Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Nango, Nobuhito*; Kubota, Shogo*; Kurosawa, Takuya*; Sasaki, Toshiki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(7), p.650 - 661, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakae, Masanori*; Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Tsuji, Koichi*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 54, p.89 - 99, 2023/03
Fundamental research on X-ray absorption imaging for elemental identification was studied. A secondary target was applied to obtain X-ray absorption images above and below the X-ray absorption edge of the target element. X-rays from an X-ray tube were irradiated to the secondary target, where the characteristic X-rays were emitted that were irradiated to the sample. X-ray absorption images were acquired with an exposure time of a few seconds with an X-ray camera. In this technique, it is difficult to change the energy of X-rays as we want, however we can apply this technique for imaging the specific element. Metal foil sample composed of Al, Cu, and Ni was analyzed. To obtain an X-ray elemental image of Ni, two X-ray absorption images were taken using the X-rays above and below the Ni K-edge. X-rays of Cu K and Zn K
and Zn K were prepared by using Cu and Zn plates as the secondary target. Finally, the Ni elemental image was obtained by subtracting two images. Furthermore, the X-ray camera had a function of setting critical energies for imaging, thus it was demonstrated that an X-ray elemental image of Ni was obtained using a single secondary target without changing the secondary target.
were prepared by using Cu and Zn plates as the secondary target. Finally, the Ni elemental image was obtained by subtracting two images. Furthermore, the X-ray camera had a function of setting critical energies for imaging, thus it was demonstrated that an X-ray elemental image of Ni was obtained using a single secondary target without changing the secondary target.
Yoshida, Yukihiko
IL Nuovo Cimento, 46(2), p.33_1 - 33_8, 2023/03
Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Nakae, Masanori*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Tsuji, Koichi*
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 199, p.106593_1 - 106593_6, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:36.12(Spectroscopy)Fuchita, Tomoki*; Urata, Taisei*; Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Ueda, Akihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Sasaki, Toshiki; Tsuji, Koichi*
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 53, p.77 - 87, 2022/03
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis is an analytical method to obtain elemental information by detecting fluorescence X-rays emitted from a sample irradiated with X-rays. It is possible to obtain two-dimensional elemental distribution images by scanning a sample with micro X-ray beam. In this study, we developed an XRF analytical instrument to rapidly obtain the elemental distributions for moving samples on a belt conveyor by applying the micro XRF technique. X-rays were widely irradiated to the belt conveyor. The elemental distributions were measured by scanning an X-ray detector, crossing above the belt conveyor. A collimator was attached to the top of the detector to limit the analyzing area. Both detection limit and spatial resolutions for moving directions of the detector and the belt conveyor were evaluated. Finally, it was demonstrated that the multi-elemental imaging was possible with the developed XRF instrument.
Nakagawa, Akinori; Oyokawa, Atsushi; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Sasaki, Toshiki; Okada, Shota; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Sakai, Akihiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki
JAEA-Technology 2021-006, 186 Pages, 2021/06
Radioactive wastes generated from R&D activities have been stored in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In order to reduce the risk of taking long time to process legacy wastes, countermeasures for acceleration of waste processing and disposal were studied. Work analysis of waste processing showed bottleneck processes, such as evaluation of radioactivity concentration, segregation of hazardous and combustibles materials. Concerning evaluation of radioactivity concentration, a radiological characterization method using a scaling factor and a nondestructive gamma-ray measurement should be developed. The number of radionuclides that are to be selected for the safety assessment of the trench type disposal facility can decrease using artificial barriers. Hazardous materials, will be identified using records and nondestructive inspection. The waste identified as hazardous will be unpacked and segregated. Preliminary calculations of waste acceptance criteria of hazardous material concentrations were conducted based on environmental standards in groundwater. The total volume of the combustibles will be evaluated using nondestructive inspection. The waste that does not comply with the waste acceptance criteria should be mixed with low combustible material waste such as dismantling concrete waste in order to satisfy the waste acceptance criteria on a disposal facility average. It was estimated that segregation throughput of compressed waste should be increased about 5 times more than conventional method by applying the countermeasures. Further study and technology development will be conducted to realize the plan.
 In
In O
O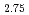 analyzed by neutron diffraction/ atomic pair distribution function
analyzed by neutron diffraction/ atomic pair distribution functionIgawa, Naoki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 43(6), p.329 - 332, 2018/12
For the understanding of the crystal structural effect on the electrical properties, the local disorder in BaSn In
In O
O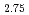 which is one of the excellent proton conductors for solid oxide fuel cells was estimated by using the Atomic Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis method with the neutron diffraction. The local structure is almost the same as the average structure which was estimated by the Rietveld analysis using the cubic crystal structure (space group,
which is one of the excellent proton conductors for solid oxide fuel cells was estimated by using the Atomic Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis method with the neutron diffraction. The local structure is almost the same as the average structure which was estimated by the Rietveld analysis using the cubic crystal structure (space group, 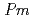
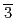
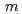 ) in the atomic distance range of
) in the atomic distance range of 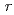
 6
6 . The PDF profile was fitted better using the tetragonal crystal structure with the space group of
. The PDF profile was fitted better using the tetragonal crystal structure with the space group of  4/
4/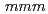 than those with
than those with 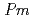
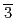
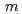 in the range
in the range 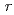
 6
6 . Those results indicate the presence of the local disorder in the lattice. In this work, the relationship between the average and local structures of BaSn
. Those results indicate the presence of the local disorder in the lattice. In this work, the relationship between the average and local structures of BaSn In
In O
O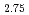 will be discussed.
will be discussed.
