BW as a BW design tool. At first, we compared the results of JUPITER with the experimental results using a mock-up BW system in water to confirm the validity of JUPITER. As a result, we confirmed that numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Thus, we showed that JUPITER could be used as a benchmark code. We also performed a benchmark simulation for the Fluent calculation using validated JUPITER to show the applicability of JUPITER as an alternative of experiments. As a result, the mean values around the BW agreed with each other, e.g., the mean velocity profile for stream and horizontal directions. Therefore, we confirmed that JUPITER showed a good performance in validating the thermal-hydraulics design tool as a fluid dynamics solver. Moreover, Fluent has enough accuracy as a thermal-hydraulics design tool for the ADS.
Sano, Naruto; Yamashita, Naoki; Watanabe, Masaya; Tsukada, Manabu*; Hoshino, Kazutoyo*; Hirai, Koki; Ikegami, Yuta*; Tashiro, Shinsuke; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Hatakeyama, Yuichi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-029, 36 Pages, 2024/03
At the Waste Safety Testing Facility (WASTEF), the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220" was relocated from the 4th Research Building of the Nuclear Science Research Institute in FY2019, and the use of gamma ray irradiation has begun. Initially, Fuel Cycle Safety Research Group, Fuel Cycle Safety Research Division, Nuclear Safety Research Center, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness, the owner of this device, conducted the tests as the main user, but since 2022, other users, including those outside the organization, have started using it. The gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220" is manufactured by Nordion International Inc. in Canada. Since it was purchased in 1989, the built-in  Co radiation source has been updated once, and safety research related to nuclear fuel cycles, etc. It is still used for this purpose to this day. This report summarizes the equipment overview of the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220", its permits and licenses at WASTEF, usage status, maintenance and inspection, and future prospects.
Co radiation source has been updated once, and safety research related to nuclear fuel cycles, etc. It is still used for this purpose to this day. This report summarizes the equipment overview of the gamma ray irradiation device "Gamma Cell 220", its permits and licenses at WASTEF, usage status, maintenance and inspection, and future prospects.
Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Machida, Masahiko
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
In order to safely carry out the decommission of reactor buildings, it is extremely important to identify the radiation source distribution. It has been reported that when the structural model of the building is constructed by uniform cells, the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). Moreover, if cells are non-uniform, we can estimate the distribution using the fused LASSO which minimizes the evaluation function that takes account of the connectivity between the adjacent cells. However, when a group of some cells is considered disconnected from the surrounding ones due to the precision of the measured structural data, the concentration of the group can be singularly high. Therefore, in order to avoid the problem, we propose a new evaluation function that can prevent the singularity. We estimated the distribution for the test model using the proposed evaluation function and confirmed the validity of the function. Moreover, we succeeded in estimating the source distribution in the pool canal circulation system room in JMTR in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency by the fused LASSO for the new function more accurately than previous analysis.
Koyama, Shinichi; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Mitsugi, Takeshi; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Tsai, T.-H.; Takano, Masahide; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Satoshi; et al.
Hairo, Osensui, Shorisui Taisaku Jigyo Jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 216 Pages, 2023/11
In FY 2021 and 2022, JAEA perfomed the subsidy program for "the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy, Thermal Bahavior Estimation, and Simplified Analysis of Fuel Debris)" started in FY 2021. This presentation material summarized the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning, Contaminated Water and Treated Water Management.
