Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
 (001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Takayanagi, Shuhei*; Ojima, Shoki*; Maeda, Motoyasu*; Origuchi, Naoki*; Ogawa, Arata*; Ikeda, Natsuki*; Aoyagi, Yoshihide*; Kabutoya, Yuito*; et al.
Langmuir, 37(42), p.12313 - 12317, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
(001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
Nakayama, Hiromasa; Takemi, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Toshiya
Atmosphere (Internet), 12(7), p.889_1 - 889_15, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:15.02(Environmental Sciences)Contaminant gas dispersion within urban area resulting from accidental or intentional release is of great concern to public health and social security. When estimating plume dispersion in a built-up urban area under real meteorological conditions by computational fluid dynamics (CFD), a crucial issue is how to prescribe the model input conditions. There are typically two approaches: using the outputs of a meso-scale meteorological simulation (MMS) model and meteorological observations (OBS). However, the influence of the different approaches on the simulation results have not been fully demonstrated. In this study, we conducted large-eddy simulations (LESs) of plume dispersion in the urban central district under real meteorological conditions by coupling with a MMS model and OBS obtained at a single stationary point, and evaluated the two different coupling simulations in comparison with the field experimental data. The LES-MMS coupling showed better performance than the LES-OBS one. However, the latter one also showed a reasonable performance comparable to the acceptance criteria on the model prediction within a factor of two of the experimental data. These facts indicate that the approach of using observations at a single stationary point still has enough potential to drive CFD models for plume dispersion under real meteorological conditions.
Yoshida, Toshiya; Takemi, Tetsuya*
Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 21(1), p.129 - 154, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.49(Environmental Sciences)The effects of obstacle-height variability on spatial characteristics of turbulent organized structures were investigated with the use of a large-eddy simulation technique for airflows over roughness obstacles. Two-types simulation cases were considered: one is uniform-height case in which uniform-height obstacles are aligned in streamwise direction, the other is height-variability case with staggered higher-height obstacles. Streaky structures were observed above the roughness sublayer (RSL) regardless of obstacle-height variability. When obstacles are uniform, flow fields within the RSL contain low- and high-speed regions along the streamwise streets. When obstacle heights vary, airflow within the RSL collides with the front-facing surfaces of taller obstacles. The statistical features of low- and high-speed structures were examined using the spatial correlations of flow fields centering on strong ejection and sweep, respectively. The ejection- and sweep-center spatial correlations extend forward and backward in the streamwise direction, respectively. Length scales were obtained from the ejection-center and sweep-center spatial correlations. The streamwise lengths vary significantly below the canopy height when obstacles are uniform. In contrast, the streamwise length scales remain nearly constant when obstacle heights vary. The horizontal aspect ratios below the canopy heights indicate that turbulent organized structures over obstacles with variable heights are more isotropic than those over uniform obstacles. The inclination angles of the organized structures were also deduced using the spatial correlations. The angles of sweep-center structures are steeper than those of the ejection-center structures. The angles of the ejection-center structures at the RSL heights become larger with obstacle-height variability.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2130, p.050001_1 - 050001_8, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.09(Physics, Nuclear)We find a novel phenomenon induced by the interplay between a strong magnetic field and finite orbital angular momenta in hadronic systems, which is analogous to the Paschen-Back effect observed in the field of atomic physics. This effect allows the wave functions to drastically deform. We discuss anisotropic decay from the deformation as a possibility to measure the strength of the magnetic field in heavy-ion collision at LHC, RHIC and SPS, which has not experimentally been measured. As an example we investigate charmonia with finite orbital angular momentum in a strong magnetic field. We calculate the mass spectra and mixing rate. To obtain anisotropic wave functions, we apply the cylindrical Gaussian expansion method, where the Gaussian bases to expand the wave functions have different widths along transverse and longitudinal directions in the cylindrical coordinate.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
International Journal of Modern Physics; Conference Series (Internet), 49, p.1960002_1 - 1960002_6, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.09(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The hadronic Paschen-Back effects in P-wave charmonia are analyzed using the constituent quark models in strong magnetic field.
