Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Masuki, Yuma*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Umemura, Ayako*; Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Minami, Masayo*; Niwa, Masakazu; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 485, p.136843_1 - 136843_10, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Lacustrine deposits have 30-fold higher As abundance than the average crustal deposit. Arsenic is mostly concentrated as discrete horizons deposited in spring and autumn. As-rich layers contain FeAsS, AsS, and As S
S but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
Kamada, Masaki*; Yoshida, Takuma*; Sugita, Tsukasa*; Okumura, Keisuke
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(2), p.83 - 86, 2024/02
, 66(2), p.83 - 86, 2024/02
no abstracts in English
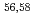 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 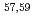 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 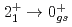 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 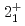 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 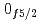 and
and 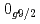 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
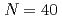 island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in
island of inversion; First study of low-lying bound excited states in  V and
V and  V
VElekes, Z.*; Juh sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064321_1 - 064321_10, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.00(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying level structure of  V and
V and  V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for
V was investigated for the first time. The neutron knockout reaction and inelastic proton scattering were applied for  V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for
V while the neutron knock-out reaction provided the data for  V. Four and five new transitions were determined for
V. Four and five new transitions were determined for  V and
V and  V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed
V, respectively. Based on the comparison to our shell-model calculations using the Lenzi-Nowacki-Poves-Sieja (LNPS) interaction, three of the observed  rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2
rays for each isotope could be placed in the level scheme and assigned to the decay of the first 11/2 and 9/2
and 9/2 levels. The (
levels. The ( ,
,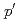 ) excitation cross sections for
) excitation cross sections for  V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,
V were analyzed by the coupled-channels formalism assuming quadrupole plus hexadecapole deformations. Due to the role of the hexadecapole deformation,  V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
V could not be unambiguously placed on the island of inversion.
 Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 Ca from direct reactions
Ca from direct reactionsBrowne, F.*; Chen, S.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Kazuki; Achouri, N. L.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Calvet, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(25), p.252501_1 - 252501_7, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Direct proton-knockout reactions of  Sc were studied at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. Populated states of
Sc were studied at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. Populated states of  Ca were investigated through
Ca were investigated through  -ray and invariant-mass spectroscopy. Level energies were calculated from the nuclear shell model employing a phenomenological inter-nucleon interaction. Theoretical cross sections to states were calculated from distorted-wave impulse approximation estimates multiplied by the shell model spectroscopic factors. Despite the calculations showing a significant amplitude of excited neutron configurations in the ground-state of
-ray and invariant-mass spectroscopy. Level energies were calculated from the nuclear shell model employing a phenomenological inter-nucleon interaction. Theoretical cross sections to states were calculated from distorted-wave impulse approximation estimates multiplied by the shell model spectroscopic factors. Despite the calculations showing a significant amplitude of excited neutron configurations in the ground-state of  Sc, valence proton removals populated predominantly the ground-state of
Sc, valence proton removals populated predominantly the ground-state of  Ca. This counter-intuitive result is attributed to pairing effects leading to a dominance of the ground-state spectroscopic factor. Owing to the ubiquity of the pairing interaction, this argument should be generally applicable to direct knockout reactions from odd-even to even-even nuclei.
Ca. This counter-intuitive result is attributed to pairing effects leading to a dominance of the ground-state spectroscopic factor. Owing to the ubiquity of the pairing interaction, this argument should be generally applicable to direct knockout reactions from odd-even to even-even nuclei.
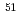 Ar by the (
Ar by the ( ,2
,2 ) reaction
) reactionJuh sz, M. M.*; Elekes, Z.*; Sohler, D.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Kazuki; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
sz, M. M.*; Elekes, Z.*; Sohler, D.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Kazuki; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Baba, Hidetada*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 814, p.136108_1 - 136108_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:63.10(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The nuclear structure of 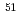 Ar was studied by the (
Ar was studied by the ( ,2
,2 ) reaction using
) reaction using  -ray spectroscopy for the bound and unbound states. Comparing the results to our shell-model calculations, two bound and six unbound states were established. The low cross sections populating the two bound states of
-ray spectroscopy for the bound and unbound states. Comparing the results to our shell-model calculations, two bound and six unbound states were established. The low cross sections populating the two bound states of 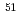 Ar could be interpreted as a clear signature for the presence of significant sub-shell closures at neutron numbers 32 and 34 in argon isotopes.
