Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oshima, Takeshi; Yokoseki, Takashi; Murata, Koichi; Matsuda, Takuma; Mitomo, Satoshi; Abe, Hiroshi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(1S), p.01AD01_1 - 01AD01_4, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:53.64(Physics, Applied)Takeyama, Akinori; Matsuda, Takuma; Yokoseki, Takashi; Mitomo, Satoshi; Murata, Koichi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.134 - 137, 2015/11
Hijikata, Yasuto*; Mitomo, Satoshi*; Matsuda, Takuma*; Murata, Koichi*; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Makino, Takahiro; Takeyama, Akinori; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Applications (RASEDA-11) (Internet), p.130 - 133, 2015/11
Yokoseki, Takashi; Abe, Hiroshi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Oshima, Takeshi
Materials Science Forum, 821-823, p.705 - 708, 2015/07
 ray irradiation dose dependence of electrical characterizations of SiC-MOS capacitors
ray irradiation dose dependence of electrical characterizations of SiC-MOS capacitorsTanaka, Kazuya; Yokoseki, Takashi; Fujita, Natsuko; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; Hijikata, Yasuto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation response of silicon carbide semiconductor devices; Extremely high radiation resistance
-ray irradiation response of silicon carbide semiconductor devices; Extremely high radiation resistanceSato, Shinichiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Makino, Takahiro; Fujita, Natsuko; Oshima, Takeshi; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
We investigate the threshold voltage shift of Si-MOSFETs, SiC-MOSFETs, SiC-MESFETs, and SiC SITs (Static Induction Transistors) due to  irradiation. As a result, no significant threshold voltage shift was observed up to the absorbed dose of 10
irradiation. As a result, no significant threshold voltage shift was observed up to the absorbed dose of 10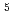 Gy in all the SiC transistors, whereas the serious degradation was observed in the Si-MOSFETs. This strongly indicates that radiation resistance of SiC-MOSFETs and the other SiC-transistors is far superior to that of Si-MOSFETs. The radiation resistance of SiC-MOSFETs fabricated by pyrogenic oxidation is higher than that of the SiC-MOSFETs fabricated by dry oxidation. This result reflects that radiation resistance of SiC-MOSFETs strongly depends on the gate oxidation process since the formed oxide layers have different properties. Also, radiation resistance of SiC-SITs and SiC MESFETs is higher than that of SiC-MOSFETs, since SITs and MESFETs do not have gate oxide layer.
Gy in all the SiC transistors, whereas the serious degradation was observed in the Si-MOSFETs. This strongly indicates that radiation resistance of SiC-MOSFETs and the other SiC-transistors is far superior to that of Si-MOSFETs. The radiation resistance of SiC-MOSFETs fabricated by pyrogenic oxidation is higher than that of the SiC-MOSFETs fabricated by dry oxidation. This result reflects that radiation resistance of SiC-MOSFETs strongly depends on the gate oxidation process since the formed oxide layers have different properties. Also, radiation resistance of SiC-SITs and SiC MESFETs is higher than that of SiC-MOSFETs, since SITs and MESFETs do not have gate oxide layer.
 -rays
-raysYokoseki, Takashi; Makino, Takahiro; Abe, Hiroshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; Hijikata, Yasuto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -rays at elevated temperature
-rays at elevated temperatureMatsuda, Takuma; Yokoseki, Takashi; Mitomo, Satoshi; Murata, Koichi; Makino, Takahiro; Takeyama, Akinori; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
Silicon carbide (SiC) is expected to be applied to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) FETs used in harsh radiation environments to decommission TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors. To develop radiation resistant SiC MOS FETs, clarification of their radiation response under elevated temperature is required. We measured capacitance-voltage (C-V) characteristics of SiC MOSFETs irradiated with  -rays at 423 K in nitrogen atmosphere. The samples were vertical power 4H-SiC MOSFETs with the blocking voltage of 1200 V and the rated current of 20 A with the gate oxide thickness of 45 nm. Typical C-V curve of a SiC MOSFET irradiated even up to 5 kGy was shifted to negative voltage side, suggesting that the positive charges generated in gate oxide by irradiation. While, no significant change in the slope of the curve was observed, indicating that interface traps between the gate oxide and SiC were merely generated. The radiation response of SiC MOS FETs under elevated temperature predominantly depends on the amount of positive charges generated in the gate oxide.
-rays at 423 K in nitrogen atmosphere. The samples were vertical power 4H-SiC MOSFETs with the blocking voltage of 1200 V and the rated current of 20 A with the gate oxide thickness of 45 nm. Typical C-V curve of a SiC MOSFET irradiated even up to 5 kGy was shifted to negative voltage side, suggesting that the positive charges generated in gate oxide by irradiation. While, no significant change in the slope of the curve was observed, indicating that interface traps between the gate oxide and SiC were merely generated. The radiation response of SiC MOS FETs under elevated temperature predominantly depends on the amount of positive charges generated in the gate oxide.
