Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Onoe, Hironori*; Yoshida, Fumiko*; Hamamoto, Takafumi*; Saegusa, Hiromitsu*; Ishida, Keisuke*; Sawada, Atsushi
NUMO-TR-24-03, p.71 - 75, 2024/10
no abstracts in English
Kitamura, Akihiro; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Sakuma, Kazuyuki; Malins, A.; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko; Mori, Koji*; Tada, Kazuhiro*; Tawara, Yasuhiro*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*; et al.
Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 41(12), p.1708 - 1726, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:53.85(Geography, Physical)Sediment erosion and transport processes that are considered to be important in predicting the future radioactive material distribution through sediment-sorbed form in Fukushima Prefecture are simulated. Since large portion of the sediment is considered to be supplied into the rivers, it is important to trace their migration process in terms of each river basin. We choose five river basins, namely the Odaka, the Ukedo, the Maeda, the Kuma, and the Tomioka, from north to south, because of their importance in contamination aspects and prediction studies. The results are summarized as comprehensive dataset of sediment migration for particular river basins in typical typhoon events that account for the most of annual soil erosion. Detail calculations implemented for the amount of sediment supplied in to the river, deposited on river and dam beds, and exported to the ocean.
Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 79(11), p.1159 - 1164, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.02(Chemistry, Physical)Much of this past research has focused on finding more effective reactions between charged reactive species in room temperature ionic liquid (RTILs), which have a coulombic field. Reactions in RTILs involving the charged reactive species, particularly solvated electrons, have been studied by the techniques of radiation chemistry. The reaction behavior of halophenols in RTILs were investigated by  ray and pulsed electron radiolysis. The yield of CP decomposition in the RTILs was almost the same as that of solvated electrons formation. The yield of CP decomposition and phenol formation in the RTILs was low in the presence of electron scavengers such as nitrous oxide, indicating that solvated electrons primarily contributed to the decomposition of CP. The type of halogen group with the exception of fluorine had a negligible effect on the decomposition of halophenols in the RTILs. Therefore, RTILs could be applied as an reaction media for the reduction by ionizing radiation.
ray and pulsed electron radiolysis. The yield of CP decomposition in the RTILs was almost the same as that of solvated electrons formation. The yield of CP decomposition and phenol formation in the RTILs was low in the presence of electron scavengers such as nitrous oxide, indicating that solvated electrons primarily contributed to the decomposition of CP. The type of halogen group with the exception of fluorine had a negligible effect on the decomposition of halophenols in the RTILs. Therefore, RTILs could be applied as an reaction media for the reduction by ionizing radiation.
Kondo, Takafumi*; Asano, Akira*; Yang, J.*; Norizawa, Kimihiro*; Takahashi, Kenji*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kato, Ryuji*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1157 - 1160, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:84.59(Chemistry, Physical)Spectrum and kinetic behavior of solvated electrons (e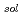
 ) in alkyl ammonium ionic liquids (ILs),
) in alkyl ammonium ionic liquids (ILs),  DEMMA-TFSI, DEMMA-BF4, TMPA-TFSI, PP13-TFSI, P13-TFSI and P14-TFSI were investigated by pulse radiolysis method. The e
DEMMA-TFSI, DEMMA-BF4, TMPA-TFSI, PP13-TFSI, P13-TFSI and P14-TFSI were investigated by pulse radiolysis method. The e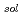
 in the ILs have same absorption peak at 1100 nm with a molar absorption coefficient of 1.5-2.3
in the ILs have same absorption peak at 1100 nm with a molar absorption coefficient of 1.5-2.3 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol cm
cm . The reaction rate constant of e
. The reaction rate constant of e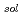
 with Pyrene (Py) was 1.5-3.5
with Pyrene (Py) was 1.5-3.5 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol s
s . These values were about one order of magnitude higher than that of diffusion controlled limit, which was calculated from measured viscosity. The dry electron (e
. These values were about one order of magnitude higher than that of diffusion controlled limit, which was calculated from measured viscosity. The dry electron (e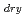
 ) reacts with Py, and its rate constant in DEMMA-TFSI was 7.9
) reacts with Py, and its rate constant in DEMMA-TFSI was 7.9 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol s
s , three orders of magnitude higher than that of the e
, three orders of magnitude higher than that of the e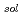
 reactions.
reactions.