Iwasaki, Sachio; Oka, Makoto; Suzuki, Kei*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*
Physics Letters B, 790, p.71 - 76, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:71.88(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We find a novel phenomenon induced by the interplay between a strong magnetic field and finite orbital angular momenta in hadronic systems, which is analogous to the Paschen-Back effect observed in the field of atomic physics. This effect allows the wave functions to drastically deform. We discuss anisotropic decay from the deformation as a possibility to measure the strength of the magnetic field in heavy-ion collision at LHC, RHIC and SPS, which has not experimentally been measured. As an example we investigate charmonia with finite orbital angular momentum in a strong magnetic field. We calculate the mass spectra and mixing rate. To obtain anisotropic wave functions, we apply the cylindrical Gaussian expansion method, where the Gaussian bases to expand the wave functions have different widths along transverse and longitudinal directions in the cylindrical coordinate.
 Mo
Mo O
O
Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Mizuno, Yusuke*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(6), p.064803_1 - 064803_6, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.03(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hosaka, Atsushi; Hiyama, Emiko; Kim, S.-H.*; Kim, H.-C.*; Nagahiro, Hideko*; Noumi, Hiroyuki*; Oka, Makoto; Shirotori, Kotaro*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Nuclear Physics A, 954, p.341 - 351, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.8(Physics, Nuclear)In this paper, we discuss reactions involving charmed baryons to explore their unique features. A well known phenomenon, the separation of the two internal motions of the  and
and  types of a three-quark system is revisited. First we discuss the mass spectrum of low-lying excitations as functions of the heavy quark mass, smoothly connecting the
types of a three-quark system is revisited. First we discuss the mass spectrum of low-lying excitations as functions of the heavy quark mass, smoothly connecting the 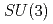 and heavy quark limits. The properties of these modes can be tested in the production and decay reactions of the baryons. For the productions, we consider a one step process which excites dominantly
and heavy quark limits. The properties of these modes can be tested in the production and decay reactions of the baryons. For the productions, we consider a one step process which excites dominantly  mode excitations. We find abundant production rates for some of excited states. For decays, we study pion emission process, which provides a clean tool to test the structure of heavy quark systems due to well controlled low energy dynamics of the pion and quark. Both productions and decays of the charmed baryons are the issues of the future experiments at J-PARC.
mode excitations. We find abundant production rates for some of excited states. For decays, we study pion emission process, which provides a clean tool to test the structure of heavy quark systems due to well controlled low energy dynamics of the pion and quark. Both productions and decays of the charmed baryons are the issues of the future experiments at J-PARC.
Nishikiori, Ryo; Kojima, Atsushi; Hanada, Masaya; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Yoshida, Masafumi; Ichikawa, Masahiro; Hiratsuka, Junichi; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 11, p.2401014_1 - 2401014_4, 2016/03
One of critical issues for high-energy high-current beam acceleration in ITER and JT-60SA is the high voltage holding which is dominated by vacuum discharges. The past results suggest that vacuum discharge occurs beyond the threshold of the dark current. The dark current can be derived from F-N theory where electric field enhancement factor beta is included. Though, beta could only be evaluated from the experiment previously. Therefore, the method to decide beta without experiment is required. This time dark currents were measured at three different areas to compare beta in different electric field. As a result, the effective electric field  E, where E is average electric field, were found to be almost constant for different areas although the beta is largely different. By applying
E, where E is average electric field, were found to be almost constant for different areas although the beta is largely different. By applying  E, beta can be evaluated analytically, leading to the analytical prediction of the dark current and voltage holding capability without the measurements.
E, beta can be evaluated analytically, leading to the analytical prediction of the dark current and voltage holding capability without the measurements.