 Mo
Mo O
O
Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Mizuno, Yusuke*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 86(6), p.064803_1 - 064803_6, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary) (R=rare earth elements)
(R=rare earth elements)Yasui, Yukio*; Miyamoto, Takuma*; Kori, Shunsuke*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yoshizawa, Daichi*; Mitsuru, Akaki*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; et al.
no journal, ,
We have measured the specific heat and magnetization up to 50 T of polycrystalline samples of RCrTiO (R=Pr, Nd, Eu, Sm and Gd) and also carried out powder neutron diffraction experiments of NdCrTiO
(R=Pr, Nd, Eu, Sm and Gd) and also carried out powder neutron diffraction experiments of NdCrTiO and Nd
and Nd Pr
Pr CrTiO
CrTiO . From the analyses of specific heat data and magnetization curves up to 50 T of the systems, we have evaluated the magnetic interactions between the Cr
. From the analyses of specific heat data and magnetization curves up to 50 T of the systems, we have evaluated the magnetic interactions between the Cr - Cr
- Cr magnetic moments and between the Cr
magnetic moments and between the Cr -R
-R ones. The temperature dependence of neutron magnetic reflection intensities of NdCrTiO
ones. The temperature dependence of neutron magnetic reflection intensities of NdCrTiO indicate that both the Cr
indicate that both the Cr -moments and the Nd
-moments and the Nd -moments simultaneously order at
-moments simultaneously order at 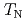 . Basis of the obtained magnetic behavior, the mechanism of magnetoelectric effect of RCrTiO
. Basis of the obtained magnetic behavior, the mechanism of magnetoelectric effect of RCrTiO will be discussed.
will be discussed.
Yoshida, Yukihiko; Sasaki, Toshiki; Murakami, Masashi
no journal, ,
Applications of AI for waste processing are widely considered from the rational viewpoints at JAEA. One useful plan is the application of AI to waste segregation in waste pretreatment. In waste segregating process, there are problems such as high cost of waste segregation, large amount of work, and possibility of worker exposure. The AI solutions of these problems can be expected from the remarkable progress of AI recognition techniques in recent years. In this presentation, we report the application results of AI for object recognition of waste by image.
Matsuyama, Tsugufumi*; Nakae, Masanori*; Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Machida, Masahiko; Tsuji, Koichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Taniguchi, Takumi; Okada, Takashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Osugi, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Junya; Takahashi, Yuta; Sunahara, Jun*; Saito, Toshimitsu*; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Osugi, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Osawa, Norihisa*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Taniguchi, Takumi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Okada, Takashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Osugi, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Ryo*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Kobayashi, Yutaro*; Haga, Kazuko*; Taniguchi, Takumi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Okada, Takashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Osugi, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yutaro*; Osawa, Norihisa*; Haga, Kazuko*; Kaneda, Yoshihisa*; Chaerun, R. I.; Sato, Tsutomu*; Taniguchi, Takumi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Okada, Takashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ribbon system A
ribbon system A Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O (A=Rb, Cs)
(A=Rb, Cs)Fujimura, Akio*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kono, Yohei*; Kittaka, Shunichiro*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The magnetic behavior and magnetic structure of A Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O (A=Rb, Cs) with CuO
(A=Rb, Cs) with CuO ribbon chains have been studied by using specific heat measurement and neutron diffraction method. Cs
ribbon chains have been studied by using specific heat measurement and neutron diffraction method. Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O showed collinear-antiferromagnetic structure analyzed by the neutron diffraction. The relation between magnetic behavior and magnetic for those materials are discussed.
showed collinear-antiferromagnetic structure analyzed by the neutron diffraction. The relation between magnetic behavior and magnetic for those materials are discussed.
Matsumoto, Saori; Kuramochi, Ryo*; Shimizu, Koki; Sato, Junya; Taniguchi, Takumi; Kuroki, Ryoichiro; Okada, Takashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Osugi, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 In
In O
O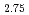 as electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cell analyzed by neutron diffraction
as electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cell analyzed by neutron diffractionIgawa, Naoki; Kodama, Katsuaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The average and local structures of BaSn In
In O
O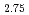 which is one of the excellent solid electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells were analyzed by using the Rietveld method and the Atomic Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis method with the neutron diffraction to research the crystal structural effect on the electrical properties. PDF profile which was obtained from the neutron diffraction data of BaSn
which is one of the excellent solid electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells were analyzed by using the Rietveld method and the Atomic Pair Distribution Function (PDF) analysis method with the neutron diffraction to research the crystal structural effect on the electrical properties. PDF profile which was obtained from the neutron diffraction data of BaSn In
In O
O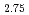 was fitted by using the crystal structure with the space group,
was fitted by using the crystal structure with the space group, 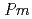 -3
-3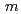 which corresponds with the average structure, and the fitting relatively good reproduces the observed data. In this work, the relationship between the average and local structures of hydrogen doped and undoped BaSn
which corresponds with the average structure, and the fitting relatively good reproduces the observed data. In this work, the relationship between the average and local structures of hydrogen doped and undoped BaSn In
In O
O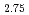 will be discussed.
will be discussed.
 Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O
Yasui, Yukio*; Fujimura, Akio*; Omori, Kiyoshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The magnetic structure of Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O with CuO
with CuO ribbon chains have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. The magnetic reflections were observed below
ribbon chains have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. The magnetic reflections were observed below 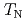 = 1.85 K and all of the magnetic reflections overlapped Bragg reflections. Considering that these are 16-Cu
= 1.85 K and all of the magnetic reflections overlapped Bragg reflections. Considering that these are 16-Cu ions in the unit cell, Cs
ions in the unit cell, Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O has the collinear-antiferromagnetic structure.
has the collinear-antiferromagnetic structure.