Asano, Akira*; Yang, J.*; Kondo, Takafumi*; Norizawa, Kimihiro*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Takahashi, Kenji*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1244 - 1247, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.22(Chemistry, Physical)The molar extinction coefficient and the radiolytic yield of solvated electrons in ionic liquid of DEMMA-TFSI were estimated respectively to be 2.3 10
10 L mol
L mol cm
cm and 0.8
and 0.8 10
10 mol J
mol J by observing the reaction and kinetics of solvated electron and dry electron in the ionic liquid. The solvated electron in DEMMA-TFSI has a very broad absorption spectrum peaking at 1100 nm and reacts slowly with pyrene with a rate constant of 3.5
by observing the reaction and kinetics of solvated electron and dry electron in the ionic liquid. The solvated electron in DEMMA-TFSI has a very broad absorption spectrum peaking at 1100 nm and reacts slowly with pyrene with a rate constant of 3.5 10
10 L mol
L mol s
s , while the dry electron is captured rapidly by pyrene with C
, while the dry electron is captured rapidly by pyrene with C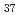 value of 0.065 mol L
value of 0.065 mol L .
.
Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1253 - 1257, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.29(Chemistry, Physical)Yang, J.*; Kondo, Takafumi*; Norizawa, Kimihiro*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Takahashi, Kenji*; Kato, Ryuji*; Anishchik, S. V.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Tagawa, Seiichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1233 - 1238, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:81.22(Chemistry, Physical)First observation of picosecond dynamics in ionic liquid of DEMMA-TFSI in radiation chemistry was reported. It is found that the electron produced by ionization is solvated to full solvation in ionic liquid with a rate constant of 3.9 10
10 s
s . The yield of solvated electrons in picosecond time region is 1.2
. The yield of solvated electrons in picosecond time region is 1.2 10
10 mol J
mol J . The dry electron in ionic liquid reacts rapidly with biphenyl and pyrene with a rate constant of 3.8 to 7.9
. The dry electron in ionic liquid reacts rapidly with biphenyl and pyrene with a rate constant of 3.8 to 7.9 10
10 L mol
L mol s
s . The geminate ion recombination in n-dodecane and n-hexane was also observed by monitoring the transient absorptions at 523 nm.
. The geminate ion recombination in n-dodecane and n-hexane was also observed by monitoring the transient absorptions at 523 nm.
Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Kan, Koichi*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 160, 2008/03
no abstracts in English
Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Kan, Koichi*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 141, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Aoyama, Takafumi; Sekine, Takashi; Maeda, Shigetaka; Yoshida, Akihiro; Maeda, Yukimoto; Suzuki, Soju; Takeda, Toshikazu*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 237(4), p.353 - 368, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:72.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)Many changes were made in the recent upgrade of the experimental fast reactor JOYO to the MK-III design. The core changes which were made to achieve a fourfold increase in irradiation capacity include the introduction of a second enrichment zone, an increase in core radius and a decrease in core height. Performance tests done at low power, during the rise to power, and at full power, which focus on the neutronics characteristics, are presented. These tests include the nuclear instrumentation system response, the approach to criticality and excess reactivity evaluation, control rod worth calibration, isothermal temperature coefficient evaluation, the calibration of the nuclear instrumentation system with reactor thermal power, and the burn-up reactivity coefficient evaluation. The measurements and comparisons with calculated predictions are shown. The design predictions are consistent with the performance test results, and all technical safety specifications are satisfied. The JOYO MK-III core will provide enhanced irradiation testing capability, as well as serve as a test bed for improving fast reactor operation, performance and safety. Through the performance test evaluation, the core characteristics of a small size sodium cooled fast reactor with a hard neutron spectrum are clarified.
