Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Shinotsuka, Hiroshi*; Nagata, Kenji*; Yoshikawa, Hideki*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Applied Surface Science, 685, p.162001_1 - 162001_11, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Chemistry, Physical)Silicon (Si) 2p photoelectron spectra of thermally oxidized Si(001) surfaces were analyzed using Bayesian estimation, a type of mathematical statistical processing, considering spin-orbit interactions. The accuracy of the estimation of fitting parameters and the model selection of the number of peaks were discussed. The spectral analysis was performed without any prior information on the positions of other Si peaks, except for the prominent bulk Si peak, and without using chemical-state assumptions. Our method completely verified previous findings on the surface species and the changes in peaks due to oxidation-induced strain as oxidation progressed.
Suzuki, Seiya; Katsube, Daiki*; Yano, Masahiro; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Terasawa, Tomoo; Ozawa, Takahiro*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; Kim, Y.*; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yuhara, Junji*; et al.
Small Methods, 9(3), p.2400863_1 - 2400863_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Kobata, Masaaki; Okane, Tetsuo; Satou, Yukihiko; Okochi, Takuo*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 23(1), p.16 - 21, 2025/02
Fukada, Yukimasa; Aoyagi, Yumito*; Yokoyama, Misaki*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Kano, Jun*; Kaneda, Miyu*; Fujii, Tatsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; et al.
Journal of Electronic Materials, 54, p.686 - 692, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
 Cl on Cu oxide Surfaces; Cu
Cl on Cu oxide Surfaces; Cu O(111) and bulk Cu
O(111) and bulk Cu O precursor "29"; Structure on Cu(111)
O precursor "29"; Structure on Cu(111)Hayashida, Koki*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Yamada, Takashi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 669, p.160475_1 - 160475_6, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Kato, Hiroyuki S.*; Muroyama, Mizuho*; Kobayakawa, Nano*; Muneyasu, Riku*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Watanabe, Seiya*; Yamada, Takashi*; Kanematsu, Yusuke*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 15(43), p.10769 - 10776, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical) 7
7Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Anai, Ryota*; Saiki, Taiju*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(31), p.13052 - 13063, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)0xidation at the interface and the surface of Si(111) substrate with thin Hf films were studied using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy in conjunction with supersonic oxygen molecular beams (SOMB). An Hf/Si(111) with a coverage of 0.5 monolayer (ML) included HfSi and HfSi . Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf
. Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi
valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi could be oxidized into the Hf
could be oxidized into the Hf . Following the thermal O
. Following the thermal O exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO
exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO
via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO was generated on the surface.
was generated on the surface.
Kamiya, Junichiro; Abe, Kazuhide; Fujimori, Shinichi; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Kobata, Masaaki; Morohashi, Yuko; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yamada, Ippei; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 22(4), p.316 - 326, 2024/08
The activation and deterioration mechanisms of the Ti-Zr-V non-evaporable getter (NEG) coating have been investigated. Operando analysis of the surface chemical composition change of the Ti-Zr-V coating was performed by the synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy (SRPES) during the process of raising the sample temperature to 250 C, corresponding to the activation process of NEG coating. The surface oxidation process was also characterized by the SRPES during the injection of O_2 gas into the chamber while keeping the sample temperature at 250
C, corresponding to the activation process of NEG coating. The surface oxidation process was also characterized by the SRPES during the injection of O_2 gas into the chamber while keeping the sample temperature at 250 C, corresponding to the deterioration process of NEG coating, i.e. surface oxidation and oxygen diffusion to the coating interior. The depth profile of the oxidized sample was measured with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results shows, in the activation process, the surface Zr gets the oxygen from the oxides of Ti and V at the first stage, resulting in the metallic Ti and V on the surface, and the oxygen of the Zr-oxide and/or Zr sub-oxides diffuse to the interior of the coating in the continuous temperature rise, resulting in the metallic Zr on the surface. It is further suggested that the deterioration of the Ti-Zr-V NEG coating means the Zr and secondary Ti are oxidized deep into the coating, resulting in the restriction of the oxygen migration from the NEG compositions on the surface and consequently the lack of surface metallization.
C, corresponding to the deterioration process of NEG coating, i.e. surface oxidation and oxygen diffusion to the coating interior. The depth profile of the oxidized sample was measured with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results shows, in the activation process, the surface Zr gets the oxygen from the oxides of Ti and V at the first stage, resulting in the metallic Ti and V on the surface, and the oxygen of the Zr-oxide and/or Zr sub-oxides diffuse to the interior of the coating in the continuous temperature rise, resulting in the metallic Zr on the surface. It is further suggested that the deterioration of the Ti-Zr-V NEG coating means the Zr and secondary Ti are oxidized deep into the coating, resulting in the restriction of the oxygen migration from the NEG compositions on the surface and consequently the lack of surface metallization.