Ar could be interpreted as a clear signature for the presence of significant sub-shell closures at neutron numbers 32 and 34 in argon isotopes.
 = 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of
= 32 shell closure below calcium; Low-lying structure of  Ar
ArCort s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men
s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Men ndez, J.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Schwenk, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
ndez, J.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Schwenk, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Simonis, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(6), p.064320_1 - 064320_9, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:75.82(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying excited states in the  = 32 isotope
= 32 isotope  Ar were investigated by in-beam
Ar were investigated by in-beam  -ray spectroscopy following proton- and neutron-knockout, multinucleon removal, and proton inelastic scattering at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. The energies of the two previously reported transitions have been confirmed, and five additional states are presented for the first time, including a candidate for a 3
-ray spectroscopy following proton- and neutron-knockout, multinucleon removal, and proton inelastic scattering at the RIKEN Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory. The energies of the two previously reported transitions have been confirmed, and five additional states are presented for the first time, including a candidate for a 3 state. The level scheme built using
state. The level scheme built using 
 coincidences was compared to shell-model calculations in the
coincidences was compared to shell-model calculations in the 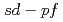 model space and to
model space and to  predictions based on chiral two- and three-nucleon interactions. Theoretical proton- and neutron-knockout cross sections suggest that two of the new transitions correspond to 2
predictions based on chiral two- and three-nucleon interactions. Theoretical proton- and neutron-knockout cross sections suggest that two of the new transitions correspond to 2 states, while the previously proposed 4
states, while the previously proposed 4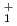 state could also correspond to a 2
state could also correspond to a 2 state.
state.
 = 40 isotones towards
= 40 isotones towards  Ca; First spectroscopy of
Ca; First spectroscopy of  Ti
TiCort s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Lenzi, S. M.*; Men
s, M. L.*; Rodriguez, W.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Holt, J. D.*; Lenzi, S. M.*; Men ndez, J.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Poves, A.*; et al.
ndez, J.*; Nowacki, F.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Poves, A.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135071_1 - 135071_7, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:95.72(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Excited states in the  = 40 isotone
= 40 isotone  Ti were populated via the
Ti were populated via the  V(
V( ,
,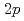 )
) Ti reaction at
Ti reaction at  200 MeV/nucleon at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory and studied using
200 MeV/nucleon at the Radioactive Isotope Beam Factory and studied using  -ray spectroscopy. The energies of the
-ray spectroscopy. The energies of the 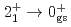 and
and 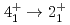 transitions, observed here for the first time, indicate a deformed Ti ground state. These energies are increased compared to the neighboring
transitions, observed here for the first time, indicate a deformed Ti ground state. These energies are increased compared to the neighboring  Cr and
Cr and 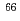 Fe isotones, suggesting a small decrease of quadrupole collectivity. The present measurement is well reproduced by large-scale shell-model calculations based on effective interactions, while ab initio and beyond mean-field calculations do not yet reproduce our findings.
Fe isotones, suggesting a small decrease of quadrupole collectivity. The present measurement is well reproduced by large-scale shell-model calculations based on effective interactions, while ab initio and beyond mean-field calculations do not yet reproduce our findings.