Yoshida, Tetsuya*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Hosaka, Atsushi*; Oka, Makoto; Sadato, Katsunori*
Physical Review D, 92(11), p.114029_1 - 114029_19, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:173 Percentile:99.11(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Single- and double-heavy baryons are studied in the constituent quark model. The model Hamiltonian is chosen as a standard one with two exceptions: (1) the color-Coulomb term depends on quark masses and (2) an antisymmetric 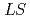 (spin-orbit) force is introduced. Model parameters are fixed by the strange baryon spectra,
(spin-orbit) force is introduced. Model parameters are fixed by the strange baryon spectra,  and
and  baryons. The masses of the observed charmed and bottomed baryons are, then, fairly well reproduced. Our focus is on the low-lying negative-parity states, in which the heavy baryons show specific excitation modes reflecting the mass differences of heavy and light quarks. By changing quark masses from the SU(3) limit to the strange quark mass, and, further, to the charm and bottom quark masses, we demonstrate that the spectra change from the SU(3) symmetry patterns to the heavy-quark-symmetry ones.
baryons. The masses of the observed charmed and bottomed baryons are, then, fairly well reproduced. Our focus is on the low-lying negative-parity states, in which the heavy baryons show specific excitation modes reflecting the mass differences of heavy and light quarks. By changing quark masses from the SU(3) limit to the strange quark mass, and, further, to the charm and bottom quark masses, we demonstrate that the spectra change from the SU(3) symmetry patterns to the heavy-quark-symmetry ones.
Ito, Shinichi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Soda, Minoru*; Ikeda, Yoichi*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Kawana, Daichi*; Sato, Taku*; Nambu, Yusuke*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.034001_1 - 034001_6, 2015/09
Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kanagawa, Tetsuya*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2015/05
From the viewpoint of protecting containment and suppressing diffusion of the radioactive materials at severe accidents of nuclear power plant, it is important to install filtered venting devices to permit release of high pressure pollutant gas to the atmosphere by eliminating radioactive materials in the gas. A Multi Venturi Scrubber System (MVSS) is one of the devices for the filtered venting, and is used to realize filtered venting without any power supply. The MVSS is composed of a "Venturi Scrubbers" part and a "bubble column" part. In the Venturi Scrubbers part of the MVSS, there are hundreds of the Venturi scrubbers (VS). In an operation mode of the MVSS, the radioactive materials are eliminated through the gas-liquid interface from the pollutant gas to the liquid phase of a dispersed flow in the VS and a bubbly flow in the bubble column part. In the VS, the dispersed flow is formed from the liquid, which is suctioned through the hole for suction (called self-priming). In previous studies, an evaluation method to evaluate the liquid flow rate by the self-priming was developed. However, to develop evaluation methods of performance of the VSs, the two-phase flow behavior must be investigated, including droplet size and velocity difference of liquid and gas phases. Two-phase flow behavior in the VS is complicated, and it is difficult to estimate two-phase flow behavior of the VS by only experimental procedures. In this study, to investigate the hydraulic behavior of the VS, we tried to apply a detailed numerical simulation method of two-phase flow to the numerical simulation of the VS. In the simulation, TPFIT developed in JAEA was used as the detailed numerical simulation method. In this paper, we performed the numerical simulation air-water two-phase flow in the of the lab scale VS by the TPFIT, and numerical results were compared with experimental results.
Kato, Yuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Yokoyama, Ryotaro*; Kanagawa, Tetsuya*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Monji, Hideaki*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 23rd International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-23) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2015/05
Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kanagawa, Tetsuya*; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 9th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-9) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2014/11
Yokota, Wataru; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Okumura, Susumu; Kurashima, Satoshi; Miyawaki, Nobumasa; Kashiwagi, Hirotsugu; Yoshida, Kenichi; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2014-018, 103 Pages, 2014/09
The world's first microbeam focusing technology for heavy ions of hundreds MeV accelerated by a cyclotron has been developed at the TIARA facility in the Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The technology enables us to form a microbeam of less than 1  m in diameter and to shoot a specified point on a target by one ion (single-ion hit) with spatial accuracy of microbeam size. In the course of the development, a cyclotron technology to accelerate a small energy-spread beam of hundres MeV, which is necessary for focusing to 1
m in diameter and to shoot a specified point on a target by one ion (single-ion hit) with spatial accuracy of microbeam size. In the course of the development, a cyclotron technology to accelerate a small energy-spread beam of hundres MeV, which is necessary for focusing to 1  m, has been developed as well as a beam focusing apparatus, beam size measurement and so forth based on the several-MeV microbeam/single-ion hit system of the TIARA electrostatic accelerators. Applicability of the technologies was examined by actual use in irradiation experiment and the result were fed back to them. This paper reports the process and the results of the development over ten years.