 00) MOS structures by means of electrical measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
00) MOS structures by means of electrical measurements and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopyKobayashi, Takuma*; Suzuki, Asato*; Nakanuma, Takato*; Sometani, Mitsuru*; Okamoto, Mitsuo*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 175, p.108251_1 - 108251_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:73.58(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) Cl dissociation, CH
Cl dissociation, CH abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH
abstraction, and Cl adsorption from the dissociative scattering of supersonic CH Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)
Cl on Cu(111) and Cu(410)Makino, Takamasa*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Di o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
o, W. A.*; Okada, Michio*
Applied Surface Science, 642, p.158568_1 - 158568_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:37.63(Chemistry, Physical)Arai, Taiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Motohashi, Mitsuya*
Zairyo No Kagaku To Kogaku, 60(5), p.153 - 158, 2023/10
Si oxide films are currently widely used as insulating materials in electronic devices and biomaterials. The atomic bonding state of these films significantly influences the properties of each device, thus it is particularly necessary to understand and control the chemical bonding state between Si and O in the films. In this study, the Si oxide films formed by anodic oxidation on Si substrate surfaces in extremely low concentrations of HF solutions were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy mainly focusing on Si2p and F1s spectra. Although the HF concentration is in the order of ppm, the films contain percent order of F atoms, suggesting the formation of Si-F and Si-O-F bonds in the films. It was also found that the different depth profiles for F and O atoms was observed, indicating that the surface reaction processes seem to be different depending on each element.
Nakamura, Takafumi*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Arakawa, Masakazu*; Maruyama, Akio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Sangyo Oyo Kogakukai Rombunshi, 11(2), p.109 - 114, 2023/09
Surface chemistry experimental end-station at BL23SU in SPring-8 is widely used to study various surfaces and interfaces of functional materials by means of soft X-rays synchrotron radiation. To analyze surface chemical reactions between gas and solid surfaces, an accurate control of flow-rates of gases is essential. This paper describes a computerized automatic gas flow control system to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of gas-surface reaction experiments in the pressure range of ultra-high vacuum (molecular flow) conditions. The system uses feedback control to operate the slow-leak valve to control the gas-pressure. As a result, the system achieved results equivalent to those of a skilled experimenter.
 /GaN interfaces with suppressed Ga-oxide interlayer via sputter deposition of SiO
/GaN interfaces with suppressed Ga-oxide interlayer via sputter deposition of SiO
Onishi, Kentaro*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Mizobata, Hidetoshi*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 62(5), p.050903_1 - 050903_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:47.87(Physics, Applied)While the formation of an GaO interlayer is key to achieving SiO
interlayer is key to achieving SiO /GaN interfaces with low defect density, it can affect the reliability and stability of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices if the annealing conditions are not properly designed. In the present study, we aimed to minimize the growth of the GaO
/GaN interfaces with low defect density, it can affect the reliability and stability of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices if the annealing conditions are not properly designed. In the present study, we aimed to minimize the growth of the GaO layer on the basis of the sputter deposition of SiO
layer on the basis of the sputter deposition of SiO on GaN. Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectrometry measurements confirmed the suppressed growth of the GaO
on GaN. Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectrometry measurements confirmed the suppressed growth of the GaO layer compared with a SiO
layer compared with a SiO /GaN structure formed by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Negligible GaO
/GaN structure formed by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Negligible GaO growth was also observed when subsequent oxygen annealing up to 600
growth was also observed when subsequent oxygen annealing up to 600 C was performed. A MOS device with negligible capacitance-voltage hysteresis, nearly ideal flat-band voltage, and low leakage current was demonstrated by performing oxygen and forming gas annealing at temperatures of 600
C was performed. A MOS device with negligible capacitance-voltage hysteresis, nearly ideal flat-band voltage, and low leakage current was demonstrated by performing oxygen and forming gas annealing at temperatures of 600 C and 400
C and 400 C, respectively.