Yamashita, Susumu; Sato, Takumi; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(9), p.1029 - 1045, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Yamashita, Susumu; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 10(4), p.22-00485_1 - 22-00485_25, 2023/08
A detailed evaluation for air cooling of fuel debris in actual reactors will be essential in fuel debris retrieval under dry conditions. To understand the heat transfer in and around fuel debris, which is assumed as a porous medium in the primary containment vessel (PCV) mechanistically, we newly applied the porous medium model to the multiphase and multicomponent computational fluid dynamics code named JUPITER (JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research). We applied the Darcy-Brinkman model as for the porous medium model. This model has high compatibility with JUPITER because it can treat both a pure fluid and a porous medium phase simultaneously in the same manner as the one-fluid model in multiphase flow simulation. We addressed the case of natural convection with a high-velocity flow standing out nonlinear effects by implementing the Forchheimer model, including the term of the square of the velocity as a nonlinear effect to the momentum transport equation of JUPITER. We performed some simple verification and validation simulations, such as the natural convection simulation in a square cavity and the natural convective heat transfer experiment with the porous medium, to confirm the validity of the implemented model. We confirmed that the result of JUPITER agreed well with these simulations and experiments. In addition, as an application of the updated JUPITER, we performed the preliminary simulation of air cooling of fuel debris in the condition of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station unit 2 including the actual core materials. As a result, JUPITER calculated the temperature and velocity field stably in and around the fuel debris inside the PCV. Therefore, JUPITER has the potential to estimate the detailed and accurate thermal-hydraulics behaviors of fuel debris.
Watanabe, Nao; Yamashita, Susumu; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Nishihara, Kenji; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.3522 - 3534, 2023/08
Accelerator-driven system (ADS), the coolant of which is lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE), has been designed by Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Estimating corrosion rate at the wall surface of LBE channel is an important issue in considering safety and the life of the entire structure. The corrosion rate depends on state of oxygen layers forming at the material surface. Therefore, this study aims to develop a method to evaluate the corrosion rate in ADS for the design study by estimation of the oxide layer growth and dissolution (OLGD) rates by means of numerical analysis. The OLGD rates, mass transfer rates of oxygen and iron between the material and LBE and advection-diffusion rates of them in LBE depend on each other. Therefore, in order to estimate OLGD rates, the three numerical analysis models should be coupled. For the advection-diffusion calculation, to use CFD code should be reasonable approach to analyze complex flow in ADS, while for the OLGD and the mass transfer calculation, to use some correlation equations should be reasonable because their scales are much smaller than the advection-diffusion. The present work has developed the analysis method of OLGD rates by using JUPITER code, which is CFD code developed in JAEA. In terms of the correlation equations of OLGD and mass transfer rates, existing models used in a previous study were used with modified.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:46.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 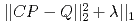 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:62.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)Uesawa, Shinichiro; Yamashita, Susumu; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2023/05
For contaminated water management in decommissioning Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Stations, reduction in water injection, intermittent injection water and air cooling are considered. However, since there are uncertainties of fuel debris in the PCV, it is necessary to examine and evaluate optimal cooling methods according to the distribution state of the fuel debris and the progress of the fuel debris retrieval work in advance. We have developed a method for estimating the thermal behavior in the air cooling, including the influence of the position, heat generation and the porosity of fuel debris. Since a large-scale thermal-hydraulics analysis of natural convection is necessary for the method, JUPITER developed independently by JAEA is used. It is however difficult to perform the large-scale thermal-hydraulics analysis with JUPITER by modeling the internal structure of the debris which may consist of a porous medium. Therefore, it is possible to analyze the heat transfer of the porous medium by adding porous models to JUPITER. In this study, we report the validation of JUPITER applied the porous model and discuss which heat transfer models are most effective in porous models such as series, parallel and geometric mean models. To obtain validation data of JUPITER for the natural convective heat transfer analysis around the porous medium, we performed the heat transfer and the flow visualization experiments of the natural convection in the experimental system including the porous medium. In the comparison between the experiment and the numerical analysis with each model, the numerical result with the geometric mean model was the closest of the models to the experimental results. However, the numerical results of the temperature and the velocity were overestimated for those experimental results. In particular, the temperature near the interface between the porous medium and air was more overestimated.
Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Tobita, Daiki*; Monji, Hideaki*; Yamashita, Susumu; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Sugawara, Takanori
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10