 -ray irradiation under high temperature and humidity circumstance on the electrical characteristics of SiC MOSFETs
-ray irradiation under high temperature and humidity circumstance on the electrical characteristics of SiC MOSFETsTakeyama, Akinori; Matsuda, Takuma; Yokoseki, Takashi; Mitomo, Satoshi; Murata, Koichi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray radiation response of SiC MOSFETs
-ray radiation response of SiC MOSFETsTakeyama, Akinori; Murata, Koichi*; Mitomo, Satoshi*; Matsuda, Takuma*; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
Deterioration of electrical property of SiCMOSFETs due to irradiation was reduced compared with no biased ones, when the SiC MOSFETs with switching bias were irradiated. In order to clarify this mechanism, SiCMOSFETs were irradiated up to 50 kGy with switching bias applied to gate oxide from 4.5 to 0 V. As a result, the large negative shift of threshold voltage V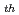 due to irradiation with positive bias significantly recovered in the cases that the bias switched to zero. It shows electrical property of SiCMOSFETs were immediately relieved when applied bias was removed by switching.
due to irradiation with positive bias significantly recovered in the cases that the bias switched to zero. It shows electrical property of SiCMOSFETs were immediately relieved when applied bias was removed by switching.
 ray irradiation
ray irradiationTanaka, Kazuya*; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Fujita, Natsuko; Iwamoto, Naoya; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 rays from Co-60
rays from Co-60Yokoseki, Takashi*; Tanaka, Kazuya*; Fujita, Natsuko; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; Hijikata, Yasuto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation effect on SiC MOSFETs with gate-bias voltage
-ray irradiation effect on SiC MOSFETs with gate-bias voltageMurata, Koichi; Mitomo, Satoshi; Matsuda, Takuma; Yokoseki, Takashi; Makino, Takahiro; Abe, Hiroshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation
-ray irradiationTakeyama, Akinori; Matsuda, Takuma*; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Mitomo, Satoshi*; Murata, Koichi*; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
Effect of  -ray irradiation under high temperature and humidity circumstances on the electrical characteristics of Silicon Carbide (SiC) Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) was investigated. In the case of irradiation under high humidity circumstance, trapped oxide and interface charges densities generated due to irradiation were smaller than those for irradiation in dry circumstance. It is concluded that humidity circumstance suppressed the degradation of the electrical properties due to irradiation including threshold voltage shift and leakage current.
-ray irradiation under high temperature and humidity circumstances on the electrical characteristics of Silicon Carbide (SiC) Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) was investigated. In the case of irradiation under high humidity circumstance, trapped oxide and interface charges densities generated due to irradiation were smaller than those for irradiation in dry circumstance. It is concluded that humidity circumstance suppressed the degradation of the electrical properties due to irradiation including threshold voltage shift and leakage current.
 ray
rayYokoseki, Takashi; Tanaka, Kazuya; Fujita, Natsuko; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; Hijikata, Yasuto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray radiation resistant SiC-MOSFETs
-ray radiation resistant SiC-MOSFETsTakeyama, Akinori; Mitomo, Satoshi*; Matsuda, Takuma*; Murata, Koichi*; Yokoseki, Takashi*; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Oxide thickness dependence of  -ray irradiation response on Silicon Carbide (SiC) Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) was investigated. As a result of irradiation, the threshold voltage V
-ray irradiation response on Silicon Carbide (SiC) Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) was investigated. As a result of irradiation, the threshold voltage V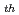 for both SiC MOSFETs with gate oxide of 30 nm or 60 nm thick shifted to negative voltage-side gently. However, the V
for both SiC MOSFETs with gate oxide of 30 nm or 60 nm thick shifted to negative voltage-side gently. However, the V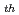 for 60 nm thick more immediately decreased over 400 kGy. It is found that SiCMOSFETs with smaller thickness has a higher radiation tolerance.
for 60 nm thick more immediately decreased over 400 kGy. It is found that SiCMOSFETs with smaller thickness has a higher radiation tolerance.
 -rays by thermal treatments
-rays by thermal treatmentsYokoseki, Takashi; Abe, Hiroshi; Makino, Takahiro; Onoda, Shinobu; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; Yoshie, Toru*; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Oshima, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -rays at elevated temperature
-rays at elevated temperatureMatsuda, Takuma; Yokoseki, Takashi; Mitomo, Satoshi; Murata, Koichi; Makino, Takahiro; Abe, Hiroshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; Kandori, Mikio*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray irradiation effect on SiC-MOSFET
-ray irradiation effect on SiC-MOSFETMitomo, Satoshi*; Matsuda, Takuma*; Murata, Koichi*; Yokoseki, Takashi; Makino, Takahiro; Abe, Hiroshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Oshima, Takeshi; Okubo, Shuichi*; Tanaka, Yuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English