C, respectively.
 by monolayer hexagonal boron nitride coating for improved photo- and thermionic-cathodes
by monolayer hexagonal boron nitride coating for improved photo- and thermionic-cathodesYamaguchi, Hisato*; Yusa, Ryunosuke*; Wang, G.*; Pettes, M. T.*; Liu, F.*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Moody, N. A.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 122(14), p.141901_1 - 141901_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:62.75(Physics, Applied)A lowering of work function for LaB by monolayer hexagonal BN coating is reported. Photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM) and thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) both revealed that the hBN coated region of a LaB
by monolayer hexagonal BN coating is reported. Photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM) and thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) both revealed that the hBN coated region of a LaB (100) single crystal has lower work function compared to the bare (i.e., non-coated) and graphene coated regions. A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB
(100) single crystal has lower work function compared to the bare (i.e., non-coated) and graphene coated regions. A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB (100) compared to graphene coated LaB
(100) compared to graphene coated LaB (100) was qualitatively supported by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adding an oxide layer in the calculations improved consistency between the calculation and experimental results. We followed up our calculations with synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) and confirmed the presence of an oxide layer on our LaB
(100) was qualitatively supported by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adding an oxide layer in the calculations improved consistency between the calculation and experimental results. We followed up our calculations with synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) and confirmed the presence of an oxide layer on our LaB .
.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya*; Okigawa, Yuki*; Masuzawa, Tomoaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Yamada, Takatoshi*
Applied Surface Science, 605, p.154748_1 - 154748_6, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.60(Chemistry, Physical)Immersion of graphene in KOH solution improves its mobility on SiO /Si wafers. This is thought to be due to electron doping by modification with K atoms, but the K atom concentration C
/Si wafers. This is thought to be due to electron doping by modification with K atoms, but the K atom concentration C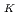 in the graphene has not been clarified yet. In this study, the C
in the graphene has not been clarified yet. In this study, the C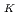 was determined by XPS analysis using high-brilliance synchrotron radiation. The time evolution of C
was determined by XPS analysis using high-brilliance synchrotron radiation. The time evolution of C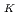 was determined by real-time observation, and the C
was determined by real-time observation, and the C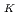 before irradiation of synchrotron radiation was estimated to be 0.94%. The C 1s spectrum shifted to the low binding energy side with the desorption of K atoms. This indicates that the electron doping concentration into graphene is decreasing, and it is experimentally confirmed that K atoms inject electrons into graphene.
before irradiation of synchrotron radiation was estimated to be 0.94%. The C 1s spectrum shifted to the low binding energy side with the desorption of K atoms. This indicates that the electron doping concentration into graphene is decreasing, and it is experimentally confirmed that K atoms inject electrons into graphene.
 species at SiO
species at SiO /Si interfaces in Si dry oxidation; Comparison between p-Si(001) and n-Si(001) surfaces
/Si interfaces in Si dry oxidation; Comparison between p-Si(001) and n-Si(001) surfacesTsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Sakamoto, Tetsuya*; Yamamoto, Yoshiki*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 157(23), p.234705_1 - 234705_21, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.89(Chemistry, Physical) (001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Inami, Eiichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abe, Masayuki*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 65(11), p.526 - 530, 2022/11
The oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O
(001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
 molecule at SiO
molecule at SiO /Si(001) interface during Si dry oxidation
/Si(001) interface during Si dry oxidationTsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Sakamoto, Tetsuya*; Takakuwa, Yuji*
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 21(1), p.30 - 39, 2022/11
 /GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000
/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates
) substratesMizobata, Hidetoshi*; Tomigahara, Kazuki*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Hosoi, Takuji*; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Applied Physics Letters, 121(6), p.062104_1 - 062104_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Physics, Applied)The interface properties and energy band alignment of SiO /GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000
/GaN metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structures fabricated on N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates were investigated by electrical measurements and synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. They were then compared with those of SiO
) substrates were investigated by electrical measurements and synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. They were then compared with those of SiO /GaN MOS structures on Ga-polar GaN(0001). Although the SiO
/GaN MOS structures on Ga-polar GaN(0001). Although the SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) structure was found to be more thermally unstable than that on the GaN(0001) substrate, excellent electrical properties were obtained for the SiO
) structure was found to be more thermally unstable than that on the GaN(0001) substrate, excellent electrical properties were obtained for the SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) structure by optimizing conditions for post-deposition annealing. However, the conduction band offset for SiO
) structure by optimizing conditions for post-deposition annealing. However, the conduction band offset for SiO /GaN(000
/GaN(000 ) was smaller than that for SiO
) was smaller than that for SiO /GaN(0001), leading to increased gate leakage current. Therefore, caution is needed when using N-polar GaN(000
/GaN(0001), leading to increased gate leakage current. Therefore, caution is needed when using N-polar GaN(000 ) substrates for MOS device fabrication.
) substrates for MOS device fabrication.