Yoshida, Yoichi*; Yang, J.*; Kondo, Takafumi*; Seki, Shuhei*; Kozawa, Takahiro*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji; Namba, Hideki
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.183 - 185, 2006/01
A heavy-ion-pulse radiolysis technology was developed using a single-photon-counting system. In the system, the ion beam was injected a thin scintillator before irradiating the sample. The light emitted from the scintillator by the ion irradiation was used as analyzing source to detect the absorption of primary species in water. Measurement of time-dependent absorption of hydrated electrons in water was achieved using the system, which demonstrates the usefulness of this technique.
Maeda, Yukimoto; Aoyama, Takafumi; Yoshida, Akihiro; Sekine, Takashi; Ariyoshi, Masahiko; Ito, Chikara; Nemoto, Masaaki; Murakami, Takanori; Isozaki, Kazunori; Hoshiba, Hideaki; et al.
JNC TN9410 2003-011, 197 Pages, 2004/03
MK-III performance tests began in June 2003 to fully characterize the upgraded core and heat transfer system. Then, the last pre-use inspection was finished in November 2003.This report summarize the result of each performance test.
; Yoshida, Akihiro; Aoyama, Takafumi; Maeda, Yukimoto
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (21), p.17 - 25, 2003/00
Design works on the MK-III upgrading core were carried out and detailed core specification was determined from a viewpoint of increasing a fast neutron flux and a capacity for irradiation rigs. Based on the results of nuclear, thermal hydraulic calculation and shielding calculation, it was confirmed that the MK-III core shows expected core performance along with the integrity of the whole core.
; Yoshida, Akihiro; Aoyama, Takafumi; Maeda, Yukimoto
Saikuru Kiko Giho, (21), p.5 - 25, 2003/00
A Joyo upgrade program named MK-III program was started to develop future FBR in 1987. The main objectives of this program are increasing the capability as an irradiation test bed core and developing innovative FBR technologies.In order to modify the irradiation capability, the core and plant modification program which consists of increasing the neutron flux density of the core, modification of the cooling system, modification of the plant availability factor and upgrading irradiation technologies were decided based on the result s of survey calculations. The licensing work completed in 1995, and all the modification work completed in 2003. JOYO will start rated power operation along with several irradiation tests in 2004. Also the installation and demonstration program of innovative technologies such as Self-actuated shut down system for demonstration FBR and double-walled steam generator for future FBR were investigated.
 U enriched fueled MK-III core
U enriched fueled MK-III coreYoshida, Akihiro; Aoyama, Takafumi
PNC TN9410 98-084, 37 Pages, 1998/08
The investigation is underway to reduce the  U enrichment of Joyo MK-III core fuel. The difficulties of obtaining enriched Uranium and reducing fuel fabrication costs are the items being investigated. In addition, the utilization of weapon-grade Plutonium, of which
U enrichment of Joyo MK-III core fuel. The difficulties of obtaining enriched Uranium and reducing fuel fabrication costs are the items being investigated. In addition, the utilization of weapon-grade Plutonium, of which  Pu content exceeds 90%, instead of current reactor-grade Pu, is also under investigation. Initially, specification of the MK-III core fuel was adjusted in order to have the same reactivity worth as the current fuel. The
Pu content exceeds 90%, instead of current reactor-grade Pu, is also under investigation. Initially, specification of the MK-III core fuel was adjusted in order to have the same reactivity worth as the current fuel. The  U enrichment were reduced from 18% to 10%, and in some cases as low as 5%. The results are as follows: (1)When Pu content was improved from 30% to 35%, or when weapon-grade Pu was adopted,
U enrichment were reduced from 18% to 10%, and in some cases as low as 5%. The results are as follows: (1)When Pu content was improved from 30% to 35%, or when weapon-grade Pu was adopted,  U enrichment can be decreased lower than 5% for the inner core fuel. (2)To decrease
U enrichment can be decreased lower than 5% for the inner core fuel. (2)To decrease  U enrichment lower than 5% for outer core fuel, Pu content must be improved up to 37%. Then deplated Uranium can be adopted for the inner core fuel. When weapon-grade Pu was adopted and Pu content was improved up to 33%, deplated Uranium can be utilized for both inner and outer core fuel. The nuclear characteristics of the low