m, has been developed as well as a beam focusing apparatus, beam size measurement and so forth based on the several-MeV microbeam/single-ion hit system of the TIARA electrostatic accelerators. Applicability of the technologies was examined by actual use in irradiation experiment and the result were fed back to them. This paper reports the process and the results of the development over ten years.
Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Tobari, Hiroyuki; Kojima, Atsushi; Yoshida, Masafumi; Taniguchi, Masaki; Dairaku, Masayuki; Maejima, Tetsuya; Yamanaka, Haruhiko; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(2), p.02B320_1 - 02B320_3, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:75.28(Instruments & Instrumentation)The negative ion extractor for high power and long-pulse operations is newly developed toward the neutral beam injector (NBI) for heating & current drive of future fusion machines such as ITER, JT-60 Super Advanced (SA) and DEMO reactor. The satisfactory cooling capability is designed in the thermal analysis. A negative ion production and a suppression of electrons are experimentally validated for this new extractor. As the results, the negative ion current shows increases by a factor of 1.3 with suppressing the electron current. The beam divergence angle is also maintained small enough, 4 mrad.
Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Naganuma, Masaki; Nohiro, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Kimikazu*; Makita, Akinori*; Sakate, Mitsuo*; Irisawa, Takumi*; Murashita, Tatsuya*
JAEA-Technology 2012-048, 39 Pages, 2013/03
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Ningyo-Toge Environmental Engineering Center, exploration for uranium and technical development of uranium refining, conversion and enrichment which are the front end of a nuclear fuel cycle have been performed since 1955. By these research and development, about 15000 radioactive waste (200 liter drum) has occurred by now. The analytical and measurement technique of the amount of uranium which are included in radioactive waste drum were very an inexperienced in those days. Therefore, measurement strict till 2002 was not able to be started. Such a situation as this, we introduced "Q2 low-level-waste drum measuring system" which is a bulk measuring method of the passive  ray using a NaI scintillation detector in 2002. As a result, the total amount of uranium in a waste drum was estimated as about 20 tons.
ray using a NaI scintillation detector in 2002. As a result, the total amount of uranium in a waste drum was estimated as about 20 tons.
Fukui, Kunihiro*; Igawa, Yusuke*; Arimitsu, Naoki*; Suzuki, Masahiro; Segawa, Tomoomi; Fujii, Kanichi*; Yamamoto, Tetsuya*; Yoshida, Hideto*
Chemical Engineering Journal, 211-212, p.1 - 8, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.13(Engineering, Environmental)The process for synthesizing metallic oxide powders by the microwave denitration method was investigated using hexahydrated nickel nitrate and trihydrated copper nitrate aqueous solutions, and the electrical field and the temperature distributions in the reactor were numerically simulated. Although CuO powder can be obtained from a trihydrated copper nitrate aqueous solution by the microwave denitration method, a hexahydrated nickel nitrate aqueous solution cannot be heated up to over 270  C by microwave irradiation. It was also found that the reaction routes for microwave heating are the same as those for conventional external heating. This finding indicates that the success of producing oxide particles by microwave denitration depends not only on the microwave absorptivity of the intermediate and the metallic oxide, but also on the temperature difference.
C by microwave irradiation. It was also found that the reaction routes for microwave heating are the same as those for conventional external heating. This finding indicates that the success of producing oxide particles by microwave denitration depends not only on the microwave absorptivity of the intermediate and the metallic oxide, but also on the temperature difference.
Yoshida, Yukari*; Suzuki, Yoshiyuki*; Al-Jahdari, W. S.*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Shirai, Katsuyuki*; Kato, Hiroyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Nakano, Takashi*
Journal of Radiation Research, 53(1), p.87 - 92, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:41.9(Biology)