 Ca corroborates arising
Ca corroborates arising 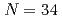 neutron magic number
neutron magic numberChen, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Raimondi, F.*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Raimondi, F.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 123(14), p.142501_1 - 142501_7, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:93.11(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Kawamura, Takuma; Uesawa, Shinichiro; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 27th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-27) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2019/05
A dry method is one of practical methods for decommissioning the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been evaluating the air cooling performance by using the JUPITER code. However, the JUPITER code requires a large computational cost to capture debris' structures. To accelerate such CFD analyses, we use the CityLBM code, which is based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) and is highly optimized for GPUs. The CityLBM code is validated against free convective heat transfer experiments at JAEA, and the similar accuracy as the JUPITER code is confirmed regarding the prediction capability of heat transfer and the resulting temperature distributions. It is also shown that the elapse time of a CityLBM simulation on GPUs is reduced to 1/6 compared with that of the corresponding JUPITER simulation on CPUs with the same number of GPUs and CPUs. The results show that the LBM is promising for accelerating thermal convective simulations.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Momose, Takumaro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 11, p.070008_1 - 070008_6, 2016/11
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kano, Takuma
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2007 - March 2008, p.217 - 221, 2008/09
no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Kano, Takuma; Merzari, E.*; Ninokata, Hisashi*
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2006 - March 2007, p.223 - 228, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Momose, Takumaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 126(1-4), p.168 - 173, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.18(Environmental Sciences)The authors developed a model calculating angular neutron fluence distributions for radionuclide neutron sources which are heavily encapsulated or surrounded with some source support structures such as a source holder and a source movement system. These structures cause a highly anisotropic neutron fluence distribution, and hence it should be properly corrected for calibration of neutron measuring instruments. The calculations were made for two types of widely used neutron sources,  Am-Be and
Am-Be and  Cf, by a combination of the in-house code simulating
Cf, by a combination of the in-house code simulating  Be(
Be( ,n) reactions and the Monte Carlo code MCNP4C. As a result, anisotropy factors in the direction perpendicular to the source capsule axis for bare neutron sources were evaluated to be 1.012, 1.030 and 1.035 for
,n) reactions and the Monte Carlo code MCNP4C. As a result, anisotropy factors in the direction perpendicular to the source capsule axis for bare neutron sources were evaluated to be 1.012, 1.030 and 1.035 for  Cf in a standard Amersham X1 capsule,
Cf in a standard Amersham X1 capsule,  Am-Be in a X3 capsule and
Am-Be in a X3 capsule and  Am-Be in a X4 capsule, respectively. These values are in reasonable agreements with published data. In contrast, anisotropy factors for these neutron sources including support structures increased by approximately 10% due to scattering of neutrons.
Am-Be in a X4 capsule, respectively. These values are in reasonable agreements with published data. In contrast, anisotropy factors for these neutron sources including support structures increased by approximately 10% due to scattering of neutrons.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie; Momose, Takumaro; Nunomiya, Tomoya*; Aoyama, Kei*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 126(1-4), p.261 - 264, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.94(Environmental Sciences)The authors developed a new neutron measuring-instrument that was designed to measure neutron personal dose equivalent, 
 (10). This detector is composed a central thermal neutron detector, a core-polyethylene moderator, a front-hemispherical polyethylene moderator and rear-hemispherical boron-contained polyethylene absorber. Dimensions of each part were determined so as to provide energy- and angular-responses close to energy- and angular-dependencies of neutron
(10). This detector is composed a central thermal neutron detector, a core-polyethylene moderator, a front-hemispherical polyethylene moderator and rear-hemispherical boron-contained polyethylene absorber. Dimensions of each part were determined so as to provide energy- and angular-responses close to energy- and angular-dependencies of neutron 
 (10), based on the Monte Carlo calculations.
(10), based on the Monte Carlo calculations.
Tsujimura, Norio; Takada, Chie; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Momose, Takumaro
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 125(1-4), p.383 - 386, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.69(Environmental Sciences)no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Kano, Takuma; Akimoto, Hajime
Annual Report of the Earth Simulator Center April 2005 - March 2006, p.261 - 265, 2007/01
no abstracts in English
 Al
AlOzawa, Akira*; Matsuta, Kensaku*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Mihara, Mototsugu*; Yamada, Kazunari*; Yamaguchi, Takayuki*; Otsubo, Takashi*; Momota, Sadao*; Izumikawa, Takuji*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 74(2), p.021301_1 - 021301_4, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:88.92(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kano, Takuma; Aoki, Takayuki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Dai-12-Ki Sogo Koenkai Koen Rombunshu, p.229 - 230, 2006/03
no abstracts in English