U enrichment lower than 5% for outer core fuel, Pu content must be improved up to 37%. Then deplated Uranium can be adopted for the inner core fuel. When weapon-grade Pu was adopted and Pu content was improved up to 33%, deplated Uranium can be utilized for both inner and outer core fuel. The nuclear characteristics of the low  U enriched fueled core were calculated and compared with that of the MK-III standard core (reference corc). The results are as follows: (1)With the increase of
U enriched fueled core were calculated and compared with that of the MK-III standard core (reference corc). The results are as follows: (1)With the increase of  Pu and
Pu and  Pu, burn-up reactivity increase. By increasing the substitution reactivity between a spent fuel and fresh fuel subassembly, burn-up reactivity could be compensated. (2)When weapon-grade Pu was adopted, the change of Pu vector per unit burn-up increased when compared with current core fuel. However, the nuclear characteristics were almost the same when compared with the standard core.
Pu, burn-up reactivity increase. By increasing the substitution reactivity between a spent fuel and fresh fuel subassembly, burn-up reactivity could be compensated. (2)When weapon-grade Pu was adopted, the change of Pu vector per unit burn-up increased when compared with current core fuel. However, the nuclear characteristics were almost the same when compared with the standard core.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Aoyagi, Noboru; Shinha, Yusuke; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Radiolytic reactions in ionic liquids of thiocyanate salts were studied by means of the nano-second pulse radiolysis technique. One of the significant ionization sites of liquids was found out to be thiocyanate ion by observing direct formation of its dimer radical anion, not via the diffusion reaction between thiocyanate radical and ion. The formation and reaction behaviors of solvated electron and dimer were examined by changing the composition of liquids and by adding electron scavengers to the liquid.
Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Takahashi, Kenji*; Kato, Ryuji*
no journal, ,
The effect of the coexistence water on the solvated electrons in ammonium ionic liquids was studied by the electron pulse radiolysis method. The optical absorption band of the solvation electron decreased by coexistence of water, and new absorption band like a hydrated electron were generated in the medium wavelength region between solvated electron and hydrated electron. Furthermore, if quantity of water increase in the hydrophilic ionic liquid, it was found that the spectrum changed into the hydrated electron.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Aoyagi, Noboru; Shinha, Yusuke; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Radiolytic reactions in ionic liquids of thiocyanate salts were studied by means of the nano-second pulse radiolysis technique. One of the significant ionization sites of liquids was found out to be thiocyanate ion by observing direct formation of its dimer radical ion, not 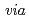 the diffusive encounter between thiocyanate radical and ion. The formation and reaction behaviors of solvated electron and dimer were examined by changing the composition of liquids and by adding electron scavengers to the liquid.
the diffusive encounter between thiocyanate radical and ion. The formation and reaction behaviors of solvated electron and dimer were examined by changing the composition of liquids and by adding electron scavengers to the liquid.
Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hirota, Koichi; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Aoyagi, Noboru; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
no journal, ,
Radiolytic reactions in ionic liquids of thiocyanate salts were studied by means of the pulse radiolysis technique. In the imidazolium salts, transient absorption of dimer radical anion of thiocyanate was observed as well as that originated from imidazolium cation. In the ammonium salts containing two anions, the initial absorption of dimer increased with increasing the concentration of thiocyanate anion in the salts. These suggest that one of the main ionization sites of ionic liquids is thiocyanate anion to generate electron and thiocyanate radical, and then that the rapid formation of dimer is mainly due to the direct dimerization between the radical and its surrounding anion, not via their diffusion encounter.